6.9. Users —
Only Organization Administrators can see the Users tab on the top navigation bar. If you click the Users tab, the Users category and links appear. These pages enable you to grant and edit permissions for those who administer your system groups. Click in the User List to modify users within your organization.
6.9.1. User List ⇒ Active —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
This tab lists all active users of your RHN account. It displays the following basic information about each user: their username, real name, roles, and the date of their last sign in.
As shown in Figure 6.20, “User List”, each row in the User List represents a user within your organization. There are four columns of information for each user:
- Username — The login name of the user. If you click on a username, the User Details page for the user is displayed. Refer to Section 6.9.1.1, “User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details —
 ” for more information.
” for more information.
- Real Name — The full name of the user (last name first).
- Roles — List of the user's privileges, such as Organization Administrator, Channel Administrator and normal user. Users can have multiple roles.
- Last Sign In — Shows when the user last logged into RHN.
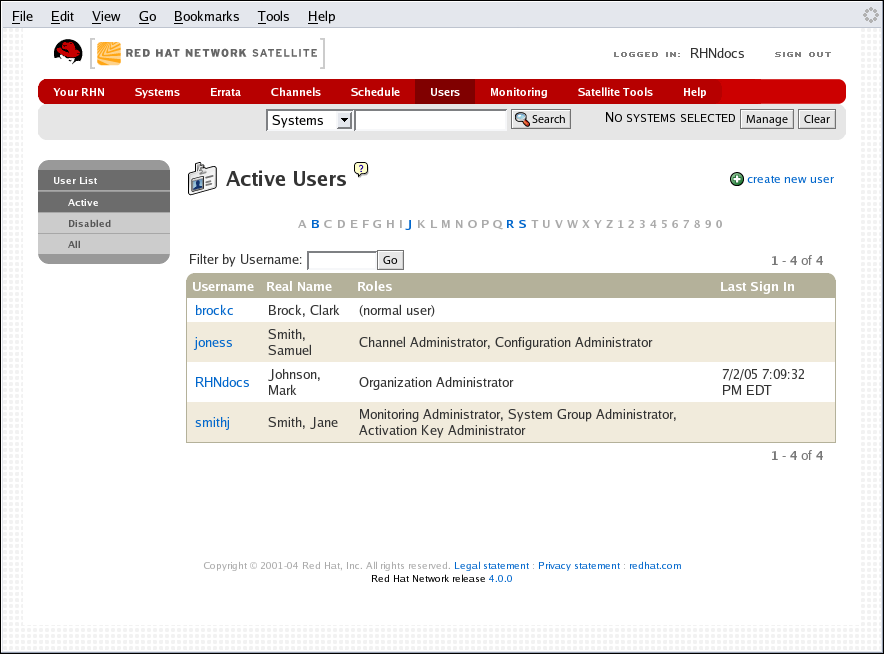
Figure 6.20. User List
6.9.1.1. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The User Details page allows Organization Administrators to manage the permissions and activity of all users.
6.9.1.1.1. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Details —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
User Details are maintained on the Red Hat account management pages. Organization Administrators can manage contact details, access permissions and general Red Hat website preferences, such as language and timezone for all users created in their Red Hat account.
Through Red Hat account management pages Organization Administrators can deactivate other users within their account. Users may be deactivated by Organization Administrators, or users may deactivate their own accounts. Deactivated users cannot log in to the RHN web interface, nor may they schedule any actions. Organization Administrators may not be deactivated until that role is removed from their account. Actions scheduled by a user prior to their deactivation remain in the action queue. For added flexibility, deactivated users may be reactivated by Organization Administrators.
To delegate responsibilities within your organization, Red Hat Network provides several roles with varying degrees of responsibility and access. This list describes the permissions of each and the differences between them:
- Activation Key Administrator — This role is designed to manage your organization's collection of activation keys. This person can create, modify, and delete any key within your overarching account.
- Channel Administrator — This role has complete access to the software channels and related associations within your organization. It requires RHN Satellite Server or RHN Proxy Server. This person may change the base channels of systems, make channels globally subscribable, and create entirely new channels.
- Configuration Administrator — This role enables the user to manage the configuration of systems in the organization using either the RHN website or the Red Hat Network Configuration Manager.
- Monitoring Administrator — This role allows for the scheduling of probes and oversight of other Monitoring infrastructure. This role is available only on Monitoring-enabled RHN Satellite Server version 3.6 or later.
- Organization Administrator — This role can perform any function available within Red Hat Network. As the master account for your organization, the person holding this role can alter the privileges of all other accounts, as well as conduct any of the tasks available to the other roles. Like the other roles, multiple Organization Administrators may exist.
- System Group Administrator — This role is one step below Organization Administrator in that it has complete authority over the systems and system groups to which it is granted access. This person can create new system groups, delete any assigned systems groups, add systems to groups, and manage user access to groups.
While it is possible for one Organization Administrator to remove Organization Administrator rights from another user, it is impossible to remove Organization Administrator rights from the sole remaining Organization Administrator. It is possible to remove your own Organization Administrator privileges so long as you are not the last Organization Administrator.
To assign a user a new role, select the appropriate checkbox. Remember that Organization Administrators are automatically granted administration access to all other roles, signified by grayed-out checkboxes. To grant a user the ability to manage the configuration of systems, select the Configuration Administrator checkbox. When satisfied with the changes, click .
6.9.1.1.2. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ System Groups —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
This tab displays a list of system groups that the user may administer. Organization Administrators may use the check boxes to set this user's access permissions to each system group. Check or uncheck the box to the left of the system group and click the button to save the changes.
Organization Administrators may select one or more default system groups for this user. When the user registers a system, that system is assigned to the selected group or groups. This allows the user to have access to the newly-registered system immediately, if he or she has permissions to one or more of the groups to which the system is assigned. System Groups to which this user has access are preceded by an (*).
6.9.1.1.3. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Systems —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
This tab lists all systems to which the user has access permission. These systems come from the system groups assigned to the user on the previous tab. You may choose a set of systems to work with by checking the boxes to the left of the systems and clicking the button. Use the System Set Manager page to execute actions on those systems. Clicking the name of a system takes you to its System Details page. Refer to Section 6.4.2.9, “System Details” for more information.
6.9.1.1.4. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Channel Permissions —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
This tab lists all channels available to your organization. You may grant explicit channel subscription permission to this user for each of the channels listed by checking the box to the left of the channel and clicking the button. Permissions granted through Organization Administrator status, certificate authority status, or because the channel is globally subscribable have no checkbox, but display a check icon instead.
6.9.1.1.4.1. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Channel Permissions ⇒ Subscription —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Identifies channels to which the user may subscribe systems. To change these, select or unselect the appropriate checkboxes and click the button. Note that channels subscribable through the user's admin status or the channel's global setting cannot be altered. They are identified with a check icon.
6.9.1.1.4.2. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Channel Permissions ⇒ Management —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Identifies channels the user may manage. To change these, select or unselect the appropriate checkboxes and click the button. This status does not enable the user to create new channels. Note that channels automatically manageable through the user's admin status cannot be altered. They are identified with a check icon. Remember, Organization Administrators and Channel Administrators can subscribe to or manage any channel.
6.9.1.1.5. User List ⇒ Active ⇒ User Details ⇒ Preferences —
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
This page allows you to configure whether the user receives email notifications, the number of entries displayed per list page, and the timezone of the user. Make selections and click the button to update.
- Email Notification — Determine whether this user should receive email every time an Errata Alert is applicable to one or more systems in his or her RHN account, as well as daily summaries of system events.
- RHN List Page Size — Maximum number of items that appear in a list on a single page. If more items are in the list, clicking the Next button displays the next group of items. This preference applies to the user's view of system lists, Errata lists, package lists, and so on.
To modify any of these options, make your changes and click the button.