2.4. Configuration
The Red Hat Update Agent offers various options to configure its settings.
If you are not running the X Window System or prefer the command line version, skip to Section 2.4.2, “Command Line Version”.
2.4.1. Using the Red Hat Update Agent Configuration Tool
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
You must be root to run the Red Hat Update Agent Configuration Tool. If started by a user other than root, the Red Hat Update Agent prompts you for the root password. The Red Hat Update Agent Configuration Tool can be started by typing the command
up2date --config at a shell prompt (for example, an xterm or a gnome-terminal).
2.4.1.1. General Settings
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The General tab allows you to enable an HTTP Proxy Server. If your network connection requires you to use an HTTP Proxy Server to make HTTP connections, select the Enable HTTP Proxy option and type your proxy server in the text field with the format http://HOST:PORT. For example, to use the proxy server squid.mysite.org on port 3128, you would enter
squid.mysite.org:3128 in the text field. Additionally, if your proxy server requires a username and password, select the Use Authentication option and enter your username and password in the respective text fields.
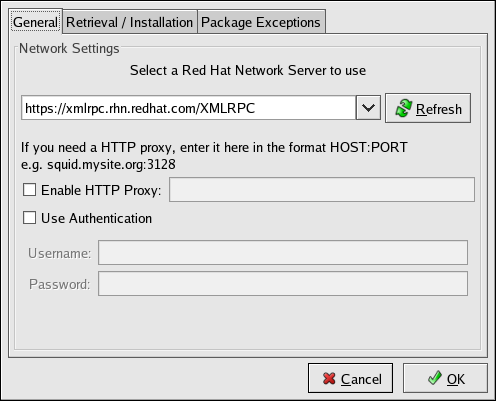
Figure 2.16. General Settings
In addition, RHN Proxy and Satellite customers have the option of selecting Red Hat Network Servers here. These customers should refer to the RHN Client Configuration Guide for detailed instructions.
2.4.1.2. Retrieval/Installation Settings
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The Retrieval/Installation tab allows you to customize your software package retrieval and package installation preferences.
Warning
You must use Red Hat Update Agent Version 2.5.4 or higher to upgrade your kernel automatically. Red Hat Update Agent will install the updated kernel and configure LILO or GRUB to boot the new kernel the next time the system is rebooted.
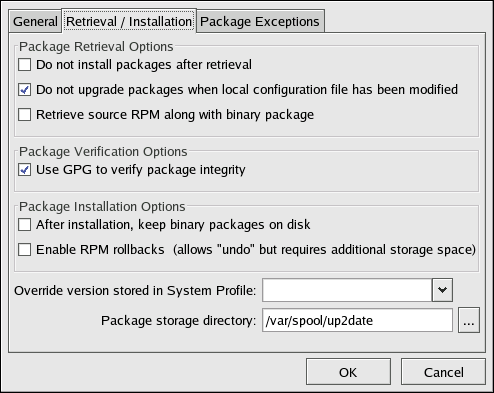
Figure 2.17. Retrieval/Installation Settings
The following package retrieval options can be selected (see Figure 2.17, “Retrieval/Installation Settings”):
- — download selected RPM packages to the desired directory and ignore the installation preferences
- — if the configuration file has been modified for a package such as
apacheorsquid, do not attempt to upgrade it. This option is useful if you are installing custom RPMs on your system and you do not want them updated or reverted to the default Red Hat Enterprise Linux packages. - — download both the source (
*.src.rpm) and the binary (*.[architecture].rpm) files
The following installation options are configurable (see Figure 2.17, “Retrieval/Installation Settings”):
- — before installing packages, verify Red Hat's GPG signature (highly recommended for security reasons)
- — save binary packages in the desired directory instead of deleting them after installation
The following additional options are configurable from this tab:
- — override the Red Hat Linux version in your System Profile
- — change the directory where packages are downloaded; the default location is
/var/spool/up2date/
2.4.1.3. Package Exceptions Settings
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The Package Exceptions tab allows you to define which packages to exclude from the list of updated RPM packages according to the package name or file name (see Figure 2.18, “Package Exceptions Settings”).
To define a set of packages to be excluded according to the package name, enter a character string including wild cards (*) in the Add new text field under in the Package Names to Skip section heading. A wild card at the end of the character string indicates that all packages beginning with the character string are excluded from the list. A wild card at the beginning of the character string indicates that any packages that end with the character string are excluded from the list.
For example, if the string
kernel* is in the Package Names to Skip section, the Red Hat Update Agent will not display any packages beginning with kernel.
To exclude packages by file name, apply the same rules to the field below File Names to Skip section heading.
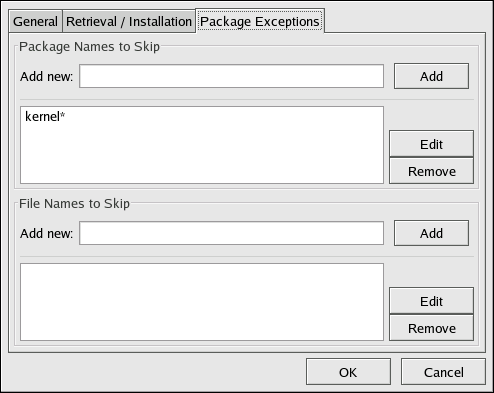
Figure 2.18. Package Exceptions Settings