Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
18.2. Bridged Mode
When using Bridged mode, all of the guest virtual machines appear within the same subnet as the host physical machine. All other physical machines on the same physical network are aware of the virtual machines, and can access the virtual machines. Bridging operates on Layer 2 of the OSI networking model.
It is possible to use multiple physical interfaces on the hypervisor by joining them together with a bond. The bond is then added to a bridge and then guest virtual machines are added onto the bridge as well. However, the bonding driver has several modes of operation, and only a few of these modes work with a bridge where virtual guest machines are in use.
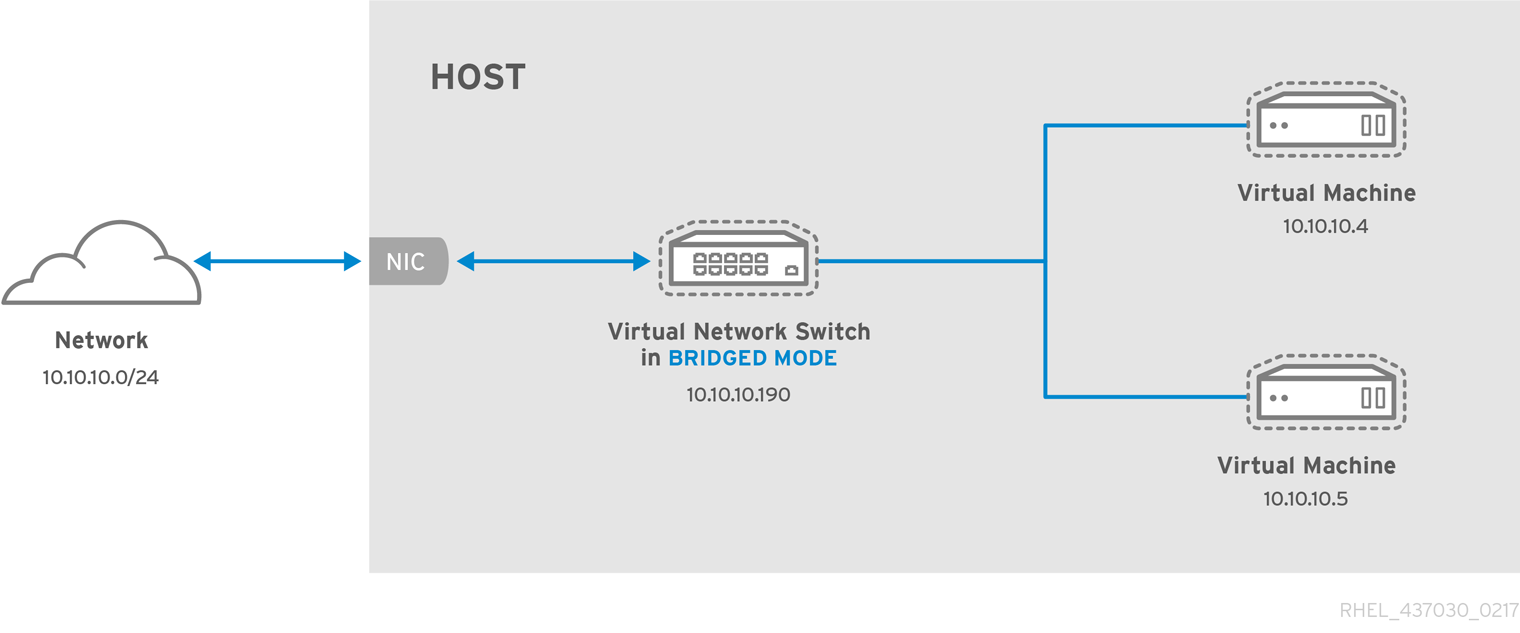
Figure 18.2. Virtual network switch in bridged mode
Warning
The only bonding modes that should be used with a guest virtual machine are Mode 1, Mode 2, and Mode 4. Under no circumstances should Modes 0, 3, 5, or 6 be used. It should also be noted that mii-monitoring should be used to monitor bonding modes as arp-monitoring does not work.
For more information on bonding modes, refer to the knowledgebase article on bonding modes, or The Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Deployment Guide.
For a detailed explanation of bridge_opts parameters, see the Red Hat Virtualization Administration Guide.