Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
29.2. Authentication
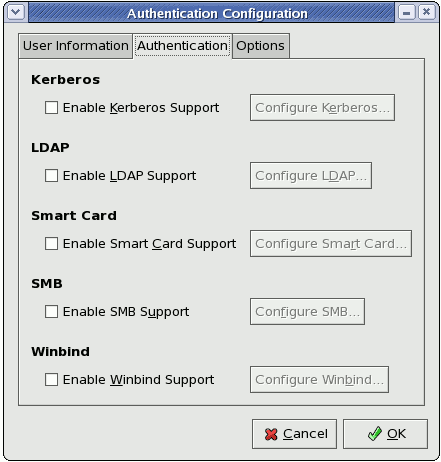
Figure 29.2. Authentication
The Enable Kerberos Support option enables Kerberos authentication. Click the button to open the dialogue and configure the following:
- Realm — Configures the realm for the Kerberos server. The realm is the network that uses Kerberos, composed of one or more KDCs and a potentially large number of clients.
- KDC — Defines the Key Distribution Center (KDC), which is the server that issues Kerberos tickets.
- Admin Servers — Specifies the administration server(s) running
kadmind.
krb5-libs and krb5-workstation packages must be installed for this option to work. For more information about Kerberos, refer to Section 48.6, “Kerberos”.
The Enable LDAP Support option instructs standard PAM-enabled applications to use LDAP for authentication. The button allows you to configure LDAP support with options identical to those present in Configure LDAP... under the tab. For more information about these options, refer to Section 29.1, “User Information”.
openldap-clients package must be installed for this option to work.
The Enable Smart Card Support option enables Smart Card authentication. This allows users to log in using a certificate and key associated stored on a smart card. Click the button for more options.
pam_pkcs11 and coolkey packages must be installed for this option to work. For more information about smart cards, refer to Section 48.3.1.3, “Supported Smart Cards” under Section 48.3, “Single Sign-on (SSO)”.
The Enable SMB Support option configures PAM to use a Server Message Block (SMB) server to authenticate users. SMB refers to a client-server protocol used for cross-system communication; it is also the protocol used by Samba to appear as a Windows server to Windows clients. Click the button to specify the following:
- Workgroup — Specifies the SMB workgroup to use.
- Domain Controllers — Specifies the SMB domain controllers to use.
The Enable Winbind Support option configures the system to connect to a Windows Active Directory or a Windows domain controller. User information from the specified directory or domain controller can then be accessed, and server authentication options can be configured.