10.5. Quick start content guidelines
10.5.1. Card copy
You can customize the title and description on a quick start card, but you cannot customize the status.
- Keep your description to one to two sentences.
Start with a verb and communicate the goal of the user. Correct example:
Create a serverless application.
Create a serverless application.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.2. Introduction
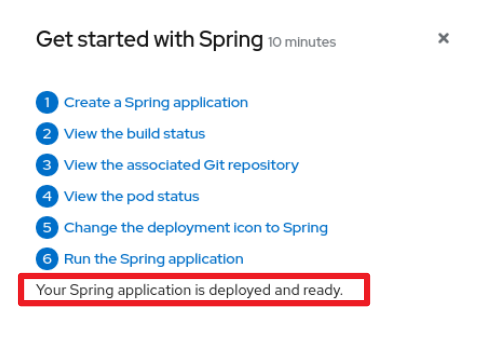
After clicking a quick start card, a side panel slides in that introduces the quick start and lists the tasks within it.
- Make your introduction content clear, concise, informative, and friendly.
- State the outcome of the quick start. A user should understand the purpose of the quick start before they begin.
Give action to the user, not the quick start.
Correct example:
In this quick start, you will deploy a sample application to {product-title}.In this quick start, you will deploy a sample application to {product-title}.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
This quick start shows you how to deploy a sample application to {product-title}.This quick start shows you how to deploy a sample application to {product-title}.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- The introduction should be a maximum of four to five sentences, depending on the complexity of the feature. A long introduction can overwhelm the user.
List the quick start tasks after the introduction content, and start each task with a verb. Do not specify the number of tasks because the copy would need to be updated every time a task is added or removed.
Correct example:
Tasks to complete: Create a serverless application; Connect an event source; Force a new revision
Tasks to complete: Create a serverless application; Connect an event source; Force a new revisionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
You will complete these 3 tasks: Creating a serverless application; Connecting an event source; Forcing a new revision
You will complete these 3 tasks: Creating a serverless application; Connecting an event source; Forcing a new revisionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.3. Task steps
After the user clicks Start, a series of steps appears that they must perform to complete the quick start.
Follow these general guidelines when writing task steps:
- Use "Click" for buttons and labels. Use "Select" for checkboxes, radio buttons, and drop-down menus.
Use "Click" instead of "Click on"
Correct example:
Click OK.
Click OK.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
Click on the OK button.
Click on the OK button.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Tell users how to navigate between Administrator and Developer perspectives. Even if you think a user might already be in the appropriate perspective, give them instructions on how to get there so that they are definitely where they need to be.
Examples:
Enter the Developer perspective: In the main navigation, click the dropdown menu and select Developer. Enter the Administrator perspective: In the main navigation, click the dropdown menu and select Admin.
Enter the Developer perspective: In the main navigation, click the dropdown menu and select Developer. Enter the Administrator perspective: In the main navigation, click the dropdown menu and select Admin.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the "Location, action" structure. Tell a user where to go before telling them what to do.
Correct example:
In the node.js deployment, hover over the icon.
In the node.js deployment, hover over the icon.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
Hover over the icon in the node.js deployment.
Hover over the icon in the node.js deployment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Keep your product terminology capitalization consistent.
- If you must specify a menu type or list as a dropdown, write "dropdown” as one word without a hyphen.
Clearly distinguish between a user action and additional information on product functionality.
User action:
Change the time range of the dashboard by clicking the dropdown menu and selecting time range.
Change the time range of the dashboard by clicking the dropdown menu and selecting time range.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Additional information:
To look at data in a specific time frame, you can change the time range of the dashboard.
To look at data in a specific time frame, you can change the time range of the dashboard.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Avoid directional language, like "In the top-right corner, click the icon". Directional language becomes outdated every time UI layouts change. Also, a direction for desktop users might not be accurate for users with a different screen size. Instead, identify something using its name.
Correct example:
In the navigation menu, click Settings.
In the navigation menu, click Settings.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
In the left-hand menu, click Settings.
In the left-hand menu, click Settings.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Do not identify items by color alone, like "Click the gray circle". Color identifiers are not useful for sight-limited users, especially colorblind users. Instead, identify an item using its name or copy, like button copy.
Correct example:
The success message indicates a connection.
The success message indicates a connection.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
The message with a green icon indicates a connection.
The message with a green icon indicates a connection.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use the second-person point of view, you, consistently:
Correct example:
Set up your environment.
Set up your environment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Incorrect example:
Let's set up our environment.
Let's set up our environment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.4. Check your work module
After a user completes a step, a Check your work module appears. This module prompts the user to answer a yes or no question about the step results, which gives them the opportunity to review their work. For this module, you only need to write a single yes or no question.
- If the user answers Yes, a check mark will appear.
- If the user answers No, an error message appears with a link to relevant documentation, if necessary. The user then has the opportunity to go back and try again.
10.5.5. Formatting UI elements
Format UI elements using these guidelines:
- Copy for buttons, dropdowns, tabs, fields, and other UI controls: Write the copy as it appears in the UI and bold it.
- All other UI elements—including page, window, and panel names: Write the copy as it appears in the UI and bold it.
- Code or user-entered text: Use monospaced font.
- Hints: If a hint to a navigation or masthead element is included, style the text as you would a link.
- CLI commands: Use monospaced font.
- In running text, use a bold, monospaced font for a command.
- If a parameter or option is a variable value, use an italic monospaced font.
- Use a bold, monospaced font for the parameter and a monospaced font for the option.