17.9. Managing Hosts
The Hosts tab allows you to add, edit, or remove hosts from the
/etc/hosts file. This file contains IP addresses and their corresponding hostnames.
When your system tries to resolve a hostname to an IP address or tries to determine the hostname for an IP address, it refers to the
/etc/hosts file before using the name servers (if you are using the default Red Hat Enterprise Linux configuration). If the IP address is listed in the /etc/hosts file, the name servers are not used. If your network contains computers whose IP addresses are not listed in DNS, it is recommended that you add them to the /etc/hosts file.
To add an entry to the
/etc/hosts file, go to the Hosts tab, click the button on the toolbar, provide the requested information, and click OK. Select => or press Ctrl+S to save the changes to the /etc/hosts file. The network or network services do not need to be restarted since the current version of the file is referred to each time an address is resolved.
Warning
Do not remove the
localhost entry. Even if the system does not have a network connection or have a network connection running constantly, some programs need to connect to the system via the localhost loopback interface.
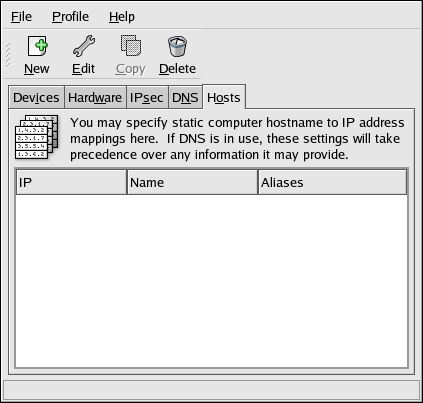
Figure 17.15. Hosts Configuration
Note
To change lookup order, edit the
/etc/host.conf file. The line order hosts, bind specifies that /etc/hosts takes precedence over the name servers. Changing the line to order bind, hosts configures the system to resolve hostnames and IP addresses using the name servers first. If the IP address cannot be resolved through the name servers, the system then looks for the IP address in the /etc/hosts file.