第66章 プロセスエンジンのコアエンジン API
プロセスエンジンは、ビジネスプロセスを実行します。プロセスを定義するには、プロセス定義やカスタムタスクなどの ビジネスアセット を作成します。
Core Engine API を使用して、プロセスエンジンでプロセスを読み込み、実行、および管理できます。
複数の制御レベルが利用できます。
- 最小レベルでは、KIE ベース と KIE セッション を直接作成できます。KIE ベースは、ビジネスプロセスのすべてのアセットを表します。KIE セッションは、ビジネスプロセスのインスタンスを実行するプロセスエンジン内のエンティティーです。このレベルは粒度の細かい制御を提供しますが、コード内のプロセスインスタンス、タスクハンドラー、イベントハンドラー、およびその他のプロセスエンジンエンティティーの明示的な宣言および設定が必要になります。
-
RuntimeManager クラスを使用してセッションおよびプロセスを管理できます。このクラスは設定可能なストラテジーを使用して、必要なプロセスインスタンスのセッションを提供します。KIE セッションとタスクサービスとの間の対話を自動的に設定します。不要になったプロセスエンジンエンティティーを破棄し、リソースを最適に使用できるようにします。Fluent API を使用して、必要なビジネスアセットで
RuntimeManagerをインスタンス化し、その環境を設定できます。 Services API を使用してプロセスの実行を管理することができます。たとえば、デプロイメントサービスはビジネスアセットをエンジンにデプロイし、デプロイメントユニット を形成します。プロセスサービスは、このデプロイメントユニットからプロセスを実行します。
プロセスエンジンをアプリケーションに埋め込む場合、サービス API はエンジンの設定および管理に関する詳細を非表示にするため、最も便利なオプションになります。
最後に、KJAR ファイルからビジネスアセットを読み込んでプロセスを実行する KIE Server をデプロイできます。KIE Server は、プロセスの読み込みおよび管理のための REST API を提供します。Business Central を使用して KIE Server を管理することもできます。
KIE Server を使用する場合は、Core Engine API を使用する必要はありません。KIE Server へのプロセスのデプロイおよび管理に関する情報は、Red Hat Process Automation Manager プロジェクトのパッケージ化およびデプロイ を参照してください。
すべてのパブリックプロセスエンジン API 呼び出しに関する完全なリファレンス情報は、Java ドキュメント を参照してください。他の API クラスもコードに存在しますが、今後のバージョンで変更できる内部 API です。開発および維持するアプリケーションでパブリック API を使用します。
66.1. KIE ベースおよび KIE セッション
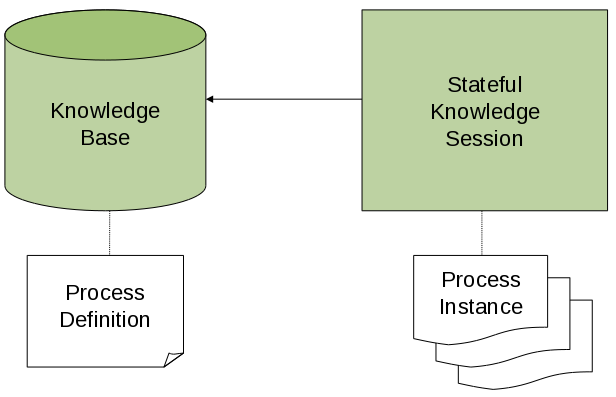
KIE base には、すべてのプロセス定義およびプロセスに関連するその他のアセットへの参照が含まれます。エンジンはこの KIE ベースを使用してプロセスの全情報を検索するか、必要に応じて複数のプロセスについて検索します。
クラスパス、ファイルシステム、プロセスリポジトリーなど、さまざまなソースからアセットを KIE ベースに読み込むことができます。KIE ベースの作成は、さまざまなソースからのアセットの読み込みおよび解析を行う必要があるため、リソース負荷の高い操作です。KIE ベースを動的に変更して、ランタイム時にプロセス定義やその他のアセットを追加または削除できます。
KIE ベースを作成したら、この KIE ベースに基づいて KIE セッション をインスタンス化できます。この KIE セッションを使用して、KIE ベースの定義に基づいてプロセスを実行します。
KIE セッションを使用してプロセスを開始すると、新しい プロセスインスタンス が作成されます。このインスタンスは、特定のプロセス状態を維持します。同じ KIE セッションで異なるインスタンスは同じプロセス定義を使用できますが、状態は異なります。
図66.1 プロセスエンジンの KIE ベースおよび KIE セッション
たとえば、アプリケーションを開発して売上注文を処理する場合は、注文の処理方法を決定する 1 つ以上のプロセス定義を作成できます。アプリケーションの起動時に、これらのプロセス定義を含む KIE ベースを作成する必要があります。次に、この KIE ベースに基づいてセッションを作成できます。新しい売上注文が終了したら、注文用の新しいプロセスインスタンスを開始します。このプロセスインスタンスには、特定の売上リクエストのプロセスの状態が含まれます。
同じ KIE ベースに多くの KIE セッションを作成でき、同じ KIE セッション内に、プロセスのインスタンスを多数作成できます。KIE セッションを作成して、KIE セッション内にプロセスインスタンスを作成し、KIE ベースを作成するよりもはるかに少ないリソースを使用します。KIE ベースを変更する場合は、これを使用する KIE セッションで変更を自動的に使用できます。
ほとんどの単純なユースケースでは、1 つの KIE セッションを使用してすべてのプロセスを実行できます。必要に応じて、複数のセッションを使用することもできます。たとえば、異なる顧客による注文処理を完全に独立させる場合は、顧客ごとに KIE セッションを作成できます。スケーラビリティーの理由から複数のセッションを使用することもできます。
一般的なアプリケーションでは、KIE ベースまたは KIE セッションを直接作成する必要はありません。ただし、プロセスエンジン API の他のレベルを使用する場合は、このレベルが定義する API の要素と対話することができます。
66.1.1. Kie ベース
KIE ベースには、アプリケーションによるビジネスプロセスの実行に必要となる可能性のあるプロセス定義およびその他のアセットがすべて含まれます。
KIE ベースを作成するには、KieHelper インスタンスを使用して、クラスパスやファイルシステムなどの各種リソースからプロセスを読み込み、新規の KIE ベースを作成します。
以下のコードスニペットは、クラスパスから読み込まれるプロセス定義が 1 つだけの KIE ベースを作成する方法を示しています。
1 つのプロセス定義を含む KIE ベースの作成
KieHelper kieHelper = new KieHelper();
KieBase kieBase = kieHelper
.addResource(ResourceFactory.newClassPathResource("MyProcess.bpmn"))
.build();
KieHelper kieHelper = new KieHelper();
KieBase kieBase = kieHelper
.addResource(ResourceFactory.newClassPathResource("MyProcess.bpmn"))
.build();
ResourceFactory クラスには、ファイル、URL、InputStream、Reader、およびその他のソースからリソースを読み込む同様のメソッドがあります。
KIE ベースを作成するこの手動プロセスは、他の方法よりも簡単ですが、アプリケーションが管理しにくくなります。RuntimeManager クラスやサービス API など、KIE ベースを作成する他の方法を使用して、開発および維持が長い期間にわたって予定されているアプリケーションに使用します。
66.1.2. KIE セッション
KIE ベースを作成して読み込んだら、KIE セッションを作成してプロセスエンジンと対話できます。このセッションを使用してプロセスを開始および管理し、イベントにシグナルを送信できます。
以下のコードスニペットは、以前に作成した KIE ベースに基づいてセッションを作成し、プロセスインスタンスを開始し、プロセス定義で ID を参照します。
KIE セッションの作成およびプロセスインスタンスの開始
KieSession ksession = kbase.newKieSession();
ProcessInstance processInstance = ksession.startProcess("com.sample.MyProcess");
KieSession ksession = kbase.newKieSession();
ProcessInstance processInstance = ksession.startProcess("com.sample.MyProcess");66.1.3. ProcessRuntime インターフェイス
KieSession クラスは、以下の定義が示すように、プロセスと対話するためのすべてのセッションメソッドを定義する ProcessRuntime インターフェイスを公開します。
ProcessRuntime インターフェイスの定義
66.1.4. 相関キー
プロセスを処理する場合には、ビジネス ID をプロセスインスタンスに割り当ててから、生成されたインスタンス ID を保存せずに、割り当てたビジネス ID を使用してインスタンスを参照しなければならない場合があります。
このような機能を提供するために、プロセスエンジンは CorrelationKey インターフェイスを使用して CorrelationProperties を定義できます。CorrelationKey を実装するクラスには、記述される単一のプロパティーまたはマルチプロパティーセットがあります。プロパティーの値または複数のプロパティーの値の組み合わせは一意のインスタンスを参照します。
KieSession クラスは、相関機能をサポートする CorrelationAwareProcessRuntime インターフェイスを実装します。このインターフェイスは以下のメソッドを公開します。
CorrelationAwareProcessRuntime インターフェイスのメソッド
相関は通常、長時間実行されるプロセスで使用されます。相関情報を永続的に保存する場合は、永続性を有効にする必要があります。