3.2. State Management
The broker is responsible for managing persistent data for OpenShift Enterprise using three distinct interfaces that represent the complete state. Three interfaces are used because each data store is pluggable and each type of data is usually managed by a separate system. The following table describes each section of application data.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| State | This is the general application state where the data is stored using MongoDB by default. |
| DNS | This is the dynamic DNS state where BIND handles the data by default. |
| Auth | This is the user state for authentication and authorization. This state is stored using any authentication mechanism supported by Apache, such as mod_auth_ldap and mod_auth_kerb. |
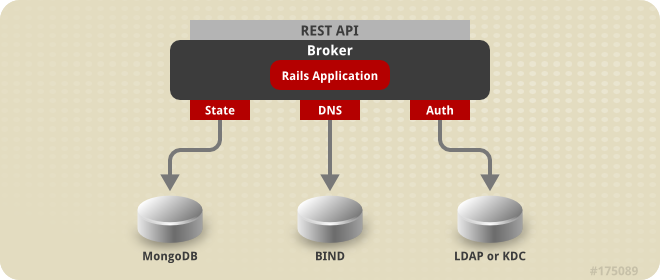
Figure 3.4. OpenShift Enterprise State Management