Chapter 17. Delegating Access to Hosts and Services
To manage in the context of this chapter means being able to retrieve a keytab and certificates for another host or service. Every host and service has a
managedby entry which lists what hosts or services can manage it. By default, a host can manage itself and all of its services. It is also possible to allow a host to manage other hosts, or services on other hosts, by updating the appropriate delegations or providing a suitable managedby entry.
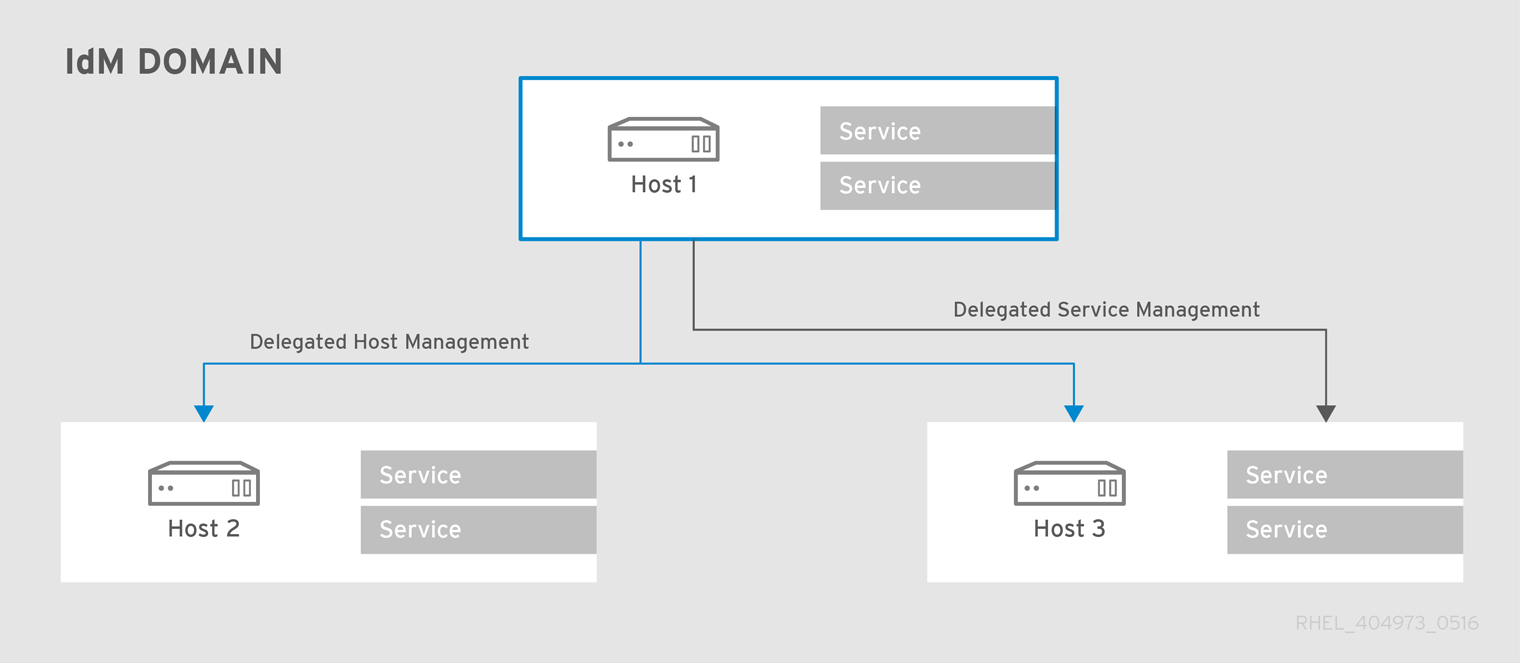
An IdM service can be managed from any IdM host, as long as that host has been granted, or delegated, permission to access the service. Likewise, hosts can be delegated permissions to other hosts within the domain.
Figure 17.1. Host and Service Delegation
Note
If a host is delegated authority to another host through a managedBy entry, it does not mean that the host has also been delegated management for all services on that host. Each delegation has to be performed independently.
17.1. Delegating Service Management
A host is delegated control over a service using the service-add-host utility:
# ipa service-add-host principal --hosts=hostname
There are two parts to delegating the service:
- Specifying the principal using the principal argument.
- Identifying the hosts with the control using the
--hostsoption.
For example:
[root@server ~]# ipa service-add HTTP/web.example.com [root@server ~]# ipa service-add-host HTTP/web.example.com --hosts=client1.example.com
Once the host is delegated authority, the host principal can be used to manage the service:
[root@client1 ~]# kinit -kt /etc/krb5.keytab host/client1.example.com [root@client1 ~]# ipa-getkeytab -s server.example.com -k /tmp/test.keytab -p HTTP/web.example.com Keytab successfully retrieved and stored in: /tmp/test.keytab
To create a ticket for this service, create a certificate request on the host with the delegated authority:
[root@client1]# kinit -kt /etc/krb5.keytab host/client1.example.com [root@client1]# openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -subj '/CN=web.example.com/O=EXAMPLE.COM' -keyout /etc/pki/tls/web.key -out /tmp/web.csr -nodes Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key .............................................................+++ ............................................................................................+++ Writing new private key to '/etc/pki/tls/private/web.key'
Use the cert-request utility to create a service entry and load the certification information:
[root@client1]# ipa cert-request --principal=HTTP/web.example.com web.csr Certificate: MIICETCCAXqgA...[snip] Subject: CN=web.example.com,O=EXAMPLE.COM Issuer: CN=EXAMPLE.COM Certificate Authority Not Before: Tue Feb 08 18:51:51 2011 UTC Not After: Mon Feb 08 18:51:51 2016 UTC Serial number: 1005
For more information on creating certificate requests and using ipa cert-request, see Section 24.1.1, “Requesting New Certificates for a User, Host, or Service”.