Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 3. Installing a cluster on OpenStack with customizations
In OpenShift Container Platform version 4.14, you can install a customized cluster on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP). To customize the installation, modify parameters in the install-config.yaml before you install the cluster.
3.1. Prerequisites
- You reviewed details about the OpenShift Container Platform installation and update processes.
- You read the documentation on selecting a cluster installation method and preparing it for users.
- You verified that OpenShift Container Platform 4.14 is compatible with your RHOSP version by using the Supported platforms for OpenShift clusters section. You can also compare platform support across different versions by viewing the OpenShift Container Platform on RHOSP support matrix.
- You have a storage service installed in RHOSP, such as block storage (Cinder) or object storage (Swift). Object storage is the recommended storage technology for OpenShift Container Platform registry cluster deployment. For more information, see Optimizing storage.
- You understand performance and scalability practices for cluster scaling, control plane sizing, and etcd. For more information, see Recommended practices for scaling the cluster.
- You have the metadata service enabled in RHOSP.
3.2. Resource guidelines for installing OpenShift Container Platform on RHOSP
To support an OpenShift Container Platform installation, your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) quota must meet the following requirements:
| Resource | Value |
|---|---|
| Floating IP addresses | 3 |
| Ports | 15 |
| Routers | 1 |
| Subnets | 1 |
| RAM | 88 GB |
| vCPUs | 22 |
| Volume storage | 275 GB |
| Instances | 7 |
| Security groups | 3 |
| Security group rules | 60 |
| Server groups | 2 - plus 1 for each additional availability zone in each machine pool |
A cluster might function with fewer than recommended resources, but its performance is not guaranteed.
If RHOSP object storage (Swift) is available and operated by a user account with the swiftoperator role, it is used as the default backend for the OpenShift Container Platform image registry. In this case, the volume storage requirement is 175 GB. Swift space requirements vary depending on the size of the image registry.
By default, your security group and security group rule quotas might be low. If you encounter problems, run openstack quota set --secgroups 3 --secgroup-rules 60 <project> as an administrator to increase them.
An OpenShift Container Platform deployment comprises control plane machines, compute machines, and a bootstrap machine.
3.2.1. Control plane machines
By default, the OpenShift Container Platform installation process creates three control plane machines.
Each machine requires:
- An instance from the RHOSP quota
- A port from the RHOSP quota
- A flavor with at least 16 GB memory and 4 vCPUs
- At least 100 GB storage space from the RHOSP quota
3.2.2. Compute machines
By default, the OpenShift Container Platform installation process creates three compute machines.
Each machine requires:
- An instance from the RHOSP quota
- A port from the RHOSP quota
- A flavor with at least 8 GB memory and 2 vCPUs
- At least 100 GB storage space from the RHOSP quota
Compute machines host the applications that you run on OpenShift Container Platform; aim to run as many as you can.
3.2.3. Bootstrap machine
During installation, a bootstrap machine is temporarily provisioned to stand up the control plane. After the production control plane is ready, the bootstrap machine is deprovisioned.
The bootstrap machine requires:
- An instance from the RHOSP quota
- A port from the RHOSP quota
- A flavor with at least 16 GB memory and 4 vCPUs
- At least 100 GB storage space from the RHOSP quota
3.2.4. Load balancing requirements for user-provisioned infrastructure
Before you install OpenShift Container Platform, you can provision your own API and application ingress load balancing infrastructure to use in place of the default, internal load balancing solution. In production scenarios, you can deploy the API and application Ingress load balancers separately so that you can scale the load balancer infrastructure for each in isolation.
If you want to deploy the API and application Ingress load balancers with a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) instance, you must purchase the RHEL subscription separately.
The load balancing infrastructure must meet the following requirements:
API load balancer: Provides a common endpoint for users, both human and machine, to interact with and configure the platform. Configure the following conditions:
- Layer 4 load balancing only. This can be referred to as Raw TCP or SSL Passthrough mode.
- A stateless load balancing algorithm. The options vary based on the load balancer implementation.
ImportantDo not configure session persistence for an API load balancer. Configuring session persistence for a Kubernetes API server might cause performance issues from excess application traffic for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster and the Kubernetes API that runs inside the cluster.
Configure the following ports on both the front and back of the load balancers:
Expand Table 3.2. API load balancer Port Back-end machines (pool members) Internal External Description 6443Bootstrap and control plane. You remove the bootstrap machine from the load balancer after the bootstrap machine initializes the cluster control plane. You must configure the
/readyzendpoint for the API server health check probe.X
X
Kubernetes API server
22623Bootstrap and control plane. You remove the bootstrap machine from the load balancer after the bootstrap machine initializes the cluster control plane.
X
Machine config server
NoteThe load balancer must be configured to take a maximum of 30 seconds from the time the API server turns off the
/readyzendpoint to the removal of the API server instance from the pool. Within the time frame after/readyzreturns an error or becomes healthy, the endpoint must have been removed or added. Probing every 5 or 10 seconds, with two successful requests to become healthy and three to become unhealthy, are well-tested values.Application Ingress load balancer: Provides an ingress point for application traffic flowing in from outside the cluster. A working configuration for the Ingress router is required for an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Configure the following conditions:
- Layer 4 load balancing only. This can be referred to as Raw TCP or SSL Passthrough mode.
- A connection-based or session-based persistence is recommended, based on the options available and types of applications that will be hosted on the platform.
TipIf the true IP address of the client can be seen by the application Ingress load balancer, enabling source IP-based session persistence can improve performance for applications that use end-to-end TLS encryption.
Configure the following ports on both the front and back of the load balancers:
Expand Table 3.3. Application Ingress load balancer Port Back-end machines (pool members) Internal External Description 443The machines that run the Ingress Controller pods, compute, or worker, by default.
X
X
HTTPS traffic
80The machines that run the Ingress Controller pods, compute, or worker, by default.
X
X
HTTP traffic
NoteIf you are deploying a three-node cluster with zero compute nodes, the Ingress Controller pods run on the control plane nodes. In three-node cluster deployments, you must configure your application Ingress load balancer to route HTTP and HTTPS traffic to the control plane nodes.
3.2.4.1. Example load balancer configuration for clusters that are deployed with user-managed load balancers
This section provides an example API and application Ingress load balancer configuration that meets the load balancing requirements for clusters that are deployed with user-managed load balancers. The sample is an /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg configuration for an HAProxy load balancer. The example is not meant to provide advice for choosing one load balancing solution over another.
In the example, the same load balancer is used for the Kubernetes API and application ingress traffic. In production scenarios, you can deploy the API and application ingress load balancers separately so that you can scale the load balancer infrastructure for each in isolation.
If you are using HAProxy as a load balancer and SELinux is set to enforcing, you must ensure that the HAProxy service can bind to the configured TCP port by running setsebool -P haproxy_connect_any=1.
Example 3.1. Sample API and application Ingress load balancer configuration
- 1
- Port
6443handles the Kubernetes API traffic and points to the control plane machines. - 2 4
- The bootstrap entries must be in place before the OpenShift Container Platform cluster installation and they must be removed after the bootstrap process is complete.
- 3
- Port
22623handles the machine config server traffic and points to the control plane machines. - 5
- Port
443handles the HTTPS traffic and points to the machines that run the Ingress Controller pods. The Ingress Controller pods run on the compute machines by default. - 6
- Port
80handles the HTTP traffic and points to the machines that run the Ingress Controller pods. The Ingress Controller pods run on the compute machines by default.NoteIf you are deploying a three-node cluster with zero compute nodes, the Ingress Controller pods run on the control plane nodes. In three-node cluster deployments, you must configure your application Ingress load balancer to route HTTP and HTTPS traffic to the control plane nodes.
If you are using HAProxy as a load balancer, you can check that the haproxy process is listening on ports 6443, 22623, 443, and 80 by running netstat -nltupe on the HAProxy node.
3.3. Internet access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.14, you require access to the internet to install your cluster.
You must have internet access to:
- Access OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the installation program and perform subscription management. If the cluster has internet access and you do not disable Telemetry, that service automatically entitles your cluster.
- Access Quay.io to obtain the packages that are required to install your cluster.
- Obtain the packages that are required to perform cluster updates.
If your cluster cannot have direct internet access, you can perform a restricted network installation on some types of infrastructure that you provision. During that process, you download the required content and use it to populate a mirror registry with the installation packages. With some installation types, the environment that you install your cluster in will not require internet access. Before you update the cluster, you update the content of the mirror registry.
3.4. Enabling Swift on RHOSP
Swift is operated by a user account with the swiftoperator role. Add the role to an account before you run the installation program.
If the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) object storage service, commonly known as Swift, is available, OpenShift Container Platform uses it as the image registry storage. If it is unavailable, the installation program relies on the RHOSP block storage service, commonly known as Cinder.
If Swift is present and you want to use it, you must enable access to it. If it is not present, or if you do not want to use it, skip this section.
RHOSP 17 sets the rgw_max_attr_size parameter of Ceph RGW to 256 characters. This setting causes issues with uploading container images to the OpenShift Container Platform registry. You must set the value of rgw_max_attr_size to at least 1024 characters.
Before installation, check if your RHOSP deployment is affected by this problem. If it is, reconfigure Ceph RGW.
Prerequisites
- You have a RHOSP administrator account on the target environment.
- The Swift service is installed.
-
On Ceph RGW, the
account in urloption is enabled.
Procedure
To enable Swift on RHOSP:
As an administrator in the RHOSP CLI, add the
swiftoperatorrole to the account that will access Swift:openstack role add --user <user> --project <project> swiftoperator
$ openstack role add --user <user> --project <project> swiftoperatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Your RHOSP deployment can now use Swift for the image registry.
3.5. Configuring an image registry with custom storage on clusters that run on RHOSP
After you install a cluster on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), you can use a Cinder volume that is in a specific availability zone for registry storage.
Procedure
Create a YAML file that specifies the storage class and availability zone to use. For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteOpenShift Container Platform does not verify the existence of the availability zone you choose. Verify the name of the availability zone before you apply the configuration.
From a command line, apply the configuration:
oc apply -f <storage_class_file_name>
$ oc apply -f <storage_class_file_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/custom-csi-storageclass created
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/custom-csi-storageclass createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file that specifies a persistent volume claim (PVC) that uses your storage class and the
openshift-image-registrynamespace. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From a command line, apply the configuration:
oc apply -f <pvc_file_name>
$ oc apply -f <pvc_file_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
persistentvolumeclaim/csi-pvc-imageregistry created
persistentvolumeclaim/csi-pvc-imageregistry createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace the original persistent volume claim in the image registry configuration with the new claim:
oc patch configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type 'json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/storage/pvc/claim", "value": "csi-pvc-imageregistry"}]'$ oc patch configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type 'json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/storage/pvc/claim", "value": "csi-pvc-imageregistry"}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster patched
config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Over the next several minutes, the configuration is updated.
Verification
To confirm that the registry is using the resources that you defined:
Verify that the PVC claim value is identical to the name that you provided in your PVC definition:
oc get configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the status of the PVC is
Bound:oc get pvc -n openshift-image-registry csi-pvc-imageregistry
$ oc get pvc -n openshift-image-registry csi-pvc-imageregistryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE csi-pvc-imageregistry Bound pvc-72a8f9c9-f462-11e8-b6b6-fa163e18b7b5 100Gi RWO custom-csi-storageclass 11m
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE csi-pvc-imageregistry Bound pvc-72a8f9c9-f462-11e8-b6b6-fa163e18b7b5 100Gi RWO custom-csi-storageclass 11mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.6. Verifying external network access
The OpenShift Container Platform installation process requires external network access. You must provide an external network value to it, or deployment fails. Before you begin the process, verify that a network with the external router type exists in Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP).
Prerequisites
Procedure
Using the RHOSP CLI, verify the name and ID of the 'External' network:
openstack network list --long -c ID -c Name -c "Router Type"
$ openstack network list --long -c ID -c Name -c "Router Type"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
+--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+ | ID | Name | Router Type | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+ | 148a8023-62a7-4672-b018-003462f8d7dc | public_network | External | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+
+--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+ | ID | Name | Router Type | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+ | 148a8023-62a7-4672-b018-003462f8d7dc | public_network | External | +--------------------------------------+----------------+-------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
A network with an external router type appears in the network list. If at least one does not, see Creating a default floating IP network and Creating a default provider network.
If the external network’s CIDR range overlaps one of the default network ranges, you must change the matching network ranges in the install-config.yaml file before you start the installation process.
The default network ranges are:
| Network | Range |
|---|---|
|
| 10.0.0.0/16 |
|
| 172.30.0.0/16 |
|
| 10.128.0.0/14 |
If the installation program finds multiple networks with the same name, it sets one of them at random. To avoid this behavior, create unique names for resources in RHOSP.
If the Neutron trunk service plugin is enabled, a trunk port is created by default. For more information, see Neutron trunk port.
3.7. Defining parameters for the installation program
The OpenShift Container Platform installation program relies on a file that is called clouds.yaml. The file describes Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) configuration parameters, including the project name, log in information, and authorization service URLs.
Procedure
Create the
clouds.yamlfile:If your RHOSP distribution includes the Horizon web UI, generate a
clouds.yamlfile in it.ImportantRemember to add a password to the
authfield. You can also keep secrets in a separate file fromclouds.yaml.If your RHOSP distribution does not include the Horizon web UI, or you do not want to use Horizon, create the file yourself. For detailed information about
clouds.yaml, see Config files in the RHOSP documentation.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If your RHOSP installation uses self-signed certificate authority (CA) certificates for endpoint authentication:
- Copy the certificate authority file to your machine.
Add the
cacertskey to theclouds.yamlfile. The value must be an absolute, non-root-accessible path to the CA certificate:clouds: shiftstack: ... cacert: "/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ca.crt.pem"clouds: shiftstack: ... cacert: "/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ca.crt.pem"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipAfter you run the installer with a custom CA certificate, you can update the certificate by editing the value of the
ca-cert.pemkey in thecloud-provider-configkeymap. On a command line, run:oc edit configmap -n openshift-config cloud-provider-config
$ oc edit configmap -n openshift-config cloud-provider-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Place the
clouds.yamlfile in one of the following locations:-
The value of the
OS_CLIENT_CONFIG_FILEenvironment variable - The current directory
-
A Unix-specific user configuration directory, for example
~/.config/openstack/clouds.yaml A Unix-specific site configuration directory, for example
/etc/openstack/clouds.yamlThe installation program searches for
clouds.yamlin that order.
-
The value of the
3.8. Setting OpenStack Cloud Controller Manager options
Optionally, you can edit the OpenStack Cloud Controller Manager (CCM) configuration for your cluster. This configuration controls how OpenShift Container Platform interacts with Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP).
For a complete list of configuration parameters, see the "OpenStack Cloud Controller Manager reference guide" page in the "Installing on OpenStack" documentation.
Procedure
If you have not already generated manifest files for your cluster, generate them by running the following command:
openshift-install --dir <destination_directory> create manifests
$ openshift-install --dir <destination_directory> create manifestsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a text editor, open the cloud-provider configuration manifest file. For example:
vi openshift/manifests/cloud-provider-config.yaml
$ vi openshift/manifests/cloud-provider-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the options according to the CCM reference guide.
Configuring Octavia for load balancing is a common case for clusters that do not use Kuryr. For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This property sets the Octavia provider that your load balancer uses. It accepts
"ovn"or"amphora"as values. If you choose to use OVN, you must also setlb-methodtoSOURCE_IP_PORT. - 2
- This property is required if you want to use multiple external networks with your cluster. The cloud provider creates floating IP addresses on the network that is specified here.
- 3
- This property controls whether the cloud provider creates health monitors for Octavia load balancers. Set the value to
Trueto create health monitors. As of RHOSP 16.2, this feature is only available for the Amphora provider. - 4
- This property sets the frequency with which endpoints are monitored. The value must be in the
time.ParseDuration()format. This property is required if the value of thecreate-monitorproperty isTrue. - 5
- This property sets the time that monitoring requests are open before timing out. The value must be in the
time.ParseDuration()format. This property is required if the value of thecreate-monitorproperty isTrue. - 6
- This property defines how many successful monitoring requests are required before a load balancer is marked as online. The value must be an integer. This property is required if the value of the
create-monitorproperty isTrue.
ImportantPrior to saving your changes, verify that the file is structured correctly. Clusters might fail if properties are not placed in the appropriate section.
ImportantYou must set the value of the
create-monitorproperty toTrueif you use services that have the value of the.spec.externalTrafficPolicyproperty set toLocal. The OVN Octavia provider in RHOSP 16.2 does not support health monitors. Therefore, services that haveETPparameter values set toLocalmight not respond when thelb-providervalue is set to"ovn".ImportantFor installations that use Kuryr, Kuryr handles relevant services. There is no need to configure Octavia load balancing in the cloud provider.
Save the changes to the file and proceed with installation.
TipYou can update your cloud provider configuration after you run the installer. On a command line, run:
oc edit configmap -n openshift-config cloud-provider-config
$ oc edit configmap -n openshift-config cloud-provider-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you save your changes, your cluster will take some time to reconfigure itself. The process is complete if none of your nodes have a
SchedulingDisabledstatus.
3.9. Obtaining the installation program
Before you install OpenShift Container Platform, download the installation file on the host you are using for installation.
Prerequisites
- You have a computer that runs Linux or macOS, with at least 1.2 GB of local disk space.
Procedure
- Go to the Cluster Type page on the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console. If you have a Red Hat account, log in with your credentials. If you do not, create an account.
- Select your infrastructure provider from the Run it yourself section of the page.
- Select your host operating system and architecture from the dropdown menus under OpenShift Installer and click Download Installer.
Place the downloaded file in the directory where you want to store the installation configuration files.
Important- The installation program creates several files on the computer that you use to install your cluster. You must keep the installation program and the files that the installation program creates after you finish installing the cluster. Both of the files are required to delete the cluster.
- Deleting the files created by the installation program does not remove your cluster, even if the cluster failed during installation. To remove your cluster, complete the OpenShift Container Platform uninstallation procedures for your specific cloud provider.
Extract the installation program. For example, on a computer that uses a Linux operating system, run the following command:
tar -xvf openshift-install-linux.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf openshift-install-linux.tar.gzCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Download your installation pull secret from Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager. This pull secret allows you to authenticate with the services that are provided by the included authorities, including Quay.io, which serves the container images for OpenShift Container Platform components.
Alternatively, you can retrieve the installation program from the Red Hat Customer Portal, where you can specify a version of the installation program to download. However, you must have an active subscription to access this page.
3.10. Creating the installation configuration file
You can customize the OpenShift Container Platform cluster you install on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP).
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
Procedure
Create the
install-config.yamlfile.Change to the directory that contains the installation program and run the following command:
./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<installation_directory>, specify the directory name to store the files that the installation program creates.
When specifying the directory:
-
Verify that the directory has the
executepermission. This permission is required to run Terraform binaries under the installation directory. Use an empty directory. Some installation assets, such as bootstrap X.509 certificates, have short expiration intervals, therefore you must not reuse an installation directory. If you want to reuse individual files from another cluster installation, you can copy them into your directory. However, the file names for the installation assets might change between releases. Use caution when copying installation files from an earlier OpenShift Container Platform version.
NoteAlways delete the
~/.powervsdirectory to avoid reusing a stale configuration. Run the following command:rm -rf ~/.powervs
$ rm -rf ~/.powervsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
At the prompts, provide the configuration details for your cloud:
Optional: Select an SSH key to use to access your cluster machines.
NoteFor production OpenShift Container Platform clusters on which you want to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, specify an SSH key that your
ssh-agentprocess uses.- Select openstack as the platform to target.
- Specify the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) external network name to use for installing the cluster.
- Specify the floating IP address to use for external access to the OpenShift API.
- Specify a RHOSP flavor with at least 16 GB RAM to use for control plane nodes and 8 GB RAM for compute nodes.
- Select the base domain to deploy the cluster to. All DNS records will be sub-domains of this base and will also include the cluster name.
- Enter a name for your cluster. The name must be 14 or fewer characters long.
-
Modify the
install-config.yamlfile. You can find more information about the available parameters in the "Installation configuration parameters" section. Back up the
install-config.yamlfile so that you can use it to install multiple clusters.ImportantThe
install-config.yamlfile is consumed during the installation process. If you want to reuse the file, you must back it up now.
3.10.1. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy during installation
Production environments can deny direct access to the internet and instead have an HTTP or HTTPS proxy available. You can configure a new OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use a proxy by configuring the proxy settings in the install-config.yaml file.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing
install-config.yamlfile. You reviewed the sites that your cluster requires access to and determined whether any of them need to bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster egress traffic is proxied, including calls to hosting cloud provider APIs. You added sites to the
Proxyobject’sspec.noProxyfield to bypass the proxy if necessary.NoteThe
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is populated with the values of thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidr,networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, andnetworking.serviceNetwork[]fields from your installation configuration.For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint (169.254.169.254).
Procedure
Edit your
install-config.yamlfile and add the proxy settings. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. - 2
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster.
- 3
- A comma-separated list of destination domain names, IP addresses, or other network CIDRs to exclude from proxying. Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass the proxy for all destinations. - 4
- If provided, the installation program generates a config map that is named
user-ca-bundlein theopenshift-confignamespace that contains one or more additional CA certificates that are required for proxying HTTPS connections. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleconfig map that merges these contents with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) trust bundle, and this config map is referenced in thetrustedCAfield of theProxyobject. TheadditionalTrustBundlefield is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle. - 5
- Optional: The policy to determine the configuration of the
Proxyobject to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The allowed values areProxyonlyandAlways. UseProxyonlyto reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map only whenhttp/httpsproxy is configured. UseAlwaysto always reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map. The default value isProxyonly.
NoteThe installation program does not support the proxy
readinessEndpointsfield.NoteIf the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the
wait-forcommand of the installer. For example:./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file and reference it when installing OpenShift Container Platform.
The installation program creates a cluster-wide proxy that is named cluster that uses the proxy settings in the provided install-config.yaml file. If no proxy settings are provided, a cluster Proxy object is still created, but it will have a nil spec.
Only the Proxy object named cluster is supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
3.10.2. Custom subnets in RHOSP deployments
Optionally, you can deploy a cluster on a Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) subnet of your choice. The subnet’s GUID is passed as the value of platform.openstack.machinesSubnet in the install-config.yaml file.
This subnet is used as the cluster’s primary subnet. By default, nodes and ports are created on it. You can create nodes and ports on a different RHOSP subnet by setting the value of the platform.openstack.machinesSubnet property to the subnet’s UUID.
Before you run the OpenShift Container Platform installer with a custom subnet, verify that your configuration meets the following requirements:
-
The subnet that is used by
platform.openstack.machinesSubnethas DHCP enabled. -
The CIDR of
platform.openstack.machinesSubnetmatches the CIDR ofnetworking.machineNetwork. - The installation program user has permission to create ports on this network, including ports with fixed IP addresses.
Clusters that use custom subnets have the following limitations:
-
If you plan to install a cluster that uses floating IP addresses, the
platform.openstack.machinesSubnetsubnet must be attached to a router that is connected to theexternalNetworknetwork. -
If the
platform.openstack.machinesSubnetvalue is set in theinstall-config.yamlfile, the installation program does not create a private network or subnet for your RHOSP machines. -
You cannot use the
platform.openstack.externalDNSproperty at the same time as a custom subnet. To add DNS to a cluster that uses a custom subnet, configure DNS on the RHOSP network.
By default, the API VIP takes x.x.x.5 and the Ingress VIP takes x.x.x.7 from your network’s CIDR block. To override these default values, set values for platform.openstack.apiVIPs and platform.openstack.ingressVIPs that are outside of the DHCP allocation pool.
The CIDR ranges for networks are not adjustable after cluster installation. Red Hat does not provide direct guidance on determining the range during cluster installation because it requires careful consideration of the number of created pods per namespace.
3.10.3. Deploying a cluster with bare metal machines
If you want your cluster to use bare metal machines, modify the install-config.yaml file. Your cluster can have compute machines running on bare metal.
Bare-metal compute machines are not supported on clusters that use Kuryr.
Be sure that your install-config.yaml file reflects whether the RHOSP network that you use for bare metal workers supports floating IP addresses or not.
Prerequisites
- The RHOSP Bare Metal service (Ironic) is enabled and accessible via the RHOSP Compute API.
- Bare metal is available as a RHOSP flavor.
- If your cluster runs on an RHOSP version that is more than 16.1.6 and less than 16.2.4, bare metal workers do not function due to a known issue that causes the metadata service to be unavailable for services on OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
- The RHOSP network supports both VM and bare metal server attachment.
- If you want to deploy the machines on a pre-existing network, a RHOSP subnet is provisioned.
- If you want to deploy the machines on an installer-provisioned network, the RHOSP Bare Metal service (Ironic) is able to listen for and interact with Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE) boot machines that run on tenant networks.
-
You created an
install-config.yamlfile as part of the OpenShift Container Platform installation process.
Procedure
In the
install-config.yamlfile, edit the flavors for machines:-
Change the value of
compute.platform.openstack.typeto a bare metal flavor. If you want to deploy your machines on a pre-existing network, change the value of
platform.openstack.machinesSubnetto the RHOSP subnet UUID of the network.An example bare metal
install-config.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Change the value of
Use the updated install-config.yaml file to complete the installation process. The compute machines that are created during deployment use the flavor that you added to the file.
The installer may time out while waiting for bare metal machines to boot.
If the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the wait-for command of the installer. For example:
./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug3.10.4. Cluster deployment on RHOSP provider networks
You can deploy your OpenShift Container Platform clusters on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) with a primary network interface on a provider network. Provider networks are commonly used to give projects direct access to a public network that can be used to reach the internet. You can also share provider networks among projects as part of the network creation process.
RHOSP provider networks map directly to an existing physical network in the data center. A RHOSP administrator must create them.
In the following example, OpenShift Container Platform workloads are connected to a data center by using a provider network:
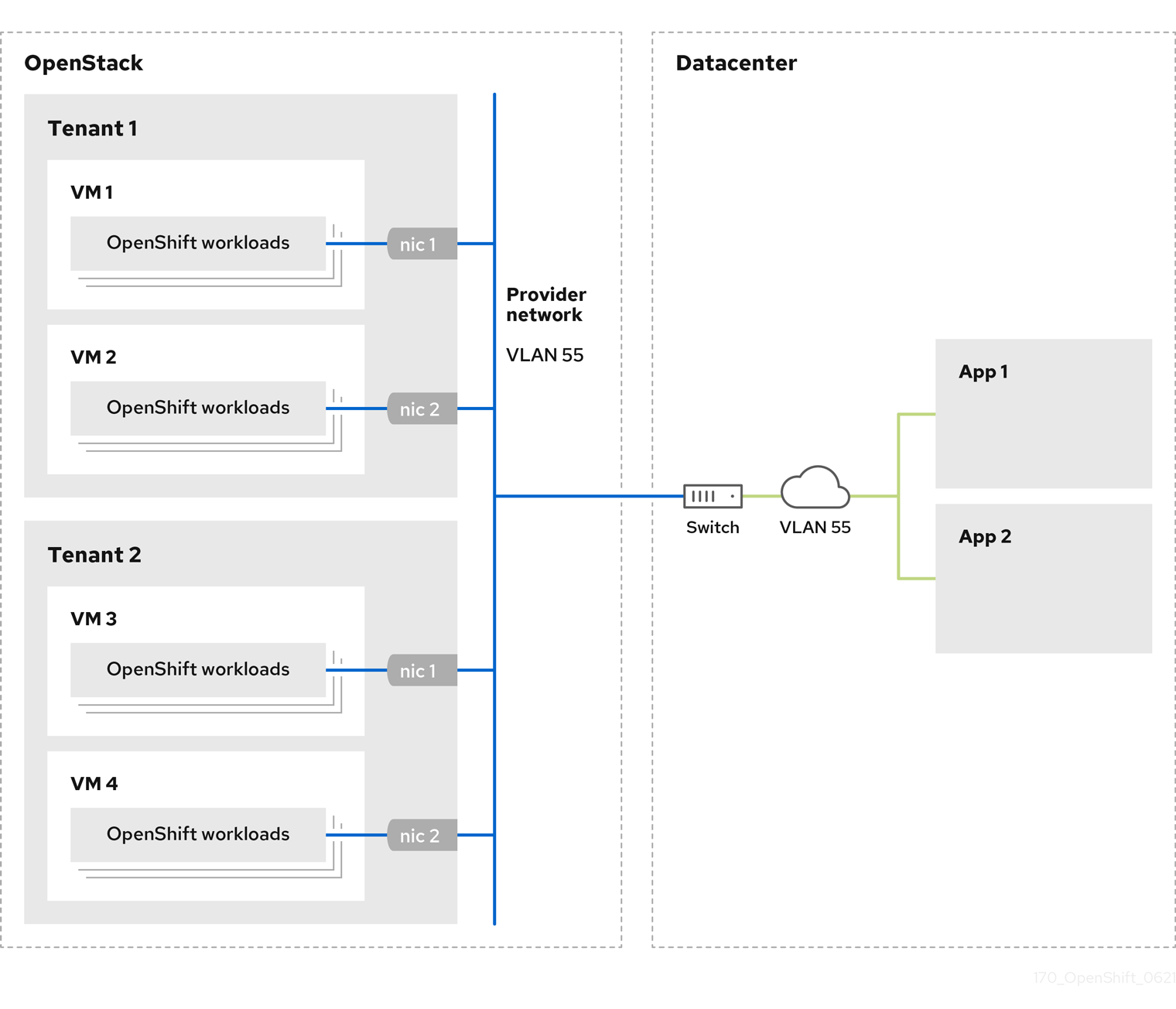
OpenShift Container Platform clusters that are installed on provider networks do not require tenant networks or floating IP addresses. The installer does not create these resources during installation.
Example provider network types include flat (untagged) and VLAN (802.1Q tagged).
A cluster can support as many provider network connections as the network type allows. For example, VLAN networks typically support up to 4096 connections.
You can learn more about provider and tenant networks in the RHOSP documentation.
3.10.4.1. RHOSP provider network requirements for cluster installation
Before you install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster, your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) deployment and provider network must meet a number of conditions:
- The RHOSP networking service (Neutron) is enabled and accessible through the RHOSP networking API.
- The RHOSP networking service has the port security and allowed address pairs extensions enabled.
The provider network can be shared with other tenants.
TipUse the
openstack network createcommand with the--shareflag to create a network that can be shared.The RHOSP project that you use to install the cluster must own the provider network, as well as an appropriate subnet.
Tip- To create a network for a project that is named "openshift," enter the following command
openstack network create --project openshift
$ openstack network create --project openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To create a subnet for a project that is named "openshift," enter the following command
openstack subnet create --project openshift
$ openstack subnet create --project openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To learn more about creating networks on RHOSP, read the provider networks documentation.
If the cluster is owned by the
adminuser, you must run the installer as that user to create ports on the network.ImportantProvider networks must be owned by the RHOSP project that is used to create the cluster. If they are not, the RHOSP Compute service (Nova) cannot request a port from that network.
Verify that the provider network can reach the RHOSP metadata service IP address, which is
169.254.169.254by default.Depending on your RHOSP SDN and networking service configuration, you might need to provide the route when you create the subnet. For example:
openstack subnet create --dhcp --host-route destination=169.254.169.254/32,gateway=192.0.2.2 ...
$ openstack subnet create --dhcp --host-route destination=169.254.169.254/32,gateway=192.0.2.2 ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optional: To secure the network, create role-based access control (RBAC) rules that limit network access to a single project.
3.10.4.2. Deploying a cluster that has a primary interface on a provider network
You can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster that has its primary network interface on an Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) provider network.
Prerequisites
- Your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) deployment is configured as described by "RHOSP provider network requirements for cluster installation".
Procedure
-
In a text editor, open the
install-config.yamlfile. -
Set the value of the
platform.openstack.apiVIPsproperty to the IP address for the API VIP. -
Set the value of the
platform.openstack.ingressVIPsproperty to the IP address for the Ingress VIP. -
Set the value of the
platform.openstack.machinesSubnetproperty to the UUID of the provider network subnet. -
Set the value of the
networking.machineNetwork.cidrproperty to the CIDR block of the provider network subnet.
The platform.openstack.apiVIPs and platform.openstack.ingressVIPs properties must both be unassigned IP addresses from the networking.machineNetwork.cidr block.
Section of an installation configuration file for a cluster that relies on a RHOSP provider network
You cannot set the platform.openstack.externalNetwork or platform.openstack.externalDNS parameters while using a provider network for the primary network interface.
When you deploy the cluster, the installer uses the install-config.yaml file to deploy the cluster on the provider network.
You can add additional networks, including provider networks, to the platform.openstack.additionalNetworkIDs list.
After you deploy your cluster, you can attach pods to additional networks. For more information, see Understanding multiple networks.
3.10.5. Sample customized install-config.yaml file for RHOSP
This sample install-config.yaml demonstrates all of the possible Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) customization options.
This sample file is provided for reference only. You must obtain your install-config.yaml file by using the installation program.
3.10.6. Optional: Configuring a cluster with dual-stack networking
Dual-stack configuration for OpenStack is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
You can create a dual-stack cluster on RHOSP. However, the dual-stack configuration is enabled only if you are using an RHOSP network with IPv4 and IPv6 subnets.
RHOSP does not support the following configurations:
- Conversion of an IPv4 single-stack cluster to a dual-stack cluster network.
- IPv6 as the primary address family for dual-stack cluster network.
3.10.6.1. Deploying the dual-stack cluster
For dual-stack networking in OpenShift Container Platform clusters, you can configure IPv4 and IPv6 address endpoints for cluster nodes.
Prerequisites
- You enabled Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on the subnets.
Procedure
Create a network with IPv4 and IPv6 subnets. The available address modes for
ipv6-ra-modeandipv6-address-modefields are:stateful,statelessandslaac.NoteThe dual-stack network MTU must accommodate both the minimum MTU for IPv6, which is
1280, and the OVN-Kubernetes encapsulation overhead, which is100.- Create the API and Ingress VIPs ports.
- Add the IPv6 subnet to the router to enable router advertisements. If you are using a provider network, you can enable router advertisements by adding the network as an external gateway, which also enables external connectivity.
For an IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack cluster where you set IPv4 as the primary endpoint for your cluster nodes, edit the
install-config.yamlfile like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Dual-stack clusters are supported only with the
TechPreviewNoUpgradevalue. - 2 3 4
- You must specify an IP address range in the
cidrfield for both IPv4 and IPv6 address families. - 5
- Specify the virtual IP (VIP) address endpoints for the Ingress VIP services to provide an interface to the cluster.
- 6
- Specify the virtual IP (VIP) address endpoints for the API VIP services to provide an interface to the cluster.
- 7
- Specify the dual-stack network details that are used by all the nodes across the cluster.
- 8
- The Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) of any subnet specified in this field must match the CIDRs listed on
networks.machineNetwork. - 9 10 11
- You can specify a value for
name,id, or both.
The ip=dhcp,dhcp6 kernel argument, which is set on all of the nodes, results in a single Network Manager connection profile that is activated on multiple interfaces simultaneously. Because of this behavior, any additional network has the same connection enforced with an identical UUID. If you need an interface-specific configuration, create a new connection profile for that interface so that the default connection is no longer enforced on it.
3.10.7. Installation configuration for a cluster on OpenStack with a user-managed load balancer
The following example install-config.yaml file demonstrates how to configure a cluster that uses an external, user-managed load balancer rather than the default internal load balancer.
3.11. Generating a key pair for cluster node SSH access
During an OpenShift Container Platform installation, you can provide an SSH public key to the installation program. The key is passed to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) nodes through their Ignition config files and is used to authenticate SSH access to the nodes. The key is added to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys list for the core user on each node, which enables password-less authentication.
After the key is passed to the nodes, you can use the key pair to SSH in to the RHCOS nodes as the user core. To access the nodes through SSH, the private key identity must be managed by SSH for your local user.
If you want to SSH in to your cluster nodes to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, you must provide the SSH public key during the installation process. The ./openshift-install gather command also requires the SSH public key to be in place on the cluster nodes.
Do not skip this procedure in production environments, where disaster recovery and debugging is required.
Procedure
If you do not have an existing SSH key pair on your local machine to use for authentication onto your cluster nodes, create one. For example, on a computer that uses a Linux operating system, run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -f <path>/<file_name>
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -f <path>/<file_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the path and file name, such as
~/.ssh/id_ed25519, of the new SSH key. If you have an existing key pair, ensure your public key is in the your~/.sshdirectory.
NoteIf you plan to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster that uses the RHEL cryptographic libraries that have been submitted to NIST for FIPS 140-2/140-3 Validation on only the
x86_64,ppc64le, ands390xarchitectures, do not create a key that uses theed25519algorithm. Instead, create a key that uses thersaorecdsaalgorithm.View the public SSH key:
cat <path>/<file_name>.pub
$ cat <path>/<file_name>.pubCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, run the following to view the
~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pubpublic key:cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pubCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the SSH private key identity to the SSH agent for your local user, if it has not already been added. SSH agent management of the key is required for password-less SSH authentication onto your cluster nodes, or if you want to use the
./openshift-install gathercommand.NoteOn some distributions, default SSH private key identities such as
~/.ssh/id_rsaand~/.ssh/id_dsaare managed automatically.If the
ssh-agentprocess is not already running for your local user, start it as a background task:eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Agent pid 31874
Agent pid 31874Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf your cluster is in FIPS mode, only use FIPS-compliant algorithms to generate the SSH key. The key must be either RSA or ECDSA.
Add your SSH private key to the
ssh-agent:ssh-add <path>/<file_name>
$ ssh-add <path>/<file_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the path and file name for your SSH private key, such as
~/.ssh/id_ed25519
Example output
Identity added: /home/<you>/<path>/<file_name> (<computer_name>)
Identity added: /home/<you>/<path>/<file_name> (<computer_name>)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
- When you install OpenShift Container Platform, provide the SSH public key to the installation program.
3.12. Enabling access to the environment
At deployment, all OpenShift Container Platform machines are created in a Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)-tenant network. Therefore, they are not accessible directly in most RHOSP deployments.
You can configure OpenShift Container Platform API and application access by using floating IP addresses (FIPs) during installation. You can also complete an installation without configuring FIPs, but the installer will not configure a way to reach the API or applications externally.
3.12.1. Enabling access with floating IP addresses
Create floating IP (FIP) addresses for external access to the OpenShift Container Platform API and cluster applications.
Procedure
Using the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) CLI, create the API FIP:
openstack floating ip create --description "API <cluster_name>.<base_domain>" <external_network>
$ openstack floating ip create --description "API <cluster_name>.<base_domain>" <external_network>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) CLI, create the apps, or Ingress, FIP:
openstack floating ip create --description "Ingress <cluster_name>.<base_domain>" <external_network>
$ openstack floating ip create --description "Ingress <cluster_name>.<base_domain>" <external_network>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add records that follow these patterns to your DNS server for the API and Ingress FIPs:
api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <API_FIP> *.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <apps_FIP>
api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <API_FIP> *.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <apps_FIP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do not control the DNS server, you can access the cluster by adding the cluster domain names such as the following to your
/etc/hostsfile:-
<api_floating_ip> api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -
<application_floating_ip> grafana-openshift-monitoring.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -
<application_floating_ip> prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -
<application_floating_ip> oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -
<application_floating_ip> console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -
application_floating_ip integrated-oauth-server-openshift-authentication.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>
The cluster domain names in the
/etc/hostsfile grant access to the web console and the monitoring interface of your cluster locally. You can also use thekubectloroc. You can access the user applications by using the additional entries pointing to the <application_floating_ip>. This action makes the API and applications accessible to only you, which is not suitable for production deployment, but does allow installation for development and testing.-
Add the FIPs to the
install-config.yamlfile as the values of the following parameters:-
platform.openstack.ingressFloatingIP -
platform.openstack.apiFloatingIP
-
If you use these values, you must also enter an external network as the value of the platform.openstack.externalNetwork parameter in the install-config.yaml file.
You can make OpenShift Container Platform resources available outside of the cluster by assigning a floating IP address and updating your firewall configuration.
3.12.2. Completing installation without floating IP addresses
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) without providing floating IP addresses.
In the install-config.yaml file, do not define the following parameters:
-
platform.openstack.ingressFloatingIP -
platform.openstack.apiFloatingIP
If you cannot provide an external network, you can also leave platform.openstack.externalNetwork blank. If you do not provide a value for platform.openstack.externalNetwork, a router is not created for you, and, without additional action, the installer will fail to retrieve an image from Glance. You must configure external connectivity on your own.
If you run the installer from a system that cannot reach the cluster API due to a lack of floating IP addresses or name resolution, installation fails. To prevent installation failure in these cases, you can use a proxy network or run the installer from a system that is on the same network as your machines.
You can enable name resolution by creating DNS records for the API and Ingress ports. For example:
api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <api_port_IP> *.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <ingress_port_IP>
api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <api_port_IP>
*.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. IN A <ingress_port_IP>
If you do not control the DNS server, you can add the record to your /etc/hosts file. This action makes the API accessible to only you, which is not suitable for production deployment but does allow installation for development and testing.
3.13. Deploying the cluster
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on a compatible cloud platform.
You can run the create cluster command of the installation program only once, during initial installation.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
- You have verified that the cloud provider account on your host has the correct permissions to deploy the cluster. An account with incorrect permissions causes the installation process to fail with an error message that displays the missing permissions.
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment:
./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \ --log-level=info$ ./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \1 --log-level=info2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
When the cluster deployment completes successfully:
-
The terminal displays directions for accessing your cluster, including a link to the web console and credentials for the
kubeadminuser. -
Credential information also outputs to
<installation_directory>/.openshift_install.log.
Do not delete the installation program or the files that the installation program creates. Both are required to delete the cluster.
Example output
-
The Ignition config files that the installation program generates contain certificates that expire after 24 hours, which are then renewed at that time. If the cluster is shut down before renewing the certificates and the cluster is later restarted after the 24 hours have elapsed, the cluster automatically recovers the expired certificates. The exception is that you must manually approve the pending
node-bootstrappercertificate signing requests (CSRs) to recover kubelet certificates. See the documentation for Recovering from expired control plane certificates for more information. - It is recommended that you use Ignition config files within 12 hours after they are generated because the 24-hour certificate rotates from 16 to 22 hours after the cluster is installed. By using the Ignition config files within 12 hours, you can avoid installation failure if the certificate update runs during installation.
3.14. Verifying cluster status
You can verify your OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s status during or after installation.
Procedure
In the cluster environment, export the administrator’s kubeconfig file:
export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<installation_directory>, specify the path to the directory that you stored the installation files in.
The
kubeconfigfile contains information about the cluster that is used by the CLI to connect a client to the correct cluster and API server.View the control plane and compute machines created after a deployment:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View your cluster’s version:
oc get clusterversion
$ oc get clusterversionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View your Operators' status:
oc get clusteroperator
$ oc get clusteroperatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View all running pods in the cluster:
oc get pods -A
$ oc get pods -ACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.15. Logging in to the cluster by using the CLI
You can log in to your cluster as a default system user by exporting the cluster kubeconfig file. The kubeconfig file contains information about the cluster that is used by the CLI to connect a client to the correct cluster and API server. The file is specific to a cluster and is created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Export the
kubeadmincredentials:export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<installation_directory>, specify the path to the directory that you stored the installation files in.
Verify you can run
occommands successfully using the exported configuration:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.16. Telemetry access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.14, the Telemetry service, which runs by default to provide metrics about cluster health and the success of updates, requires internet access. If your cluster is connected to the internet, Telemetry runs automatically, and your cluster is registered to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After you confirm that your OpenShift Cluster Manager inventory is correct, either maintained automatically by Telemetry or manually by using OpenShift Cluster Manager, use subscription watch to track your OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions at the account or multi-cluster level.