이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
10.2.4. User and System Connections
NetworkManager connections are always either user connections or system connections. Depending on the system-specific policy that the administrator has configured, users may need
root privileges to create and modify system connections. NetworkManager's default policy enables users to create and modify user connections, but requires them to have root privileges to add, modify or delete system connections.
User connections are so-called because they are specific to the user who creates them. In contrast to system connections, whose configurations are stored under the
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory (mainly in ifcfg-<network_type> interface configuration files), user connection settings are stored in the GConf configuration database and the GNOME keyring, and are only available during login sessions for the user who created them. Thus, logging out of the desktop session causes user-specific connections to become unavailable.
Note
Because NetworkManager uses the GConf and GNOME keyring applications to store user connection settings, and because these settings are specific to your desktop session, it is highly recommended to configure your personal VPN connections as user connections. If you do so, other Non-
root users on the system cannot view or access these connections in any way.
System connections, on the other hand, become available at boot time and can be used by other users on the system without first logging in to a desktop session.
NetworkManager can quickly and conveniently convert user to system connections and vice versa. Converting a user connection to a system connection causes NetworkManager to create the relevant interface configuration files under the
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory, and to delete the GConf settings from the user's session. Conversely, converting a system to a user-specific connection causes NetworkManager to remove the system-wide configuration files and create the corresponding GConf/GNOME keyring settings.
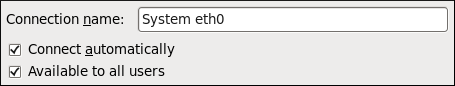
Figure 10.5. The Available to all users check box controls whether connections are user-specific or system-wide
Procedure 10.2. Changing a Connection to be User-Specific instead of System-Wide, or Vice-Versa
Note
Depending on the system's policy, you may need
root privileges on the system in order to change whether a connection is user-specific or system-wide.
- Right-click on the NetworkManager applet icon in the Notification Area and click Edit Connections. The Network Connections window appears.
- If needed, select the arrow head (on the left hand side) to hide and reveal the types of available network connections.
- Select the specific connection that you want to configure and click .
- Check the Available to all users check box to ask NetworkManager to make the connection a system-wide connection. Depending on system policy, you may then be prompted for the
rootpassword by the PolicyKit application. If so, enter therootpassword to finalize the change.Conversely, uncheck the Available to all users check box to make the connection user-specific.