Chapter 2. Installer-provisioned infrastructure
2.1. vSphere installation requirements
Before you begin an installation using installer-provisioned infrastructure, be sure that your vSphere environment meets the following installation requirements.
2.1.1. VMware vSphere infrastructure requirements
You must install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on a version of a VMware vSphere instance that meets the requirements for the components that you use:
- Version 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later
This release supports Container Storage Interface (CSI) migration, which is enabled by default on OpenShift Container Platform 4.16.
You can host the VMware vSphere infrastructure on-premise or on a VMware Cloud Verified provider that meets the requirements outlined in the following tables:
| Virtual environment product | Required version |
|---|---|
| VMware virtual hardware | 15 or later |
| vSphere ESXi hosts | 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later |
| vCenter host | 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later |
You must ensure that the time on your ESXi hosts is synchronized before you install OpenShift Container Platform. See Edit Time Configuration for a Host in the VMware documentation.
| Component | Minimum supported versions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hypervisor | vSphere 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later with virtual hardware version 15 | This hypervisor version is the minimum version that Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) supports. For more information about supported hardware on the latest version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) that is compatible with RHCOS, see Hardware on the Red Hat Customer Portal. |
| Optional: Networking (NSX-T) | vSphere 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later | For more information about the compatibility of NSX and OpenShift Container Platform, see the Release Notes section of VMware’s NSX container plugin documentation. |
| CPU micro-architecture | x86-64-v2 or higher | OpenShift Container Platform version 4.13 and later are based on the RHEL 9.2 host operating system, which raised the microarchitecture requirements to x86-64-v2. See Architectures in the RHEL documentation. |
To ensure the best performance conditions for your cluster workloads that operate on Oracle® Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and on the Oracle® Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS) service, ensure volume performance units (VPUs) for your block volume are sized for your workloads.
The following list provides some guidance in selecting the VPUs needed for specific performance needs:
- Test or proof of concept environment: 100 GB, and 20 to 30 VPUs.
- Base-production environment: 500 GB, and 60 VPUs.
- Heavy-use production environment: More than 500 GB, and 100 or more VPUs.
Consider allocating additional VPUs to give enough capacity for updates and scaling activities. See Block Volume Performance Levels (Oracle documentation).
2.1.2. Network connectivity requirements
You must configure the network connectivity between machines to allow OpenShift Container Platform cluster components to communicate.
Review the following details about the required network ports.
| Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VRRP | N/A | Required for keepalived |
| ICMP | N/A | Network reachability tests |
| TCP |
| Metrics |
|
|
Host level services, including the node exporter on ports | |
|
| The default ports that Kubernetes reserves | |
|
| openshift-sdn | UDP |
|
| virtual extensible LAN (VXLAN) | |
|
| Geneve | |
|
|
Host level services, including the node exporter on ports | |
|
| IPsec IKE packets | |
|
| IPsec NAT-T packets | TCP/UDP |
|
| Kubernetes node port | ESP |
| Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TCP |
| Kubernetes API |
| Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TCP |
| etcd server and peer ports |
2.1.3. VMware vSphere CSI Driver Operator requirements
To install the vSphere Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver Operator, the following requirements must be met:
- VMware vSphere version: 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later
- vCenter version: 8.0 Update 1 or later, or VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 or later
- Virtual machines of hardware version 15 or later
- No third-party vSphere CSI driver already installed in the cluster
If a third-party vSphere CSI driver is present in the cluster, OpenShift Container Platform does not overwrite it. The presence of a third-party vSphere CSI driver prevents OpenShift Container Platform from updating to OpenShift Container Platform 4.13 or later.
The VMware vSphere CSI Driver Operator is supported only on clusters deployed with platform: vsphere in the installation manifest.
You can create a custom role for the Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver, the vSphere CSI Driver Operator, and the vSphere Problem Detector Operator. The custom role can include privilege sets that assign a minimum set of permissions to each vSphere object. This means that the CSI driver, the vSphere CSI Driver Operator, and the vSphere Problem Detector Operator can establish a basic interaction with these objects.
Installing an OpenShift Container Platform cluster in a vCenter is tested against a full list of privileges as described in the "Required vCenter account privileges" section. By adhering to the full list of privileges, you can reduce the possibility of unexpected and unsupported behaviors that might occur when creating a custom role with a set of restricted privileges.
2.1.4. vCenter requirements
Before you install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on your vCenter that uses infrastructure that the installation program provisions, you must prepare your environment.
2.1.4.1. Required vCenter account privileges
To install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster in a vCenter, the installation program requires access to an account with privileges to read and create the required resources. Using an account that has global administrative privileges is the simplest way to access all of the necessary permissions.
If you cannot use an account with global administrative privileges, you must create roles to grant the privileges necessary for OpenShift Container Platform cluster installation. Most of the privileges are always required. Some privileges are required only if you plan for the installation program to provision a folder to contain the OpenShift Container Platform cluster on your vCenter instance, which is the default behavior. You must create or change vSphere roles for the specified objects to grant the required privileges.
The installation program requires an additional role to create a vSphere virtual machine folder.
Example 2.1. Roles and privileges required for installation in vSphere API
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges in vSphere API |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | If VMs need creation in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool | For a provided existing resource pool |
|
| vSphere Datastore | Always |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | The installation program creates the virtual machine folder. |
|
Example 2.2. Roles and privileges required for installation in vCenter graphical user interface (GUI)
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges in vCenter GUI |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | For VMs creation in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool | If providing an existing resource pool |
|
| vSphere Datastore | Always |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | The installation program creates the virtual machine folder. |
|
Additionally, the user requires some ReadOnly permissions, and some of the roles require permission to propagate the permissions to child objects. These settings vary depending on whether or not you install the cluster into an existing folder.
Example 2.3. Required permissions and propagation settings
| vSphere object | When required | Propagate to children | Permissions required |
|---|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always | False | Listed required privileges |
| vSphere vCenter data center | Existing folder | False |
|
| Installation program creates the folder | True | Listed required privileges | |
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | Existing resource pool | False |
|
| VMs in cluster root | True | Listed required privileges | |
| vSphere vCenter Datastore | Always | False | Listed required privileges |
| vSphere Switch | Always | False |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always | False | Listed required privileges |
| vSphere vCenter Virtual Machine Folder | Existing folder | True | Listed required privileges |
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool | Existing resource pool | True | Listed required privileges |
For more information about creating an account with only the required privileges, see vSphere Permissions and User Management Tasks in the vSphere documentation.
2.1.4.2. Minimum required vCenter account privileges
After you create a custom role and assign privileges to the role, you can create permissions by selecting specific vSphere objects. You can then assign the custom role to a user or group for each object.
Before you create permissions or request for the creation of permissions for a vSphere object, decide what minimum permissions apply to the vSphere object. By doing this task, you can ensure a basic interaction exists between a vSphere object and OpenShift Container Platform architecture.
If you create a custom role and you do not assign privileges to it, the vSphere Server by default assigns a Read Only role to the custom role. Note that for the cloud provider API, the custom role only needs to inherit the privileges of the Read Only role.
Consider creating a custom role when an account with global administrative privileges does not meet your needs.
Red Hat does not support configuring an account without including the required privileges. Red Hat tests OpenShift Container Platform cluster installations in vCenter against the full list of privileges described in the "Required vCenter account privileges" section. By adhering to the full list of privileges, you can reduce the possibility of unexpected behaviors that might occur when creating a custom role with a restricted set of privileges. You must retain the full set of privileges from the "Required vCenter account privileges" section after cluster installation. Reducing the account to only the permissions listed in the minimum permission tables in the "Minimum required vCenter account privileges" section after installation is not supported and can cause unexpected cluster behavior. The minimum permission tables are for reference only; they show which privileges apply to which OpenShift Container Platform components (such as storage or the Machine API) when you design or audit custom roles. The supported configuration is to assign the full set of privileges from the "Required vCenter account privileges" section at all times, both during and after installation.
The following tables specify how the required vCenter account privileges provided earlier in this document are relevant to different aspects of OpenShift Container Platform architecture.
Example 2.4. Minimum permissions on installer-provisioned infrastructure
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | If you intend to create VMs in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool |
If you included an existing resource pool in the |
|
| vSphere Datastore |
If you referenced a datastore in the |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | If the virtual machine folder does not already exist, the installation program creates the virtual machine folder. If your cluster does use the Machine API and you want to set the minimum set of permissions for the API, see the "Minimum permissions for the Machine API" table. |
|
Example 2.5. Minimum permissions for postinstallation management of components
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | If you intend to create VMs in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool |
If you included an existing resource pool in the |
|
| vSphere Datastore | Always |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | If the virtual machine folder does not already exist, the installation program creates the virtual machine folder. |
|
Example 2.6. Minimum permissions for the storage components
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | If you intend to create VMs in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool |
If you included an existing resource pool in the |
|
| vSphere Datastore | Always |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | If the virtual machine folder does not already exist, the installation program creates the virtual machine folder. |
|
Example 2.7. Minimum permissions for the Machine API
| vSphere object for role | When required | Required privileges |
|---|---|---|
| vSphere vCenter | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter Cluster | If you intend to create VMs in the cluster root |
|
| vSphere vCenter Resource Pool |
If you included an existing resource pool in the |
|
| vSphere Datastore | Always |
|
| vSphere Port Group | Always |
|
| Virtual Machine Folder | Always |
|
| vSphere vCenter data center | If the virtual machine folder does not already exist, the installation program creates the virtual machine folder. |
|
2.1.4.3. Using OpenShift Container Platform with vMotion
If you intend on using vMotion in your vSphere environment, consider the following before installing an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Using Storage vMotion can cause issues and is not supported.
Using VMware compute vMotion to migrate the workloads for both OpenShift Container Platform compute machines and control plane machines is generally supported, where generally implies that you meet all VMware best practices for vMotion.
To help ensure the uptime of your compute and control plane nodes, ensure that you follow the VMware best practices for vMotion, and use VMware anti-affinity rules to improve the availability of OpenShift Container Platform during maintenance or hardware issues.
For more information about vMotion and anti-affinity rules, see the VMware vSphere documentation for vMotion networking requirements and VM anti-affinity rules.
- If you are using VMware vSphere volumes in your pods, migrating a VM across datastores, either manually or through Storage vMotion, causes invalid references within OpenShift Container Platform persistent volume (PV) objects that can result in data loss.
OpenShift Container Platform does not support selective migration of virtual machine disks (VMDKs) across datastores, using datastore clusters for VM provisioning or for dynamic or static provisioning of PVs, or using a datastore that is part of a datastore cluster for dynamic or static provisioning of PVs.
ImportantYou can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler (SDRS), which uses Storage vMotion, is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable SDRS to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you must specify VMs across many datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement".
2.1.4.4. Cluster resources
When you deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster that uses installer-provisioned infrastructure, the installation program must be able to create several resources in your vCenter instance.
A standard OpenShift Container Platform installation creates the following vCenter resources:
- 1 Folder
- 1 Tag category
- 1 Tag
Virtual machines:
- 1 template
- 1 temporary bootstrap node
- 3 control plane nodes
- 3 compute machines
Although these resources use 856 GB of storage, the bootstrap node gets deleted during the cluster installation process. At a minimum, a standard cluster requires 800 GB of storage.
If you deploy more compute machines, the OpenShift Container Platform cluster will use more storage.
2.1.4.5. Cluster limits
Available resources vary between clusters. A limit exists for the number of possible clusters within vCenter, primarily by available storage space and any limitations on the number of required resources. Be sure to consider both limitations to the vCenter resources that the cluster creates and the resources that you require to deploy a cluster, such as IP addresses and networks.
2.1.4.6. Networking requirements
You can use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the network and configure the DHCP server to set persistent IP addresses to machines in your cluster. In the DHCP lease, you must configure the DHCP to use the default gateway.
You do not need to use the DHCP for the network if you want to provision nodes with static IP addresses.
If you are installing to a restricted environment, the VM in your restricted network must have access to vCenter so that it can provision and manage nodes, persistent volume claims (PVCs), and other resources.
Ensure that each OpenShift Container Platform node in the cluster has access to a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server that is discoverable by DHCP. Installation is possible without an NTP server. However, asynchronous server clocks can cause errors, which the NTP server prevents.
Additionally, you must create the following networking resources before you install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster:
2.1.4.6.1. Required IP addresses
For a network that uses DHCP, an installer-provisioned vSphere installation requires two static IP addresses:
- The API address for accessing the cluster API.
- The Ingress address for cluster ingress traffic.
You must give these IP addresses to the installation program when you install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
2.1.4.6.2. DNS records
You must create DNS records for two static IP addresses in the appropriate DNS server for the vCenter instance that hosts your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. In each record, <cluster_name> is the cluster name and <base_domain> is the cluster base domain that you specify when you install the cluster. A complete DNS record takes the form: <component>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>..
| Component | Record | Description |
|---|---|---|
| API VIP |
| This DNS A/AAAA or CNAME (Canonical Name) record must point to the load balancer for the control plane machines. This record must be resolvable by both clients external to the cluster and from all the nodes within the cluster. |
| Ingress VIP |
| A wildcard DNS A/AAAA or CNAME record that points to the load balancer that targets the machines that run the Ingress router pods, which are the worker nodes by default. This record must be resolvable by both clients external to the cluster and from all the nodes within the cluster. |
2.1.4.6.3. Static IP addresses for vSphere nodes
You can provision bootstrap, control plane, and compute nodes to be configured with static IP addresses in environments where Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) does not exist. To configure this environment, you must provide values to the platform.vsphere.hosts.role parameter in the install-config.yaml file.
By default, the installation program is configured to use the DHCP for the network, but this network has limited configurable capabilities.
After you define one or more machine pools in your install-config.yaml file, you can define network definitions for nodes on your network. Ensure that the number of network definitions matches the number of machine pools that you configured for your cluster.
Example network configuration that specifies different roles
- 1
- Valid network definition values include
bootstrap,control-plane, andcompute. You must list at least onebootstrapnetwork definition in yourinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. - 2
- Lists IPv4, IPv6, or both IP addresses that the installation program passes to the network interface. The machine API controller assigns all configured IP addresses to the default network interface.
- 3
- The default gateway for the network interface.
- 4
- Lists up to 3 DNS nameservers.
After you deployed your cluster to run nodes with static IP addresses, you can scale a machine to use one of these static IP addresses. Additionally, you can use a machine set to configure a machine to use one of the configured static IP addresses.
2.2. Preparing to install a cluster using installer-provisioned infrastructure
You prepare to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on vSphere by completing the following steps:
Downloading the installation program.
NoteIf you are installing in a disconnected environment, you extract the installation program from the mirrored content. For more information, see Mirroring images for a disconnected installation.
Installing the OpenShift CLI (
oc).NoteIf you are installing in a disconnected environment, install
octo the mirror host.- Generating an SSH key pair. You can use this key pair to authenticate into the OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s nodes after it is deployed.
- Adding your vCenter’s trusted root CA certificates to your system trust.
2.2.1. Obtaining the installation program
Before you install OpenShift Container Platform, download the installation file on the host you are using for installation.
Prerequisites
You have a machine that runs Linux, for example Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8, with at least 1.2 GB of local disk space.
ImportantIf you attempt to run the installation program on macOS, a known issue related to the
golangcompiler causes the installation of the OpenShift Container Platform cluster to fail. For more information about this issue, see the section named "Known Issues" in the OpenShift Container Platform 4.16 release notes document.
Procedure
Go to the Cluster Type page on the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console. If you have a Red Hat account, log in with your credentials. If you do not, create an account.
Tip- Select your infrastructure provider from the Run it yourself section of the page.
- Select your host operating system and architecture from the dropdown menus under OpenShift Installer and click Download Installer.
Place the downloaded file in the directory where you want to store the installation configuration files.
Important- The installation program creates several files on the computer that you use to install your cluster. You must keep the installation program and the files that the installation program creates after you finish installing the cluster. Both of the files are required to delete the cluster.
- Deleting the files created by the installation program does not remove your cluster, even if the cluster failed during installation. To remove your cluster, complete the OpenShift Container Platform uninstallation procedures for your specific cloud provider.
Extract the installation program. For example, on a computer that uses a Linux operating system, run the following command:
tar -xvf openshift-install-linux.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf openshift-install-linux.tar.gzCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download your installation pull secret from Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager. This pull secret allows you to authenticate with the services that are provided by the included authorities, including Quay.io, which serves the container images for OpenShift Container Platform components.
TipAlternatively, you can retrieve the installation program from the Red Hat Customer Portal, where you can specify a version of the installation program to download. However, you must have an active subscription to access this page.
2.2.2. Installing the OpenShift CLI on Linux
To manage your cluster and deploy applications from the command line, install the OpenShift CLI (oc) binary on Linux.
If you installed an earlier version of oc, you cannot use it to complete all of the commands in OpenShift Container Platform 4.16. Download and install the new version of oc.
Procedure
- Navigate to the OpenShift Container Platform downloads page on the Red Hat Customer Portal.
- Select the architecture from the Product Variant drop-down list.
- Select the appropriate version from the Version drop-down list.
- Click Download Now next to the OpenShift v4.16 Linux Clients entry and save the file.
Unpack the archive:
tar xvf <file>
$ tar xvf <file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Place the
ocbinary in a directory that is on yourPATH.To check your
PATH, execute the following command:echo $PATH
$ echo $PATHCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
After you install the OpenShift CLI, it is available using the
occommand:oc <command>
$ oc <command>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.3. Installing the OpenShift CLI on Windows
To manage your cluster and deploy applications from the command line, install OpenShift CLI (oc) binary on Windows.
If you installed an earlier version of oc, you cannot use it to complete all of the commands in OpenShift Container Platform.
Download and install the new version of oc.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Download OpenShift Container Platform page on the Red Hat Customer Portal.
- Select the appropriate version from the Version list.
- Click Download Now next to the OpenShift v4.16 Windows Client entry and save the file.
- Extract the archive with a ZIP program.
Move the
ocbinary to a directory that is on yourPATHvariable.To check your
PATHvariable, open the command prompt and execute the following command:path
C:\> pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
After you install the OpenShift CLI, it is available using the
occommand:oc <command>
C:\> oc <command>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.4. Installing the OpenShift CLI on macOS
To manage your cluster and deploy applications from the command line, install the OpenShift CLI (oc) binary on macOS.
If you installed an earlier version of oc, you cannot use it to complete all of the commands in OpenShift Container Platform.
Download and install the new version of oc.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Download OpenShift Container Platform page on the Red Hat Customer Portal.
- Select the architecture from the Product Variant list.
- Select the appropriate version from the Version list.
Click Download Now next to the OpenShift v4.16 macOS Clients entry and save the file.
NoteFor macOS arm64, choose the OpenShift v4.16 macOS arm64 Client entry.
- Unpack and unzip the archive.
Move the
ocbinary to a directory on yourPATHvariable.To check your
PATHvariable, open a terminal and execute the following command:echo $PATH
$ echo $PATHCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify your installation by using an
occommand:oc <command>
$ oc <command>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.5. Generating a key pair for cluster node SSH access
To enable secure, passwordless SSH access to your cluster nodes, provide an SSH public key during the OpenShift Container Platform installation. This ensures that the installation program automatically configures the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) nodes for remote authentication through the core user.
The SSH public key gets added to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys list for the core user on each node. After the key is passed to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) nodes through their Ignition config files, you can use the key pair to SSH in to the RHCOS nodes as the user core. To access the nodes through SSH, the private key identity must be managed by SSH for your local user.
If you want to SSH in to your cluster nodes to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, you must provide the SSH public key during the installation process. The ./openshift-install gather command also requires the SSH public key to be in place on the cluster nodes.
Do not skip this procedure in production environments, where disaster recovery and debugging is required.
You must use a local key, not one that you configured with platform-specific approaches such as AWS key pairs.
Procedure
If you do not have an existing SSH key pair on your local machine to use for authentication onto your cluster nodes, create one. For example, on a computer that uses a Linux operating system, run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -f <path>/<file_name>
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -f <path>/<file_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specifies the path and file name, such as
~/.ssh/id_ed25519, of the new SSH key. If you have an existing key pair, ensure your public key is in the your~/.sshdirectory.NoteIf you plan to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster that uses the RHEL cryptographic libraries that have been submitted to NIST for FIPS 140-2/140-3 Validation on only the
x86_64,ppc64le, ands390xarchitectures, do not create a key that uses theed25519algorithm. Instead, create a key that uses thersaorecdsaalgorithm.View the public SSH key:
cat <path>/<file_name>.pub
$ cat <path>/<file_name>.pubCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, run the following to view the
~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pubpublic key:cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pubCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the SSH private key identity to the SSH agent for your local user, if it has not already been added. SSH agent management of the key is required for password-less SSH authentication onto your cluster nodes, or if you want to use the
./openshift-install gathercommand.NoteOn some distributions, default SSH private key identities such as
~/.ssh/id_rsaand~/.ssh/id_dsaare managed automatically.If the
ssh-agentprocess is not already running for your local user, start it as a background task:eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Agent pid 31874
Agent pid 31874Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf your cluster is in FIPS mode, only use FIPS-compliant algorithms to generate the SSH key. The key must be either RSA or ECDSA.
Add your SSH private key to the
ssh-agent:ssh-add <path>/<file_name>
$ ssh-add <path>/<file_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specifies the path and file name for your SSH private key, such as
~/.ssh/id_ed25519Example output
Identity added: /home/<you>/<path>/<file_name> (<computer_name>)
Identity added: /home/<you>/<path>/<file_name> (<computer_name>)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
- When you install OpenShift Container Platform, provide the SSH public key to the installation program.
2.2.6. Adding vCenter root CA certificates to your system trust
Because the installation program requires access to your vCenter’s API, you must add your vCenter’s trusted root CA certificates to your system trust before you install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
-
From the vCenter home page, download the vCenter’s root CA certificates. Click Download trusted root CA certificates in the vSphere Web Services SDK section. The
<vCenter>/certs/download.zipfile downloads. Extract the compressed file that contains the vCenter root CA certificates. The contents of the compressed file resemble the following file structure:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the files for your operating system to the system trust. For example, on a Fedora operating system, run the following command:
cp certs/lin/* /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors
# cp certs/lin/* /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchorsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update your system trust. For example, on a Fedora operating system, run the following command:
update-ca-trust extract
# update-ca-trust extractCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3. Installing a cluster on vSphere
In OpenShift Container Platform version 4.16, you can install a cluster on your VMware vSphere instance by using installer-provisioned infrastructure.
OpenShift Container Platform supports deploying a cluster to a single VMware vCenter only. Deploying a cluster with machines/machine sets on multiple vCenters is not supported.
2.3.1. Prerequisites
- You have completed the tasks in Preparing to install a cluster using installer-provisioned infrastructure.
- You reviewed your VMware platform licenses. Red Hat does not place any restrictions on your VMware licenses, but some VMware infrastructure components require licensing.
- You reviewed details about the OpenShift Container Platform installation and update processes.
- You read the documentation on selecting a cluster installation method and preparing it for users.
-
You provisioned persistent storage for your cluster. To deploy a private image registry, your storage must provide
ReadWriteManyaccess modes. - The OpenShift Container Platform installer requires access to port 443 on the vCenter and ESXi hosts. You verified that port 443 is accessible.
- If you use a firewall, you confirmed with the administrator that port 443 is accessible. Control plane nodes must be able to reach vCenter and ESXi hosts on port 443 for the installation to succeed.
If you use a firewall, you configured it to allow the sites that your cluster requires access to.
NoteBe sure to also review this site list if you are configuring a proxy.
2.3.2. Internet access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you require access to the internet to install your cluster.
You must have internet access to:
- Access OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the installation program and perform subscription management. If the cluster has internet access and you do not disable Telemetry, that service automatically entitles your cluster.
- Access Quay.io to obtain the packages that are required to install your cluster.
- Obtain the packages that are required to perform cluster updates.
If your cluster cannot have direct internet access, you can perform a restricted network installation on some types of infrastructure that you provision. During that process, you download the required content and use it to populate a mirror registry with the installation packages. With some installation types, the environment that you install your cluster in will not require internet access. Before you update the cluster, you update the content of the mirror registry.
2.3.3. Deploying the cluster
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on a compatible cloud platform.
You can run the create cluster command of the installation program only once, during initial installation.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
- You have verified that the cloud provider account on your host has the correct permissions to deploy the cluster. An account with incorrect permissions causes the installation process to fail with an error message that displays the missing permissions.
Optional: Before you create the cluster, configure an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
ImportantYou do not need to specify API and Ingress static addresses for your installation program. If you choose this configuration, you must take additional actions to define network targets that accept an IP address from each referenced vSphere subnet. See the section "Configuring a user-managed load balancer".
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment:
./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \ --log-level=info$ ./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \1 --log-level=info2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When specifying the directory:
-
Verify that the directory has the
executepermission. This permission is required to run Terraform binaries under the installation directory. - Use an empty directory. Some installation assets, such as bootstrap X.509 certificates, have short expiration intervals, therefore you must not reuse an installation directory. If you want to reuse individual files from another cluster installation, you can copy them into your directory. However, the file names for the installation assets might change between releases. Use caution when copying installation files from an earlier OpenShift Container Platform version.
-
Verify that the directory has the
Provide values at the prompts:
Optional: Select an SSH key to use to access your cluster machines.
NoteFor production OpenShift Container Platform clusters on which you want to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, specify an SSH key that your
ssh-agentprocess uses.- Select vsphere as the platform to target.
- Specify the name of your vCenter instance.
Specify the user name and password for the vCenter account that has the required permissions to create the cluster.
The installation program connects to your vCenter instance.
ImportantSome VMware vCenter Single Sign-On (SSO) environments with Active Directory (AD) integration might primarily require you to use the traditional login method, which requires the
<domain>\construct.To ensure that vCenter account permission checks complete properly, consider using the User Principal Name (UPN) login method, such as
<username>@<fully_qualified_domainname>.- Select the data center in your vCenter instance to connect to.
Select the default vCenter datastore to use.
NoteDatastore and cluster names cannot exceed 60 characters; therefore, ensure the combined string length does not exceed the 60 character limit.
- Select the vCenter cluster to install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster in. The installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster as the default resource pool.
- Select the network in the vCenter instance that contains the virtual IP addresses and DNS records that you configured.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for control plane API access.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for cluster ingress.
- Enter the base domain. This base domain must be the same one that you used in the DNS records that you configured.
Enter a descriptive name for your cluster. The cluster name must be the same one that you used in the DNS records that you configured.
NoteDatastore and cluster names cannot exceed 60 characters; therefore, ensure the combined string length does not exceed the 60 character limit.
- Paste the pull secret from Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Verification
When the cluster deployment completes successfully:
-
The terminal displays directions for accessing your cluster, including a link to the web console and credentials for the
kubeadminuser. -
Credential information also outputs to
<installation_directory>/.openshift_install.log.
Do not delete the installation program or the files that the installation program creates. Both are required to delete the cluster.
Example output
-
The Ignition config files that the installation program generates contain certificates that expire after 24 hours, which are then renewed at that time. If the cluster is shut down before renewing the certificates and the cluster is later restarted after the 24 hours have elapsed, the cluster automatically recovers the expired certificates. The exception is that you must manually approve the pending
node-bootstrappercertificate signing requests (CSRs) to recover kubelet certificates. See the documentation for Recovering from expired control plane certificates for more information. - It is recommended that you use Ignition config files within 12 hours after they are generated because the 24-hour certificate rotates from 16 to 22 hours after the cluster is installed. By using the Ignition config files within 12 hours, you can avoid installation failure if the certificate update runs during installation.
2.3.4. Logging in to the cluster by using the CLI
To log in to your cluster as the default system user, export the kubeconfig file. This configuration enables the CLI to authenticate and connect to the specific API server created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
The kubeconfig file is specific to a cluster and is created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Export the
kubeadmincredentials:export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<installation_directory>- Specifies the path to the directory that stores the installation files.
Verify you can run
occommands successfully using the exported configuration:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3.5. Creating registry storage
After you install the cluster, you must create storage for the registry Operator.
2.3.5.1. Image registry removed during installation
On platforms that do not provide shareable object storage, the OpenShift Image Registry Operator bootstraps itself as Removed. This allows openshift-installer to complete installations on these platform types.
After installation, you must edit the Image Registry Operator configuration to switch the managementState from Removed to Managed. When this has completed, you must configure storage.
2.3.5.2. Image registry storage configuration
The Image Registry Operator is not initially available for platforms that do not provide default storage. After installation, you must configure your registry to use storage so that the Registry Operator is made available.
Configure a persistent volume, which is required for production clusters. Where applicable, you can configure an empty directory as the storage location for non-production clusters.
You can also allow the image registry to use block storage types by using the Recreate rollout strategy during upgrades.
2.3.5.2.1. Configuring registry storage for VMware vSphere
As a cluster administrator, following installation you must configure your registry to use storage.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions.
- A cluster on VMware vSphere.
Persistent storage provisioned for your cluster, such as Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation.
ImportantOpenShift Container Platform supports
ReadWriteOnceaccess for image registry storage when you have only one replica.ReadWriteOnceaccess also requires that the registry uses theRecreaterollout strategy. To deploy an image registry that supports high availability with two or more replicas,ReadWriteManyaccess is required.- Must have "100Gi" capacity.
Testing shows issues with using the NFS server on RHEL as storage backend for core services. This includes the OpenShift Container Registry and Quay, Prometheus for monitoring storage, and Elasticsearch for logging storage. Therefore, using RHEL NFS to back PVs used by core services is not recommended.
Other NFS implementations on the marketplace might not have these issues. Contact the individual NFS implementation vendor for more information on any testing that was possibly completed against these OpenShift Container Platform core components.
Procedure
To configure your registry to use storage, change the
spec.storage.pvcin theconfigs.imageregistry/clusterresource.NoteWhen you use shared storage, review your security settings to prevent outside access.
Verify that you do not have a registry pod:
oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=default
$ oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespace
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do have a registry pod in your output, you do not need to continue with this procedure.
Check the registry configuration:
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io
$ oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Leave the
claimfield blank to allow the automatic creation of animage-registry-storagepersistent volume claim (PVC). The PVC is generated based on the default storage class. However, be aware that the default storage class might provide ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volumes, such as a RADOS Block Device (RBD), which can cause issues when you replicate to more than one replica.Check the
clusteroperatorstatus:oc get clusteroperator image-registry
$ oc get clusteroperator image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3.5.2.2. Configuring block registry storage for VMware vSphere
To allow the image registry to use block storage types such as vSphere Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) during upgrades as a cluster administrator, you can use the Recreate rollout strategy.
Block storage volumes are supported but not recommended for use with image registry on production clusters. An installation where the registry is configured on block storage is not highly available because the registry cannot have more than one replica.
Procedure
Enter the following command to set the image registry storage as a block storage type, patch the registry so that it uses the
Recreaterollout strategy, and runs with only1replica:oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'$ oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Provision the PV for the block storage device, and create a PVC for that volume. The requested block volume uses the ReadWriteOnce (RWO) access mode.
Create a
pvc.yamlfile with the following contents to define a VMware vSpherePersistentVolumeClaimobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
name-
Specifies a unique name that represents the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject. namespace-
Specifies the
namespacefor thePersistentVolumeClaimobject, which isopenshift-image-registry. accessModes-
Specifies the access mode of the persistent volume claim. With
ReadWriteOnce, the volume can be mounted with read and write permissions by a single node. storage- The size of the persistent volume claim.
Enter the following command to create the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject from the file:oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registry
$ oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Enter the following command to edit the registry configuration so that it references the correct PVC:
oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yaml
$ oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By creating a custom PVC, you can leave the
claimfield blank for the default automatic creation of animage-registry-storagePVC.
For instructions about configuring registry storage so that it references the correct PVC, see Configuring the registry for vSphere.
2.3.6. Telemetry access for OpenShift Container Platform
To provide metrics about cluster health and the success of updates, the Telemetry service requires internet access. When connected, this service runs automatically by default and registers your cluster to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After you confirm that your OpenShift Cluster Manager inventory is correct, either maintained automatically by Telemetry or manually by using OpenShift Cluster Manager,use subscription watch to track your OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions at the account or multi-cluster level. For more information about subscription watch, see "Data Gathered and Used by Red Hat’s subscription services" in the Additional resources section.
2.3.7. Next steps
- Customize your cluster.
- If necessary, you can Remote health reporting.
- Set up your registry and configure registry storage.
- Optional: View the events from the vSphere Problem Detector Operator to determine if the cluster has permission or storage configuration issues.
2.4. Installing a cluster on vSphere with customizations
In OpenShift Container Platform version 4.16, you can install a cluster on your VMware vSphere instance by using installer-provisioned infrastructure. To customize the installation, you modify parameters in the install-config.yaml file before you install the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform supports deploying a cluster to a single VMware vCenter only. Deploying a cluster with machines/machine sets on multiple vCenters is not supported.
2.4.1. Prerequisites
- You have completed the tasks in Preparing to install a cluster using installer-provisioned infrastructure.
- You reviewed your VMware platform licenses. Red Hat does not place any restrictions on your VMware licenses, but some VMware infrastructure components require licensing.
- You reviewed details about the OpenShift Container Platform installation and update processes.
- You read the documentation on selecting a cluster installation method and preparing it for users.
-
You provisioned persistent storage for your cluster. To deploy a private image registry, your storage must provide
ReadWriteManyaccess modes. - The OpenShift Container Platform installer requires access to port 443 on the vCenter and ESXi hosts. You verified that port 443 is accessible.
- If you use a firewall, you confirmed with the administrator that port 443 is accessible. Control plane nodes must be able to reach vCenter and ESXi hosts on port 443 for the installation to succeed.
If you use a firewall, you configured it to allow the sites that your cluster requires access to.
NoteBe sure to also review this site list if you are configuring a proxy.
2.4.2. Internet access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you require access to the internet to install your cluster.
You must have internet access to:
- Access OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the installation program and perform subscription management. If the cluster has internet access and you do not disable Telemetry, that service automatically entitles your cluster.
- Access Quay.io to obtain the packages that are required to install your cluster.
- Obtain the packages that are required to perform cluster updates.
If your cluster cannot have direct internet access, you can perform a restricted network installation on some types of infrastructure that you provision. During that process, you download the required content and use it to populate a mirror registry with the installation packages. With some installation types, the environment that you install your cluster in will not require internet access. Before you update the cluster, you update the content of the mirror registry.
2.4.3. VMware vSphere region and zone enablement
You can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. Each data center can run multiple clusters. This configuration reduces the risk of a hardware failure or network outage that can cause your cluster to fail. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
The VMware vSphere region and zone enablement feature requires the vSphere Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver as the default storage driver in the cluster. As a result, the feature is only available on a newly installed cluster.
For a cluster that was upgraded from a previous release, you must enable CSI automatic migration for the cluster. You can then configure multiple regions and zones for the upgraded cluster.
The default installation configuration deploys a cluster to a single vSphere data center. If you want to deploy a cluster to multiple vSphere data centers, you must create an installation configuration file that enables the region and zone feature.
The default install-config.yaml file includes vcenters and failureDomains fields, where you can specify multiple vSphere data centers and clusters for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. You can leave these fields blank if you want to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster in a vSphere environment that consists of single data center.
The following list describes terms associated with defining zones and regions for your cluster:
-
Failure domain: Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. -
Region: Specifies a vCenter data center. You define a region by using a tag from the
openshift-regiontag category. -
Zone: Specifies a vCenter cluster. You define a zone by using a tag from the
openshift-zonetag category.
If you plan on specifying more than one failure domain in your install-config.yaml file, you must create tag categories, zone tags, and region tags in advance of creating the configuration file.
You must create a vCenter tag for each vCenter data center, which represents a region. Additionally, you must create a vCenter tag for each cluster than runs in a data center, which represents a zone. After you create the tags, you must attach each tag to their respective data centers and clusters.
The following table outlines an example of the relationship among regions, zones, and tags for a configuration with multiple vSphere data centers running in a single VMware vCenter.
| Data center (region) | Cluster (zone) | Tags |
|---|---|---|
| us-east | us-east-1 | us-east-1a |
| us-east-1b | ||
| us-east-2 | us-east-2a | |
| us-east-2b | ||
| us-west | us-west-1 | us-west-1a |
| us-west-1b | ||
| us-west-2 | us-west-2a | |
| us-west-2b |
2.4.4. Creating the installation configuration file
You can customize the OpenShift Container Platform cluster you install on
VMware vSphere.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
Procedure
Create the
install-config.yamlfile.Change to the directory that contains the installation program and run the following command:
./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <installation_directory>: For<installation_directory>, specify the directory name to store the files that the installation program creates.When specifying the directory:
-
Verify that the directory has the
executepermission. This permission is required to run Terraform binaries under the installation directory. - Use an empty directory. Some installation assets, such as bootstrap X.509 certificates, have short expiration intervals, therefore you must not reuse an installation directory. If you want to reuse individual files from another cluster installation, you can copy them into your directory. However, the file names for the installation assets might change between releases. Use caution when copying installation files from an earlier OpenShift Container Platform version.
At the prompts, provide the configuration details for your cloud:
Optional: Select an SSH key to use to access your cluster machines.
NoteFor production OpenShift Container Platform clusters on which you want to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, specify an SSH key that your
ssh-agentprocess uses.- Select vsphere as the platform to target.
- Specify the name of your vCenter instance.
Specify the user name and password for the vCenter account that has the required permissions to create the cluster.
The installation program connects to your vCenter instance.
Select the data center in your vCenter instance to connect to.
NoteAfter you create the installation configuration file, you can modify the file to create a multiple vSphere data center environment. This means that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. For more information about creating this environment, see the section named VMware vSphere region and zone enablement.
Select the default vCenter datastore to use.
WarningYou can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler (SDRS), which uses Storage vMotion, is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage DRS to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
You cannot specify more than one datastore path. If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement".- Select the vCenter cluster to install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster in. The installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster as the default resource pool.
- Select the network in the vCenter instance that contains the virtual IP addresses and DNS records that you configured.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for control plane API access.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for cluster ingress.
- Enter the base domain. This base domain must be the same one that you used in the DNS records that you configured.
Enter a descriptive name for your cluster.
The cluster name you enter must match the cluster name you specified when configuring the DNS records.
Modify the
install-config.yamlfile. You can find more information about the available parameters in the "Installation configuration parameters" section.NoteIf you are installing a three-node cluster, be sure to set the
compute.replicasparameter to0. This ensures that the cluster’s control planes are schedulable. For more information, see "Installing a three-node cluster on vSphere".Back up the
install-config.yamlfile so that you can use it to install multiple clusters.ImportantThe
install-config.yamlfile is consumed during the installation process. If you want to reuse the file, you must back it up now.
2.4.4.1. Sample install-config.yaml file for an installer-provisioned VMware vSphere cluster
You can customize the install-config.yaml file to specify more details about your OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s platform or modify the values of the required parameters.
- 1
- The base domain of the cluster. All DNS records must be sub-domains of this base and include the cluster name.
- 2 3
- The
controlPlanesection is a single mapping, but thecomputesection is a sequence of mappings. To meet the requirements of the different data structures, the first line of thecomputesection must begin with a hyphen,-, and the first line of thecontrolPlanesection must not. Only one control plane pool is used. - 4
- The cluster name that you specified in your DNS records.
- 5
- Optional: Provides additional configuration for the machine pool parameters for the compute and control plane machines.Important
The VIPs,
apiVIPandingressVIP, must come from the samenetworking.machineNetworksegment. ForapiVIPand foringressVIP, if thenetworking.machineNetworkis10.0.0.0/16then API VIPs and Ingress VIPs must be in one of the10.0.0.0/16machine networks. - 6
- Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. - 7
- The path to the vSphere datastore that holds virtual machine files, templates, and ISO images.Important
You can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage vMotion is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage vMotion to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement". - 8
- Optional: Provides an existing resource pool for machine creation. If you do not specify a value, the installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster.
- 9
- Optional: Each VM created by OpenShift Container Platform is assigned a unique tag that is specific to the cluster. The assigned tag enables the installation program to identify and remove the associated VMs when a cluster is decommissioned. You can list up to ten additional tag IDs to be attached to the VMs provisioned by the installation program.
- 10
- The ID of the tag to be associated by the installation program. For example,
urn:vmomi:InventoryServiceTag:208e713c-cae3-4b7f-918e-4051ca7d1f97:GLOBAL. For more information about determining the tag ID, see the vSphere Tags and Attributes documentation. - 11
- The vSphere disk provisioning method.
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.12 and later, the apiVIP and ingressVIP configuration settings are deprecated. Instead, use a list format to enter values in the apiVIPs and ingressVIPs configuration settings.
2.4.4.2. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy during installation
To enable internet access in environments that deny direct connections, configure a cluster-wide proxy in the install-config.yaml file. This configuration ensures that the new OpenShift Container Platform cluster routes traffic through the specified HTTP or HTTPS proxy.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing
install-config.yamlfile. You have reviewed the sites that your cluster requires access to and determined whether any of them need to bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster egress traffic is proxied, including calls to hosting cloud provider APIs. You added sites to the
Proxyobject’sspec.noProxyfield to bypass the proxy if necessary.NoteThe
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is populated with the values of thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidr,networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, andnetworking.serviceNetwork[]fields from your installation configuration.For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint (169.254.169.254).
Procedure
Edit your
install-config.yamlfile and add the proxy settings. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
proxy.httpProxy-
Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. proxy.httpsProxy- Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster.
proxy.noProxy-
Specifies a comma-separated list of destination domain names, IP addresses, or other network CIDRs to exclude from proxying. Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass the proxy for all destinations. You must include vCenter’s IP address and the IP range that you use for its machines. additionalTrustBundle-
If provided, the installation program generates a config map that is named
user-ca-bundlein theopenshift-confignamespace to hold the additional CA certificates. If you provideadditionalTrustBundleand at least one proxy setting, theProxyobject is configured to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleconfig map that merges the contents specified for thetrustedCAparameter with the RHCOS trust bundle. TheadditionalTrustBundlefield is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle. additionalTrustBundlePolicySpecifies the policy that determines the configuration of the
Proxyobject to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The allowed values areProxyonlyandAlways. UseProxyonlyto reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map only whenhttp/httpsproxy is configured. UseAlwaysto always reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map. The default value isProxyonly. Optional parameter.NoteThe installation program does not support the proxy
readinessEndpointsfield.NoteIf the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the
wait-forcommand of the installer. For example:+
./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Save the file and reference it when installing OpenShift Container Platform.
The installation program creates a cluster-wide proxy that is named
clusterthat uses the proxy settings in the providedinstall-config.yamlfile. If no proxy settings are provided, aclusterProxyobject is still created, but it will have a nilspec.NoteOnly the
Proxyobject namedclusteris supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
2.4.4.3. Configuring regions and zones for a VMware vCenter
You can modify the default installation configuration file, so that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter.
The default install-config.yaml file configuration from the previous release of OpenShift Container Platform is deprecated. You can continue to use the deprecated default configuration, but the openshift-installer will prompt you with a warning message that indicates the use of deprecated fields in the configuration file.
The example uses the govc command. The govc command is an open source command available from VMware; it is not available from Red Hat. The Red Hat support team does not maintain the govc command. Instructions for downloading and installing govc are found on the VMware documentation website
Prerequisites
You have an existing
install-config.yamlinstallation configuration file.ImportantYou must specify at least one failure domain for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, so that you can provision data center objects for your VMware vCenter server. Consider specifying multiple failure domains if you need to provision virtual machine nodes in different data centers, clusters, datastores, and other components. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
Enter the following
govccommand-line tool commands to create theopenshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories:ImportantIf you specify different names for the
openshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories, the installation of the OpenShift Container Platform cluster fails.govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-region
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-regionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zone
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a region tag for each region vSphere data center where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command in your terminal:
govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a zone tag for each vSphere cluster where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command:
govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach region tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>
$ govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach the zone tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1
$ govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment according to your chosen installation requirements.
Sample
install-config.yamlfile with multiple data centers defined in a vSphere centerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.5. Services for a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , configure services for a user-managed load balancer.
Configuring a user-managed load balancer depends on your vendor’s load balancer.
The information and examples in this section are for guideline purposes only. Consult the vendor documentation for more specific information about the vendor’s load balancer.
Red Hat supports the following services for a user-managed load balancer:
- Ingress Controller
- OpenShift API
- OpenShift MachineConfig API
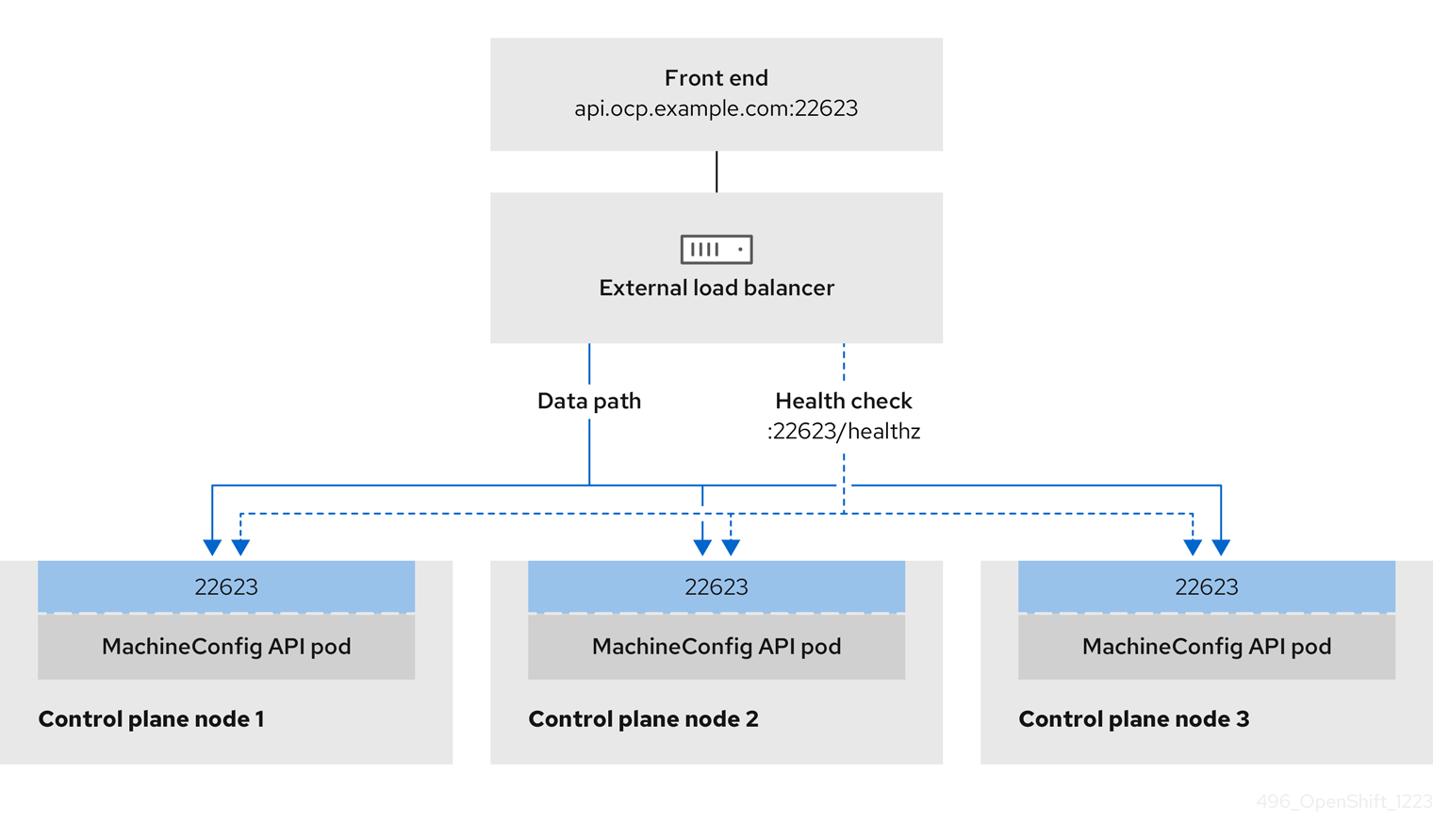
You can choose whether you want to configure one or all of these services for a user-managed load balancer. Configuring only the Ingress Controller service is a common configuration option. To better understand each service, view the following diagrams:
Figure 2.1. Example network workflow that shows an Ingress Controller operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
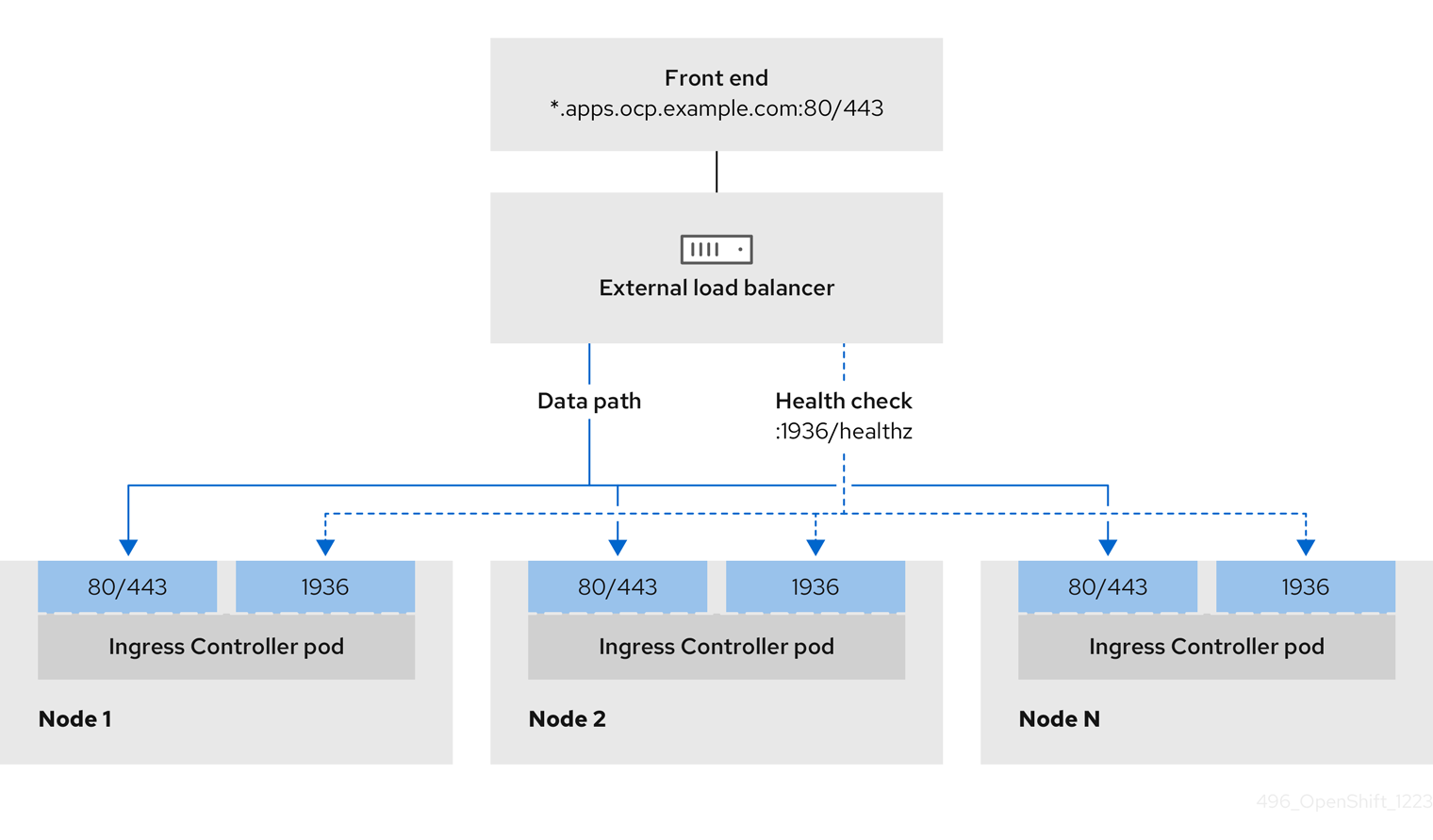
Figure 2.2. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
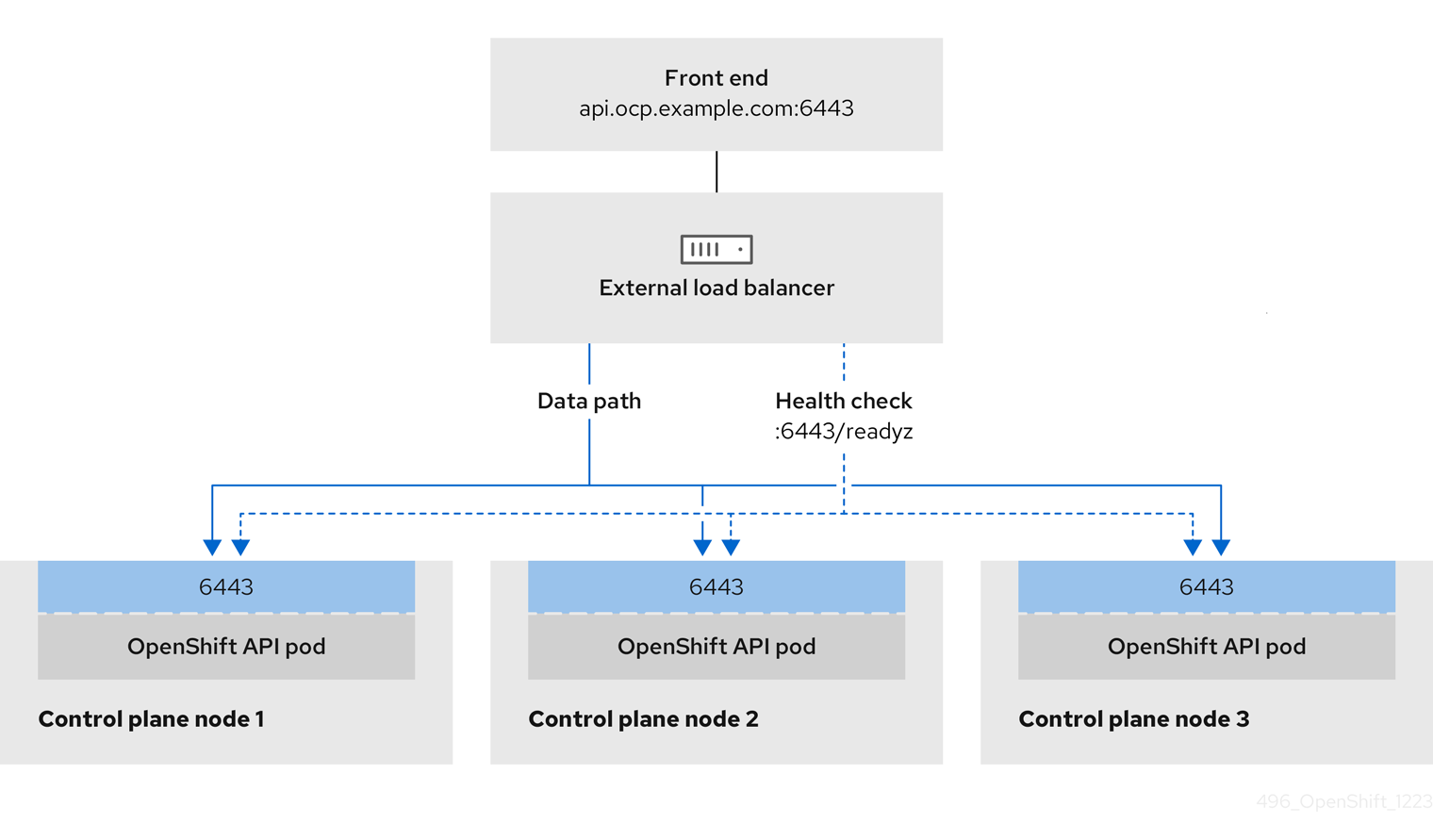
Figure 2.3. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift MachineConfig API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
The following configuration options are supported for user-managed load balancers:
- Use a node selector to map the Ingress Controller to a specific set of nodes. You must assign a static IP address to each node in this set, or configure each node to receive the same IP address from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Infrastructure nodes commonly receive this type of configuration.
Target all IP addresses on a subnet. This configuration can reduce maintenance overhead, because you can create and destroy nodes within those networks without reconfiguring the load balancer targets. If you deploy your ingress pods by using a machine set on a smaller network, such as a
/27or/28, you can simplify your load balancer targets.TipYou can list all IP addresses that exist in a network by checking the machine config pool’s resources.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, consider the following information:
- For a front-end IP address, you can use the same IP address for the front-end IP address, the Ingress Controller’s load balancer, and API load balancer. Check the vendor’s documentation for this capability.
For a back-end IP address, ensure that an IP address for an OpenShift Container Platform control plane node does not change during the lifetime of the user-managed load balancer. You can achieve this by completing one of the following actions:
- Assign a static IP address to each control plane node.
- Configure each node to receive the same IP address from the DHCP every time the node requests a DHCP lease. Depending on the vendor, the DHCP lease might be in the form of an IP reservation or a static DHCP assignment.
- Manually define each node that runs the Ingress Controller in the user-managed load balancer for the Ingress Controller back-end service. For example, if the Ingress Controller moves to an undefined node, a connection outage can occur.
2.4.5.1. Configuring a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , use a user-managed load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer, ensure that you read the "Services for a user-managed load balancer" section.
Read the following prerequisites that apply to the service that you want to configure for your user-managed load balancer.
MetalLB, which runs on a cluster, functions as a user-managed load balancer.
Prerequisites
The following list details OpenShift API prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
TCP ports 6443 and 22623 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer. Check the following items:
- Port 6443 provides access to the OpenShift API service.
- Port 22623 can provide ignition startup configurations to nodes.
- The front-end IP address and port 6443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address and port 22623 are reachable only by OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform control plane nodes on port 6443 and 22623.
The following list details Ingress Controller prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
- TCP port 443 and port 80 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all nodes that operate in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform nodes that run the Ingress Controller on ports 80, 443, and 1936.
The following list details prerequisites for health check URL specifications:
You can configure most load balancers by setting health check URLs that determine if a service is available or unavailable. OpenShift Container Platform provides these health checks for the OpenShift API, Machine Configuration API, and Ingress Controller backend services.
The following example shows a Kubernetes API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Machine Config API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Ingress Controller health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 5 Interval: 10
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 5
Interval: 10Procedure
Configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller, so that you can enable access to the cluster from your load balancer on ports 6443, 22623, 443, and 80. Depending on your needs, you can specify the IP address of a single subnet or IP addresses from multiple subnets in your HAProxy configuration.
Example HAProxy configuration with one listed subnet
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example HAProxy configuration with multiple listed subnets
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and its resources are operational:Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Kubernetes API server resource, by running the following command and observing the response:
curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Machine config server resource, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>
$ curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cache
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>
$ curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure the DNS records for your cluster to target the front-end IP addresses of the user-managed load balancer. You must update records to your DNS server for the cluster API and applications over the load balancer. The following examples shows modified DNS records:
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantDNS propagation might take some time for each DNS record to become available. Ensure that each DNS record propagates before validating each record.
For your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use the user-managed load balancer, you must specify the following configuration in your cluster’s
install-config.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
loadBalancer.type-
Set
UserManagedfor thetypeparameter to specify a user-managed load balancer for your cluster. The parameter defaults toOpenShiftManagedDefault, which denotes the default internal load balancer. For services defined in anopenshift-kni-infranamespace, a user-managed load balancer can deploy thecorednsservice to pods in your cluster but ignoreskeepalivedandhaproxyservices. loadBalancer.<api_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the Kubernetes API can communicate with the user-managed load balancer. Mandatory parameter.
loadBalancer.<ingress_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the user-managed load balancer can manage ingress traffic for your cluster. Mandatory parameter.
Verification
Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and DNS record configuration are operational:Verify that you can access the cluster API, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access the cluster machine configuration, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.6. Deploying the cluster
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on a compatible cloud platform.
You can run the create cluster command of the installation program only once, during initial installation.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
- You have verified that the cloud provider account on your host has the correct permissions to deploy the cluster. An account with incorrect permissions causes the installation process to fail with an error message that displays the missing permissions.
Optional: Before you create the cluster, configure an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
ImportantYou do not need to specify API and Ingress static addresses for your installation program. If you choose this configuration, you must take additional actions to define network targets that accept an IP address from each referenced vSphere subnet. See the section "Configuring a user-managed load balancer".
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment:
./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \ --log-level=info$ ./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \1 --log-level=info2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
When the cluster deployment completes successfully:
-
The terminal displays directions for accessing your cluster, including a link to the web console and credentials for the
kubeadminuser. -
Credential information also outputs to
<installation_directory>/.openshift_install.log.
Do not delete the installation program or the files that the installation program creates. Both are required to delete the cluster.
Example output
-
The Ignition config files that the installation program generates contain certificates that expire after 24 hours, which are then renewed at that time. If the cluster is shut down before renewing the certificates and the cluster is later restarted after the 24 hours have elapsed, the cluster automatically recovers the expired certificates. The exception is that you must manually approve the pending
node-bootstrappercertificate signing requests (CSRs) to recover kubelet certificates. See the documentation for Recovering from expired control plane certificates for more information. - It is recommended that you use Ignition config files within 12 hours after they are generated because the 24-hour certificate rotates from 16 to 22 hours after the cluster is installed. By using the Ignition config files within 12 hours, you can avoid installation failure if the certificate update runs during installation.
2.4.7. Logging in to the cluster by using the CLI
To log in to your cluster as the default system user, export the kubeconfig file. This configuration enables the CLI to authenticate and connect to the specific API server created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
The kubeconfig file is specific to a cluster and is created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Export the
kubeadmincredentials:export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<installation_directory>- Specifies the path to the directory that stores the installation files.
Verify you can run
occommands successfully using the exported configuration:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.8. Creating registry storage
After you install the cluster, you must create storage for the registry Operator.
2.4.8.1. Image registry removed during installation
On platforms that do not provide shareable object storage, the OpenShift Image Registry Operator bootstraps itself as Removed. This allows openshift-installer to complete installations on these platform types.
After installation, you must edit the Image Registry Operator configuration to switch the managementState from Removed to Managed. When this has completed, you must configure storage.
2.4.8.2. Image registry storage configuration
The Image Registry Operator is not initially available for platforms that do not provide default storage. After installation, you must configure your registry to use storage so that the Registry Operator is made available.
Configure a persistent volume, which is required for production clusters. Where applicable, you can configure an empty directory as the storage location for non-production clusters.
You can also allow the image registry to use block storage types by using the Recreate rollout strategy during upgrades.
2.4.8.2.1. Configuring registry storage for VMware vSphere
As a cluster administrator, following installation you must configure your registry to use storage.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions.
- A cluster on VMware vSphere.
Persistent storage provisioned for your cluster, such as Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation.
ImportantOpenShift Container Platform supports
ReadWriteOnceaccess for image registry storage when you have only one replica.ReadWriteOnceaccess also requires that the registry uses theRecreaterollout strategy. To deploy an image registry that supports high availability with two or more replicas,ReadWriteManyaccess is required.- Must have "100Gi" capacity.
Testing shows issues with using the NFS server on RHEL as storage backend for core services. This includes the OpenShift Container Registry and Quay, Prometheus for monitoring storage, and Elasticsearch for logging storage. Therefore, using RHEL NFS to back PVs used by core services is not recommended.
Other NFS implementations on the marketplace might not have these issues. Contact the individual NFS implementation vendor for more information on any testing that was possibly completed against these OpenShift Container Platform core components.
Procedure
To configure your registry to use storage, change the
spec.storage.pvcin theconfigs.imageregistry/clusterresource.NoteWhen you use shared storage, review your security settings to prevent outside access.
Verify that you do not have a registry pod:
oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=default
$ oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespace
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do have a registry pod in your output, you do not need to continue with this procedure.
Check the registry configuration:
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io
$ oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Leave the
claimfield blank to allow the automatic creation of animage-registry-storagepersistent volume claim (PVC). The PVC is generated based on the default storage class. However, be aware that the default storage class might provide ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volumes, such as a RADOS Block Device (RBD), which can cause issues when you replicate to more than one replica.Check the
clusteroperatorstatus:oc get clusteroperator image-registry
$ oc get clusteroperator image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.8.2.2. Configuring block registry storage for VMware vSphere
To allow the image registry to use block storage types such as vSphere Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) during upgrades as a cluster administrator, you can use the Recreate rollout strategy.
Block storage volumes are supported but not recommended for use with image registry on production clusters. An installation where the registry is configured on block storage is not highly available because the registry cannot have more than one replica.
Procedure
Enter the following command to set the image registry storage as a block storage type, patch the registry so that it uses the
Recreaterollout strategy, and runs with only1replica:oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'$ oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Provision the PV for the block storage device, and create a PVC for that volume. The requested block volume uses the ReadWriteOnce (RWO) access mode.
Create a
pvc.yamlfile with the following contents to define a VMware vSpherePersistentVolumeClaimobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
name-
Specifies a unique name that represents the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject. namespace-
Specifies the
namespacefor thePersistentVolumeClaimobject, which isopenshift-image-registry. accessModes-
Specifies the access mode of the persistent volume claim. With
ReadWriteOnce, the volume can be mounted with read and write permissions by a single node. storage- The size of the persistent volume claim.
Enter the following command to create the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject from the file:oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registry
$ oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Enter the following command to edit the registry configuration so that it references the correct PVC:
oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yaml
$ oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By creating a custom PVC, you can leave the
claimfield blank for the default automatic creation of animage-registry-storagePVC.
For instructions about configuring registry storage so that it references the correct PVC, see Configuring the registry for vSphere.
2.4.9. Telemetry access for OpenShift Container Platform
To provide metrics about cluster health and the success of updates, the Telemetry service requires internet access. When connected, this service runs automatically by default and registers your cluster to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After you confirm that your OpenShift Cluster Manager inventory is correct, either maintained automatically by Telemetry or manually by using OpenShift Cluster Manager,use subscription watch to track your OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions at the account or multi-cluster level. For more information about subscription watch, see "Data Gathered and Used by Red Hat’s subscription services" in the Additional resources section.
2.4.10. Next steps
- Customize your cluster.
- If necessary, you can Remote health reporting.
- Set up your registry and configure registry storage.
- Optional: View the events from the vSphere Problem Detector Operator to determine if the cluster has permission or storage configuration issues.
2.5. Installing a cluster on vSphere with network customizations
In OpenShift Container Platform version 4.16, you can install a cluster on your VMware vSphere instance by using installer-provisioned infrastructure with customized network configuration options. By customizing your network configuration, your cluster can coexist with existing IP address allocations in your environment and integrate with existing MTU and VXLAN configurations. To customize the installation, you modify parameters in the install-config.yaml file before you install the cluster.
You must set most of the network configuration parameters during installation, and you can modify only kubeProxy configuration parameters in a running cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform supports deploying a cluster to a single VMware vCenter only. Deploying a cluster with machines/machine sets on multiple vCenters is not supported.
2.5.1. Prerequisites
- You have completed the tasks in Preparing to install a cluster using installer-provisioned infrastructure.
- You reviewed your VMware platform licenses. Red Hat does not place any restrictions on your VMware licenses, but some VMware infrastructure components require licensing.
- You reviewed details about the OpenShift Container Platform installation and update processes.
- You read the documentation on selecting a cluster installation method and preparing it for users.
-
You provisioned persistent storage for your cluster. To deploy a private image registry, your storage must provide
ReadWriteManyaccess modes. - The OpenShift Container Platform installer requires access to port 443 on the vCenter and ESXi hosts. You verified that port 443 is accessible.
- If you use a firewall, confirm with the administrator that port 443 is accessible. Control plane nodes must be able to reach vCenter and ESXi hosts on port 443 for the installation to succeed.
If you use a firewall, you configured it to allow the sites that your cluster requires access to.
NoteBe sure to also review this site list if you are configuring a proxy.
2.5.2. Internet access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you require access to the internet to install your cluster.
You must have internet access to:
- Access OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the installation program and perform subscription management. If the cluster has internet access and you do not disable Telemetry, that service automatically entitles your cluster.
- Access Quay.io to obtain the packages that are required to install your cluster.
- Obtain the packages that are required to perform cluster updates.
If your cluster cannot have direct internet access, you can perform a restricted network installation on some types of infrastructure that you provision. During that process, you download the required content and use it to populate a mirror registry with the installation packages. With some installation types, the environment that you install your cluster in will not require internet access. Before you update the cluster, you update the content of the mirror registry.
2.5.3. VMware vSphere region and zone enablement
You can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. Each data center can run multiple clusters. This configuration reduces the risk of a hardware failure or network outage that can cause your cluster to fail. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
The VMware vSphere region and zone enablement feature requires the vSphere Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver as the default storage driver in the cluster. As a result, the feature is only available on a newly installed cluster.
For a cluster that was upgraded from a previous release, you must enable CSI automatic migration for the cluster. You can then configure multiple regions and zones for the upgraded cluster.
The default installation configuration deploys a cluster to a single vSphere data center. If you want to deploy a cluster to multiple vSphere data centers, you must create an installation configuration file that enables the region and zone feature.
The default install-config.yaml file includes vcenters and failureDomains fields, where you can specify multiple vSphere data centers and clusters for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. You can leave these fields blank if you want to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster in a vSphere environment that consists of single data center.
The following list describes terms associated with defining zones and regions for your cluster:
-
Failure domain: Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. -
Region: Specifies a vCenter data center. You define a region by using a tag from the
openshift-regiontag category. -
Zone: Specifies a vCenter cluster. You define a zone by using a tag from the
openshift-zonetag category.
If you plan on specifying more than one failure domain in your install-config.yaml file, you must create tag categories, zone tags, and region tags in advance of creating the configuration file.
You must create a vCenter tag for each vCenter data center, which represents a region. Additionally, you must create a vCenter tag for each cluster than runs in a data center, which represents a zone. After you create the tags, you must attach each tag to their respective data centers and clusters.
The following table outlines an example of the relationship among regions, zones, and tags for a configuration with multiple vSphere data centers running in a single VMware vCenter.
| Data center (region) | Cluster (zone) | Tags |
|---|---|---|
| us-east | us-east-1 | us-east-1a |
| us-east-1b | ||
| us-east-2 | us-east-2a | |
| us-east-2b | ||
| us-west | us-west-1 | us-west-1a |
| us-west-1b | ||
| us-west-2 | us-west-2a | |
| us-west-2b |
2.5.4. Creating the installation configuration file
You can customize the OpenShift Container Platform cluster you install on
VMware vSphere.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
Procedure
Create the
install-config.yamlfile.Change to the directory that contains the installation program and run the following command:
./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <installation_directory>: For<installation_directory>, specify the directory name to store the files that the installation program creates.When specifying the directory:
-
Verify that the directory has the
executepermission. This permission is required to run Terraform binaries under the installation directory. - Use an empty directory. Some installation assets, such as bootstrap X.509 certificates, have short expiration intervals, therefore you must not reuse an installation directory. If you want to reuse individual files from another cluster installation, you can copy them into your directory. However, the file names for the installation assets might change between releases. Use caution when copying installation files from an earlier OpenShift Container Platform version.
At the prompts, provide the configuration details for your cloud:
Optional: Select an SSH key to use to access your cluster machines.
NoteFor production OpenShift Container Platform clusters on which you want to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, specify an SSH key that your
ssh-agentprocess uses.- Select vsphere as the platform to target.
- Specify the name of your vCenter instance.
Specify the user name and password for the vCenter account that has the required permissions to create the cluster.
The installation program connects to your vCenter instance.
Select the data center in your vCenter instance to connect to.
NoteAfter you create the installation configuration file, you can modify the file to create a multiple vSphere data center environment. This means that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. For more information about creating this environment, see the section named VMware vSphere region and zone enablement.
Select the default vCenter datastore to use.
WarningYou can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler (SDRS), which uses Storage vMotion, is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage DRS to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
You cannot specify more than one datastore path. If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement".- Select the vCenter cluster to install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster in. The installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster as the default resource pool.
- Select the network in the vCenter instance that contains the virtual IP addresses and DNS records that you configured.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for control plane API access.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for cluster ingress.
- Enter the base domain. This base domain must be the same one that you used in the DNS records that you configured.
Enter a descriptive name for your cluster.
The cluster name you enter must match the cluster name you specified when configuring the DNS records.
-
Modify the
install-config.yamlfile. You can find more information about the available parameters in the "Installation configuration parameters" section. Back up the
install-config.yamlfile so that you can use it to install multiple clusters.ImportantThe
install-config.yamlfile is consumed during the installation process. If you want to reuse the file, you must back it up now.
2.5.4.1. Sample install-config.yaml file for an installer-provisioned VMware vSphere cluster
You can customize the install-config.yaml file to specify more details about your OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s platform or modify the values of the required parameters.
- 1
- The base domain of the cluster. All DNS records must be sub-domains of this base and include the cluster name.
- 2 3
- The
controlPlanesection is a single mapping, but thecomputesection is a sequence of mappings. To meet the requirements of the different data structures, the first line of thecomputesection must begin with a hyphen,-, and the first line of thecontrolPlanesection must not. Only one control plane pool is used. - 4
- The cluster name that you specified in your DNS records.
- 6
- Optional: Provides additional configuration for the machine pool parameters for the compute and control plane machines.Important
The VIPs,
apiVIPandingressVIP, must come from the samenetworking.machineNetworksegment. ForapiVIPand foringressVIP, if thenetworking.machineNetworkis10.0.0.0/16then API VIPs and Ingress VIPs must be in one of the10.0.0.0/16machine networks. - 7
- Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. - 8
- The path to the vSphere datastore that holds virtual machine files, templates, and ISO images.Important
You can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage vMotion is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage vMotion to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement". - 9
- Optional: Provides an existing resource pool for machine creation. If you do not specify a value, the installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster.
- 10
- Optional: Each VM created by OpenShift Container Platform is assigned a unique tag that is specific to the cluster. The assigned tag enables the installation program to identify and remove the associated VMs when a cluster is decommissioned. You can list up to ten additional tag IDs to be attached to the VMs provisioned by the installation program.
- 11
- The ID of the tag to be associated by the installation program. For example,
urn:vmomi:InventoryServiceTag:208e713c-cae3-4b7f-918e-4051ca7d1f97:GLOBAL. For more information about determining the tag ID, see the vSphere Tags and Attributes documentation. - 12
- The vSphere disk provisioning method.
- 5
- The cluster network plugin to install. The default value
OVNKubernetesis the only supported value.
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.12 and later, the apiVIP and ingressVIP configuration settings are deprecated. Instead, use a list format to enter values in the apiVIPs and ingressVIPs configuration settings.
2.5.4.2. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy during installation
To enable internet access in environments that deny direct connections, configure a cluster-wide proxy in the install-config.yaml file. This configuration ensures that the new OpenShift Container Platform cluster routes traffic through the specified HTTP or HTTPS proxy.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing
install-config.yamlfile. You have reviewed the sites that your cluster requires access to and determined whether any of them need to bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster egress traffic is proxied, including calls to hosting cloud provider APIs. You added sites to the
Proxyobject’sspec.noProxyfield to bypass the proxy if necessary.NoteThe
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is populated with the values of thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidr,networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, andnetworking.serviceNetwork[]fields from your installation configuration.For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint (169.254.169.254).
Procedure
Edit your
install-config.yamlfile and add the proxy settings. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
proxy.httpProxy-
Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. proxy.httpsProxy- Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster.
proxy.noProxy-
Specifies a comma-separated list of destination domain names, IP addresses, or other network CIDRs to exclude from proxying. Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass the proxy for all destinations. You must include vCenter’s IP address and the IP range that you use for its machines. additionalTrustBundle-
If provided, the installation program generates a config map that is named
user-ca-bundlein theopenshift-confignamespace to hold the additional CA certificates. If you provideadditionalTrustBundleand at least one proxy setting, theProxyobject is configured to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleconfig map that merges the contents specified for thetrustedCAparameter with the RHCOS trust bundle. TheadditionalTrustBundlefield is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle. additionalTrustBundlePolicySpecifies the policy that determines the configuration of the
Proxyobject to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The allowed values areProxyonlyandAlways. UseProxyonlyto reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map only whenhttp/httpsproxy is configured. UseAlwaysto always reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map. The default value isProxyonly. Optional parameter.NoteThe installation program does not support the proxy
readinessEndpointsfield.NoteIf the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the
wait-forcommand of the installer. For example:+
./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Save the file and reference it when installing OpenShift Container Platform.
The installation program creates a cluster-wide proxy that is named
clusterthat uses the proxy settings in the providedinstall-config.yamlfile. If no proxy settings are provided, aclusterProxyobject is still created, but it will have a nilspec.NoteOnly the
Proxyobject namedclusteris supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
2.5.4.3. Deploying IP addressing with dual-stack networking
When deploying IP addressing with dual-stack networking for the bootstrap virtual machine (VM), the bootstrap VM functions with a single IP version.
The following examples are for DHCP. DHCP-based dual stack clusters can deploy with one IPv4 and one IPv6 virtual IP address (VIP) each from Day 1.
Deploying a cluster with static IP addresses involves configuring IP addresses for the bootstrap VM, API, and ingress VIPs. Configuring dual-stack with a static IP set in install-config requires one VIP each for API and ingress. Add secondary VIPs after deployment.
For dual-stack networking in OpenShift Container Platform clusters, you can configure IPv4 and IPv6 address endpoints for cluster nodes. To configure IPv4 and IPv6 address endpoints for cluster nodes, edit the machineNetwork, clusterNetwork, and serviceNetwork configuration settings in the install-config.yaml file. Each setting must have two CIDR entries each. For a cluster with the IPv4 family as the primary address family, specify the IPv4 setting first. For a cluster with the IPv6 family as the primary address family, specify the IPv6 setting first.
Example NMState YAML configuration file that includes the IPv4 and IPv6 address endpoints for cluster nodes
To provide an interface to the cluster for applications that use IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, configure IPv4 and IPv6 virtual IP (VIP) address endpoints for the Ingress VIP and API VIP services. To configure IPv4 and IPv6 address endpoints, edit the apiVIPs and ingressVIPs configuration settings in the install-config.yaml file . The apiVIPs and ingressVIPs configuration settings use a list format. The order of the list indicates the primary and secondary VIP address for each service.
For a cluster with dual-stack networking configuration, you must assign both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to the same interface.
2.5.4.4. Configuring regions and zones for a VMware vCenter
You can modify the default installation configuration file, so that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter.
The default install-config.yaml file configuration from the previous release of OpenShift Container Platform is deprecated. You can continue to use the deprecated default configuration, but the openshift-installer will prompt you with a warning message that indicates the use of deprecated fields in the configuration file.
The example uses the govc command. The govc command is an open source command available from VMware; it is not available from Red Hat. The Red Hat support team does not maintain the govc command. Instructions for downloading and installing govc are found on the VMware documentation website
Prerequisites
You have an existing
install-config.yamlinstallation configuration file.ImportantYou must specify at least one failure domain for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, so that you can provision data center objects for your VMware vCenter server. Consider specifying multiple failure domains if you need to provision virtual machine nodes in different data centers, clusters, datastores, and other components. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
Enter the following
govccommand-line tool commands to create theopenshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories:ImportantIf you specify different names for the
openshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories, the installation of the OpenShift Container Platform cluster fails.govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-region
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-regionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zone
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a region tag for each region vSphere data center where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command in your terminal:
govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a zone tag for each vSphere cluster where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command:
govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach region tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>
$ govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach the zone tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1
$ govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment according to your chosen installation requirements.
Sample
install-config.yamlfile with multiple data centers defined in a vSphere centerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.5.5. Network configuration phases
There are two phases prior to OpenShift Container Platform installation where you can customize the network configuration.
- Phase 1
You can customize the following network-related fields in the
install-config.yamlfile before you create the manifest files:-
networking.networkType -
networking.clusterNetwork -
networking.serviceNetwork networking.machineNetworkFor more information, see "Installation configuration parameters".
NoteSet the
networking.machineNetworkto match the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) where the preferred subnet is located.ImportantThe CIDR range
172.17.0.0/16is reserved bylibVirt. You cannot use any other CIDR range that overlaps with the172.17.0.0/16CIDR range for networks in your cluster.
-
- Phase 2
-
After creating the manifest files by running
openshift-install create manifests, you can define a customized Cluster Network Operator manifest with only the fields you want to modify. You can use the manifest to specify an advanced network configuration.
During phase 2, you cannot override the values that you specified in phase 1 in the install-config.yaml file. However, you can customize the network plugin during phase 2.
2.5.6. Specifying advanced network configuration
You can use advanced network configuration for your network plugin to integrate your cluster into your existing network environment.
You can specify advanced network configuration only before you install the cluster.
Customizing your network configuration by modifying the OpenShift Container Platform manifest files created by the installation program is not supported. Applying a manifest file that you create, as in the following procedure, is supported.
Prerequisites
-
You have created the
install-config.yamlfile and completed any modifications to it.
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and create the manifests:
./openshift-install create manifests --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create manifests --dir <installation_directory>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<installation_directory>specifies the name of the directory that contains theinstall-config.yamlfile for your cluster.
Create a stub manifest file for the advanced network configuration that is named
cluster-network-03-config.ymlin the<installation_directory>/manifests/directory:apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1 kind: Network metadata: name: cluster spec:
apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1 kind: Network metadata: name: cluster spec:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the advanced network configuration for your cluster in the
cluster-network-03-config.ymlfile, such as in the following example:Enable IPsec for the OVN-Kubernetes network provider
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optional: Back up the
manifests/cluster-network-03-config.ymlfile. The installation program consumes themanifests/directory when you create the Ignition config files.
2.5.6.1. Specifying multiple subnets for your network
Before you install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on a vSphere host, you can specify multiple subnets for a networking implementation so that the vSphere cloud controller manager (CCM) can select the appropriate subnet for a given networking situation. vSphere can use the subnet for managing pods and services on your cluster.
For this configuration, you must specify internal and external Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) implementations in the vSphere CCM configuration. Each CIDR implementation lists an IP address range that the CCM uses to decide what subnets interact with traffic from internal and external networks.
Failure to configure internal and external CIDR implementations in the vSphere CCM configuration can cause the vSphere CCM to select the wrong subnet. This situation causes the following error:
ERROR Bootstrap failed to complete: timed out waiting for the condition ERROR Failed to wait for bootstrapping to complete. This error usually happens when there is a problem with control plane hosts that prevents the control plane operators from creating the control plane.
ERROR Bootstrap failed to complete: timed out waiting for the condition
ERROR Failed to wait for bootstrapping to complete. This error usually happens when there is a problem with control plane hosts that prevents the control plane operators from creating the control plane.
This configuration can cause new nodes that associate with a MachineSet object with a single subnet to become unusable as each new node receives the node.cloudprovider.kubernetes.io/uninitialized taint. These situations can cause communication issues with the Kubernetes API server that can cause installation of the cluster to fail.
Prerequisites
- You created Kubernetes manifest files for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
-
From the directory where you store your OpenShift Container Platform cluster manifest files, open the
manifests/cluster-infrastructure-02-config.ymlmanifest file. Add a
nodeNetworkingobject to the file and specify internal and external network subnet CIDR implementations for the object.TipFor most networking situations, consider setting the standard multiple-subnet configuration. This configuration requires that you set the same IP address ranges in the
nodeNetworking.internal.networkSubnetCidrandnodeNetworking.external.networkSubnetCidrparameters.Example of a configured
cluster-infrastructure-02-config.ymlmanifest fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.5.7. Cluster Network Operator configuration
To manage cluster networking, configure the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) Network custom resource (CR) named cluster so the cluster uses the correct IP ranges and network plugin settings for reliable pod and service connectivity. Some settings and fields are inherited at the time of install.
The CNO configuration inherits the following fields during cluster installation from the Network API in the Network.config.openshift.io API group:
clusterNetwork- IP address pools from which pod IP addresses are allocated.
serviceNetwork- IP address pool for services.
defaultNetwork.type-
Cluster network plugin.
OVNKubernetesis the only supported plugin during installation.
You can specify the cluster network plugin configuration for your cluster by setting the fields for the defaultNetwork object in the CNO object named cluster.
2.5.7.1. Cluster Network Operator configuration object
The fields for the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the CNO object. This name is always |
|
|
| A list specifying the blocks of IP addresses from which pod IP addresses are allocated and the subnet prefix length assigned to each individual node in the cluster. For example: |
|
|
| A block of IP addresses for services. The OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes network plugins support only a single IP address block for the service network. For example: spec: serviceNetwork: - 172.30.0.0/14
You can customize this field only in the |
|
|
| Configures the network plugin for the cluster network. |
|
|
| The fields for this object specify the kube-proxy configuration. If you are using the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network plugin, the kube-proxy configuration has no effect. |
For a cluster that needs to deploy objects across multiple networks, ensure that you specify the same value for the clusterNetwork.hostPrefix parameter for each network type that is defined in the install-config.yaml file. Setting a different value for each clusterNetwork.hostPrefix parameter can impact the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, where the plugin cannot effectively route object traffic among different nodes.
2.5.7.2. defaultNetwork object configuration
The values for the defaultNetwork object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Note OpenShift Container Platform uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin by default. OpenShift SDN is no longer available as an installation choice for new clusters. |
|
|
| This object is only valid for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. |
2.5.7.3. Configuration for the OpenShift SDN network plugin
The following table describes the configuration fields for the OpenShift SDN network plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Configures the network isolation mode for OpenShift SDN. The default value is
The values |
|
|
| The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the VXLAN overlay network. This is detected automatically based on the MTU of the primary network interface. You do not normally need to override the detected MTU. If the auto-detected value is not what you expect it to be, confirm that the MTU on the primary network interface on your nodes is correct. You cannot use this option to change the MTU value of the primary network interface on the nodes.
If your cluster requires different MTU values for different nodes, you must set this value to You can set the value during cluster installation or as a post-installation task. For more information, see "Changing the MTU for the cluster network" in the OpenShift Container Platform Networking document. |
|
|
|
The port to use for all VXLAN packets. The default value is If you are running in a virtualized environment with existing nodes that are part of another VXLAN network, then you might be required to change this. For example, when running an OpenShift SDN overlay on top of VMware NSX-T, you must select an alternate port for the VXLAN, because both SDNs use the same default VXLAN port number.
On Amazon Web Services (AWS), you can select an alternate port for the VXLAN between port |
2.5.7.4. Configuration for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
The following table describes the configuration fields for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) overlay network. This is detected automatically based on the MTU of the primary network interface. You do not normally need to override the detected MTU. If the auto-detected value is not what you expect it to be, confirm that the MTU on the primary network interface on your nodes is correct. You cannot use this option to change the MTU value of the primary network interface on the nodes.
If your cluster requires different MTU values for different nodes, you must set this value to |
|
|
|
The port to use for all Geneve packets. The default value is |
|
|
| Specify a configuration object for customizing the IPsec configuration. |
|
|
| Specifies a configuration object for IPv4 settings. |
|
|
| Specifies a configuration object for IPv6 settings. |
|
|
| Specify a configuration object for customizing network policy audit logging. If unset, the defaults audit log settings are used. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specify a configuration object for customizing how egress traffic is sent to the node gateway. Valid values are Note While migrating egress traffic, you can expect some disruption to workloads and service traffic until the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) successfully rolls out the changes. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| string |
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the
The default value is |
|
| string |
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the
The default value is |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| string |
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the
The default value is |
|
| string |
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the
The default value is |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| integer |
The maximum number of messages to generate every second per node. The default value is |
|
| integer |
The maximum size for the audit log in bytes. The default value is |
|
| integer | The maximum number of log files that are retained. |
|
| string | One of the following additional audit log targets:
|
|
| string |
The syslog facility, such as |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Set this field to
This field has an interaction with the Open vSwitch hardware offloading feature. If you set this field to |
|
|
|
You can control IP forwarding for all traffic on OVN-Kubernetes managed interfaces by using the |
|
|
| Optional: Specify an object to configure the internal OVN-Kubernetes masquerade address for host to service traffic for IPv4 addresses. |
|
|
| Optional: Specify an object to configure the internal OVN-Kubernetes masquerade address for host to service traffic for IPv6 addresses. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The masquerade IPv4 addresses that are used internally to enable host to service traffic. The host is configured with these IP addresses as well as the shared gateway bridge interface. The default value is |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The masquerade IPv6 addresses that are used internally to enable host to service traffic. The host is configured with these IP addresses as well as the shared gateway bridge interface. The default value is |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies the behavior of the IPsec implementation. Must be one of the following values:
|
Example OVN-Kubernetes configuration with IPSec enabled
Using OVNKubernetes can lead to a stack exhaustion problem on IBM Power®.
2.5.7.5. kubeProxyConfig object configuration (OpenShiftSDN container network interface only)
The values for the kubeProxyConfig object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The refresh period for Note
Because of performance improvements introduced in OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 and greater, adjusting the |
|
|
|
The minimum duration before refreshing kubeProxyConfig:
proxyArguments:
iptables-min-sync-period:
- 0s
|
2.5.8. Services for a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , configure services for a user-managed load balancer.
Configuring a user-managed load balancer depends on your vendor’s load balancer.
The information and examples in this section are for guideline purposes only. Consult the vendor documentation for more specific information about the vendor’s load balancer.
Red Hat supports the following services for a user-managed load balancer:
- Ingress Controller
- OpenShift API
- OpenShift MachineConfig API
You can choose whether you want to configure one or all of these services for a user-managed load balancer. Configuring only the Ingress Controller service is a common configuration option. To better understand each service, view the following diagrams:
Figure 2.4. Example network workflow that shows an Ingress Controller operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

Figure 2.5. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

Figure 2.6. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift MachineConfig API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

The following configuration options are supported for user-managed load balancers:
- Use a node selector to map the Ingress Controller to a specific set of nodes. You must assign a static IP address to each node in this set, or configure each node to receive the same IP address from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Infrastructure nodes commonly receive this type of configuration.
Target all IP addresses on a subnet. This configuration can reduce maintenance overhead, because you can create and destroy nodes within those networks without reconfiguring the load balancer targets. If you deploy your ingress pods by using a machine set on a smaller network, such as a
/27or/28, you can simplify your load balancer targets.TipYou can list all IP addresses that exist in a network by checking the machine config pool’s resources.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, consider the following information:
- For a front-end IP address, you can use the same IP address for the front-end IP address, the Ingress Controller’s load balancer, and API load balancer. Check the vendor’s documentation for this capability.
For a back-end IP address, ensure that an IP address for an OpenShift Container Platform control plane node does not change during the lifetime of the user-managed load balancer. You can achieve this by completing one of the following actions:
- Assign a static IP address to each control plane node.
- Configure each node to receive the same IP address from the DHCP every time the node requests a DHCP lease. Depending on the vendor, the DHCP lease might be in the form of an IP reservation or a static DHCP assignment.
- Manually define each node that runs the Ingress Controller in the user-managed load balancer for the Ingress Controller back-end service. For example, if the Ingress Controller moves to an undefined node, a connection outage can occur.
2.5.8.1. Configuring a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , use a user-managed load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer, ensure that you read the "Services for a user-managed load balancer" section.
Read the following prerequisites that apply to the service that you want to configure for your user-managed load balancer.
MetalLB, which runs on a cluster, functions as a user-managed load balancer.
Prerequisites
The following list details OpenShift API prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
TCP ports 6443 and 22623 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer. Check the following items:
- Port 6443 provides access to the OpenShift API service.
- Port 22623 can provide ignition startup configurations to nodes.
- The front-end IP address and port 6443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address and port 22623 are reachable only by OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform control plane nodes on port 6443 and 22623.
The following list details Ingress Controller prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
- TCP port 443 and port 80 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all nodes that operate in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform nodes that run the Ingress Controller on ports 80, 443, and 1936.
The following list details prerequisites for health check URL specifications:
You can configure most load balancers by setting health check URLs that determine if a service is available or unavailable. OpenShift Container Platform provides these health checks for the OpenShift API, Machine Configuration API, and Ingress Controller backend services.
The following example shows a Kubernetes API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Machine Config API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Ingress Controller health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 5 Interval: 10
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 5
Interval: 10Procedure
Configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller, so that you can enable access to the cluster from your load balancer on ports 6443, 22623, 443, and 80. Depending on your needs, you can specify the IP address of a single subnet or IP addresses from multiple subnets in your HAProxy configuration.
Example HAProxy configuration with one listed subnet
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example HAProxy configuration with multiple listed subnets
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and its resources are operational:Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Kubernetes API server resource, by running the following command and observing the response:
curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Machine config server resource, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>
$ curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cache
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>
$ curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure the DNS records for your cluster to target the front-end IP addresses of the user-managed load balancer. You must update records to your DNS server for the cluster API and applications over the load balancer. The following examples shows modified DNS records:
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantDNS propagation might take some time for each DNS record to become available. Ensure that each DNS record propagates before validating each record.
For your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use the user-managed load balancer, you must specify the following configuration in your cluster’s
install-config.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
loadBalancer.type-
Set
UserManagedfor thetypeparameter to specify a user-managed load balancer for your cluster. The parameter defaults toOpenShiftManagedDefault, which denotes the default internal load balancer. For services defined in anopenshift-kni-infranamespace, a user-managed load balancer can deploy thecorednsservice to pods in your cluster but ignoreskeepalivedandhaproxyservices. loadBalancer.<api_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the Kubernetes API can communicate with the user-managed load balancer. Mandatory parameter.
loadBalancer.<ingress_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the user-managed load balancer can manage ingress traffic for your cluster. Mandatory parameter.
Verification
Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and DNS record configuration are operational:Verify that you can access the cluster API, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access the cluster machine configuration, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.5.9. Deploying the cluster
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on a compatible cloud platform.
You can run the create cluster command of the installation program only once, during initial installation.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
- You have verified that the cloud provider account on your host has the correct permissions to deploy the cluster. An account with incorrect permissions causes the installation process to fail with an error message that displays the missing permissions.
Optional: Before you create the cluster, configure an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
ImportantYou do not need to specify API and Ingress static addresses for your installation program. If you choose this configuration, you must take additional actions to define network targets that accept an IP address from each referenced vSphere subnet. See the section "Configuring a user-managed load balancer".
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment:
./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \ --log-level=info$ ./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \1 --log-level=info2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
When the cluster deployment completes successfully:
-
The terminal displays directions for accessing your cluster, including a link to the web console and credentials for the
kubeadminuser. -
Credential information also outputs to
<installation_directory>/.openshift_install.log.
Do not delete the installation program or the files that the installation program creates. Both are required to delete the cluster.
Example output
-
The Ignition config files that the installation program generates contain certificates that expire after 24 hours, which are then renewed at that time. If the cluster is shut down before renewing the certificates and the cluster is later restarted after the 24 hours have elapsed, the cluster automatically recovers the expired certificates. The exception is that you must manually approve the pending
node-bootstrappercertificate signing requests (CSRs) to recover kubelet certificates. See the documentation for Recovering from expired control plane certificates for more information. - It is recommended that you use Ignition config files within 12 hours after they are generated because the 24-hour certificate rotates from 16 to 22 hours after the cluster is installed. By using the Ignition config files within 12 hours, you can avoid installation failure if the certificate update runs during installation.
2.5.10. Logging in to the cluster by using the CLI
To log in to your cluster as the default system user, export the kubeconfig file. This configuration enables the CLI to authenticate and connect to the specific API server created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
The kubeconfig file is specific to a cluster and is created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Export the
kubeadmincredentials:export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<installation_directory>- Specifies the path to the directory that stores the installation files.
Verify you can run
occommands successfully using the exported configuration:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.5.11. Creating registry storage
After you install the cluster, you must create storage for the registry Operator.
2.5.11.1. Image registry removed during installation
On platforms that do not provide shareable object storage, the OpenShift Image Registry Operator bootstraps itself as Removed. This allows openshift-installer to complete installations on these platform types.
After installation, you must edit the Image Registry Operator configuration to switch the managementState from Removed to Managed. When this has completed, you must configure storage.
2.5.11.2. Image registry storage configuration
The Image Registry Operator is not initially available for platforms that do not provide default storage. After installation, you must configure your registry to use storage so that the Registry Operator is made available.
Configure a persistent volume, which is required for production clusters. Where applicable, you can configure an empty directory as the storage location for non-production clusters.
You can also allow the image registry to use block storage types by using the Recreate rollout strategy during upgrades.
2.5.11.2.1. Configuring registry storage for VMware vSphere
As a cluster administrator, following installation you must configure your registry to use storage.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions.
- A cluster on VMware vSphere.
Persistent storage provisioned for your cluster, such as Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation.
ImportantOpenShift Container Platform supports
ReadWriteOnceaccess for image registry storage when you have only one replica.ReadWriteOnceaccess also requires that the registry uses theRecreaterollout strategy. To deploy an image registry that supports high availability with two or more replicas,ReadWriteManyaccess is required.- Must have "100Gi" capacity.
Testing shows issues with using the NFS server on RHEL as storage backend for core services. This includes the OpenShift Container Registry and Quay, Prometheus for monitoring storage, and Elasticsearch for logging storage. Therefore, using RHEL NFS to back PVs used by core services is not recommended.
Other NFS implementations on the marketplace might not have these issues. Contact the individual NFS implementation vendor for more information on any testing that was possibly completed against these OpenShift Container Platform core components.
Procedure
To configure your registry to use storage, change the
spec.storage.pvcin theconfigs.imageregistry/clusterresource.NoteWhen you use shared storage, review your security settings to prevent outside access.
Verify that you do not have a registry pod:
oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=default
$ oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespace
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do have a registry pod in your output, you do not need to continue with this procedure.
Check the registry configuration:
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io
$ oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Leave the
claimfield blank to allow the automatic creation of animage-registry-storagepersistent volume claim (PVC). The PVC is generated based on the default storage class. However, be aware that the default storage class might provide ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volumes, such as a RADOS Block Device (RBD), which can cause issues when you replicate to more than one replica.Check the
clusteroperatorstatus:oc get clusteroperator image-registry
$ oc get clusteroperator image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.5.11.2.2. Configuring block registry storage for VMware vSphere
To allow the image registry to use block storage types such as vSphere Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) during upgrades as a cluster administrator, you can use the Recreate rollout strategy.
Block storage volumes are supported but not recommended for use with image registry on production clusters. An installation where the registry is configured on block storage is not highly available because the registry cannot have more than one replica.
Procedure
Enter the following command to set the image registry storage as a block storage type, patch the registry so that it uses the
Recreaterollout strategy, and runs with only1replica:oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'$ oc patch config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"rolloutStrategy":"Recreate","replicas":1}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Provision the PV for the block storage device, and create a PVC for that volume. The requested block volume uses the ReadWriteOnce (RWO) access mode.
Create a
pvc.yamlfile with the following contents to define a VMware vSpherePersistentVolumeClaimobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
name-
Specifies a unique name that represents the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject. namespace-
Specifies the
namespacefor thePersistentVolumeClaimobject, which isopenshift-image-registry. accessModes-
Specifies the access mode of the persistent volume claim. With
ReadWriteOnce, the volume can be mounted with read and write permissions by a single node. storage- The size of the persistent volume claim.
Enter the following command to create the
PersistentVolumeClaimobject from the file:oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registry
$ oc create -f pvc.yaml -n openshift-image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Enter the following command to edit the registry configuration so that it references the correct PVC:
oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yaml
$ oc edit config.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By creating a custom PVC, you can leave the
claimfield blank for the default automatic creation of animage-registry-storagePVC.
For instructions about configuring registry storage so that it references the correct PVC, see Configuring the registry for vSphere.
2.5.12. Telemetry access for OpenShift Container Platform
To provide metrics about cluster health and the success of updates, the Telemetry service requires internet access. When connected, this service runs automatically by default and registers your cluster to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After you confirm that your OpenShift Cluster Manager inventory is correct, either maintained automatically by Telemetry or manually by using OpenShift Cluster Manager,use subscription watch to track your OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions at the account or multi-cluster level. For more information about subscription watch, see "Data Gathered and Used by Red Hat’s subscription services" in the Additional resources section.
2.5.13. Configuring network components to run on the control plane
You can configure networking components to run exclusively on the control plane nodes. By default, OpenShift Container Platform allows any node in the machine config pool to host the ingressVIP virtual IP address. However, some environments deploy compute nodes in separate subnets from the control plane nodes, which requires configuring the ingressVIP virtual IP address to run on the control plane nodes.
You can scale the remote nodes by creating a compute machine set in a separate subnet.
When deploying remote nodes in separate subnets, you must place the ingressVIP virtual IP address exclusively with the control plane nodes.

Procedure
Change to the directory storing the
install-config.yamlfile:cd ~/clusterconfigs
$ cd ~/clusterconfigsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Switch to the
manifestssubdirectory:cd manifests
$ cd manifestsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a file named
cluster-network-avoid-workers-99-config.yaml:touch cluster-network-avoid-workers-99-config.yaml
$ touch cluster-network-avoid-workers-99-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open the
cluster-network-avoid-workers-99-config.yamlfile in an editor and enter a custom resource (CR) that describes the Operator configuration:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This manifest places the
ingressVIPvirtual IP address on the control plane nodes. Additionally, this manifest deploys the following processes on the control plane nodes only:-
openshift-ingress-operator -
keepalived
-
-
Save the
cluster-network-avoid-workers-99-config.yamlfile. Create a
manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Consider backing up the
manifestsdirectory. The installer deletes themanifests/directory when creating the cluster. Modify the
cluster-scheduler-02-config.ymlmanifest to make the control plane nodes schedulable by setting themastersSchedulablefield totrue. Control plane nodes are not schedulable by default. For example:sed -i "s;mastersSchedulable: false;mastersSchedulable: true;g" clusterconfigs/manifests/cluster-scheduler-02-config.yml
$ sed -i "s;mastersSchedulable: false;mastersSchedulable: true;g" clusterconfigs/manifests/cluster-scheduler-02-config.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf control plane nodes are not schedulable after completing this procedure, deploying the cluster will fail.
2.5.14. Next steps
- Customize your cluster.
- Remote health reporting
- Set up your registry and configure registry storage.
- Optional: View the events from the vSphere Problem Detector Operator to determine if the cluster has permission or storage configuration issues.
2.6. Installing a cluster on vSphere in a restricted network
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you can install a cluster on VMware vSphere infrastructure in a restricted network by creating an internal mirror of the installation release content.
OpenShift Container Platform supports deploying a cluster to a single VMware vCenter only. Deploying a cluster with machines/machine sets on multiple vCenters is not supported.
2.6.1. Prerequisites
- You have completed the tasks in Preparing to install a cluster using installer-provisioned infrastructure.
- You reviewed your VMware platform licenses. Red Hat does not place any restrictions on your VMware licenses, but some VMware infrastructure components require licensing.
- You reviewed details about the OpenShift Container Platform installation and update processes.
- You read the documentation on selecting a cluster installation method and preparing it for users.
You created a registry on your mirror host and obtained the
imageContentSourcesdata for your version of OpenShift Container Platform.ImportantBecause the installation media is on the mirror host, you can use that computer to complete all installation steps.
- You provisioned persistent storage for your cluster. To deploy a private image registry, your storage must provide the ReadWriteMany access mode.
- The OpenShift Container Platform installer requires access to port 443 on the vCenter and ESXi hosts. You verified that port 443 is accessible.
- If you use a firewall, you confirmed with the administrator that port 443 is accessible. Control plane nodes must be able to reach vCenter and ESXi hosts on port 443 for the installation to succeed.
If you use a firewall and plan to use the Telemetry service, you configured the firewall to allow the sites that your cluster requires access to.
NoteIf you are configuring a proxy, be sure to also review this site list.
2.6.2. About installations in restricted networks
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you can perform an installation that does not require an active connection to the internet to obtain software components. Restricted network installations can be completed using installer-provisioned infrastructure or user-provisioned infrastructure, depending on the cloud platform to which you are installing the cluster.
If you choose to perform a restricted network installation on a cloud platform, you still require access to its cloud APIs. Some cloud functions, like Amazon Web Service’s Route 53 DNS and IAM services, require internet access. Depending on your network, you might require less internet access for an installation on bare metal hardware, Nutanix, or on VMware vSphere.
To complete a restricted network installation, you must create a registry that mirrors the contents of the OpenShift image registry and contains the installation media. You can create this registry on a mirror host, which can access both the internet and your closed network, or by using other methods that meet your restrictions.
2.6.2.1. Additional limits
Clusters in restricted networks have the following additional limitations and restrictions:
-
The
ClusterVersionstatus includes anUnable to retrieve available updateserror. - By default, you cannot use the contents of the Developer Catalog because you cannot access the required image stream tags.
2.6.3. Internet access for OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.16, you require access to the internet to obtain the images that are necessary to install your cluster.
You must have internet access to:
- Access OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the installation program and perform subscription management. If the cluster has internet access and you do not disable Telemetry, that service automatically entitles your cluster.
- Access Quay.io to obtain the packages that are required to install your cluster.
- Obtain the packages that are required to perform cluster updates.
2.6.4. Creating the RHCOS image for restricted network installations
Download the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) image to install OpenShift Container Platform on a restricted network VMware vSphere environment.
Prerequisites
- Obtain the OpenShift Container Platform installation program. For a restricted network installation, the program is on your mirror registry host.
Procedure
- Log in to the Red Hat Customer Portal’s Product Downloads page.
Under Version, select the most recent release of OpenShift Container Platform 4.16 for RHEL 8.
ImportantThe RHCOS images might not change with every release of OpenShift Container Platform. You must download images with the highest version that is less than or equal to the OpenShift Container Platform version that you install. Use the image versions that match your OpenShift Container Platform version if they are available.
- Download the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) - vSphere image.
- Upload the image you downloaded to a location that is accessible from the bastion server.
The image is now available for a restricted installation. Note the image name or location for use in OpenShift Container Platform deployment.
2.6.5. VMware vSphere region and zone enablement
You can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. Each data center can run multiple clusters. This configuration reduces the risk of a hardware failure or network outage that can cause your cluster to fail. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
The VMware vSphere region and zone enablement feature requires the vSphere Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver as the default storage driver in the cluster. As a result, the feature is only available on a newly installed cluster.
For a cluster that was upgraded from a previous release, you must enable CSI automatic migration for the cluster. You can then configure multiple regions and zones for the upgraded cluster.
The default installation configuration deploys a cluster to a single vSphere data center. If you want to deploy a cluster to multiple vSphere data centers, you must create an installation configuration file that enables the region and zone feature.
The default install-config.yaml file includes vcenters and failureDomains fields, where you can specify multiple vSphere data centers and clusters for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. You can leave these fields blank if you want to install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster in a vSphere environment that consists of single data center.
The following list describes terms associated with defining zones and regions for your cluster:
-
Failure domain: Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. -
Region: Specifies a vCenter data center. You define a region by using a tag from the
openshift-regiontag category. -
Zone: Specifies a vCenter cluster. You define a zone by using a tag from the
openshift-zonetag category.
If you plan on specifying more than one failure domain in your install-config.yaml file, you must create tag categories, zone tags, and region tags in advance of creating the configuration file.
You must create a vCenter tag for each vCenter data center, which represents a region. Additionally, you must create a vCenter tag for each cluster than runs in a data center, which represents a zone. After you create the tags, you must attach each tag to their respective data centers and clusters.
The following table outlines an example of the relationship among regions, zones, and tags for a configuration with multiple vSphere data centers running in a single VMware vCenter.
| Data center (region) | Cluster (zone) | Tags |
|---|---|---|
| us-east | us-east-1 | us-east-1a |
| us-east-1b | ||
| us-east-2 | us-east-2a | |
| us-east-2b | ||
| us-west | us-west-1 | us-west-1a |
| us-west-1b | ||
| us-west-2 | us-west-2a | |
| us-west-2b |
2.6.6. Creating the installation configuration file
You can customize the OpenShift Container Platform cluster you install on
VMware vSphere.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster. For a restricted network installation, these files are on your mirror host.
-
You have the
imageContentSourcesvalues that were generated during mirror registry creation. - You have obtained the contents of the certificate for your mirror registry.
- You have retrieved a Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) image and uploaded it to an accessible location.
Procedure
Create the
install-config.yamlfile.Change to the directory that contains the installation program and run the following command:
./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create install-config --dir <installation_directory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <installation_directory>: For<installation_directory>, specify the directory name to store the files that the installation program creates.When specifying the directory:
-
Verify that the directory has the
executepermission. This permission is required to run Terraform binaries under the installation directory. - Use an empty directory. Some installation assets, such as bootstrap X.509 certificates, have short expiration intervals, therefore you must not reuse an installation directory. If you want to reuse individual files from another cluster installation, you can copy them into your directory. However, the file names for the installation assets might change between releases. Use caution when copying installation files from an earlier OpenShift Container Platform version.
At the prompts, provide the configuration details for your cloud:
Optional: Select an SSH key to use to access your cluster machines.
NoteFor production OpenShift Container Platform clusters on which you want to perform installation debugging or disaster recovery, specify an SSH key that your
ssh-agentprocess uses.- Select vsphere as the platform to target.
- Specify the name of your vCenter instance.
Specify the user name and password for the vCenter account that has the required permissions to create the cluster.
The installation program connects to your vCenter instance.
Select the data center in your vCenter instance to connect to.
NoteAfter you create the installation configuration file, you can modify the file to create a multiple vSphere data center environment. This means that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter. For more information about creating this environment, see the section named VMware vSphere region and zone enablement.
Select the default vCenter datastore to use.
WarningYou can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage Distributed Resource Scheduler (SDRS), which uses Storage vMotion, is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage DRS to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
You cannot specify more than one datastore path. If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement".- Select the vCenter cluster to install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster in. The installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster as the default resource pool.
- Select the network in the vCenter instance that contains the virtual IP addresses and DNS records that you configured.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for control plane API access.
- Enter the virtual IP address that you configured for cluster ingress.
- Enter the base domain. This base domain must be the same one that you used in the DNS records that you configured.
Enter a descriptive name for your cluster.
The cluster name you enter must match the cluster name you specified when configuring the DNS records.
In the
install-config.yamlfile, set the value ofplatform.vsphere.clusterOSImageto the image location or name. For example:platform: vsphere: clusterOSImage: http://mirror.example.com/images/rhcos-43.81.201912131630.0-vmware.x86_64.ova?sha256=ffebbd68e8a1f2a245ca19522c16c86f67f9ac8e4e0c1f0a812b068b16f7265dplatform: vsphere: clusterOSImage: http://mirror.example.com/images/rhcos-43.81.201912131630.0-vmware.x86_64.ova?sha256=ffebbd68e8a1f2a245ca19522c16c86f67f9ac8e4e0c1f0a812b068b16f7265dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
install-config.yamlfile to give the additional information that is required for an installation in a restricted network.Update the
pullSecretvalue to contain the authentication information for your registry:pullSecret: '{"auths":{"<mirror_host_name>:5000": {"auth": "<credentials>","email": "you@example.com"}}}'pullSecret: '{"auths":{"<mirror_host_name>:5000": {"auth": "<credentials>","email": "you@example.com"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For
<mirror_host_name>, specify the registry domain name that you specified in the certificate for your mirror registry, and for<credentials>, specify the base64-encoded user name and password for your mirror registry.Add the
additionalTrustBundleparameter and value.additionalTrustBundle: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ -----END CERTIFICATE-----
additionalTrustBundle: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ -----END CERTIFICATE-----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value must be the contents of the certificate file that you used for your mirror registry. The certificate file can be an existing, trusted certificate authority, or the self-signed certificate that you generated for the mirror registry.
Add the image content resources, which resemble the following YAML excerpt:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For these values, use the
imageContentSourcesthat you recorded during mirror registry creation.Optional: Set the publishing strategy to
Internal:publish: Internal
publish: InternalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By setting this option, you create an internal Ingress Controller and a private load balancer.
Make any other modifications to the
install-config.yamlfile that you require.For more information about the parameters, see "Installation configuration parameters".
Back up the
install-config.yamlfile so that you can use it to install multiple clusters.ImportantThe
install-config.yamlfile is consumed during the installation process. If you want to reuse the file, you must back it up now.
2.6.6.1. Sample install-config.yaml file for an installer-provisioned VMware vSphere cluster
You can customize the install-config.yaml file to specify more details about your OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s platform or modify the values of the required parameters.
- 1
- The base domain of the cluster. All DNS records must be sub-domains of this base and include the cluster name.
- 2 3
- The
controlPlanesection is a single mapping, but thecomputesection is a sequence of mappings. To meet the requirements of the different data structures, the first line of thecomputesection must begin with a hyphen,-, and the first line of thecontrolPlanesection must not. Only one control plane pool is used. - 4
- The cluster name that you specified in your DNS records.
- 5
- Optional: Provides additional configuration for the machine pool parameters for the compute and control plane machines.Important
The VIPs,
apiVIPandingressVIP, must come from the samenetworking.machineNetworksegment. ForapiVIPand foringressVIP, if thenetworking.machineNetworkis10.0.0.0/16then API VIPs and Ingress VIPs must be in one of the10.0.0.0/16machine networks. - 6
- Establishes the relationships between a region and zone. You define a failure domain by using vCenter objects, such as a
datastoreobject. A failure domain defines the vCenter location for OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes. - 7
- The path to the vSphere datastore that holds virtual machine files, templates, and ISO images.Important
You can specify the path of any datastore that exists in a datastore cluster. By default, Storage vMotion is automatically enabled for a datastore cluster. Red Hat does not support Storage vMotion, so you must disable Storage vMotion to avoid data loss issues for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you must specify VMs across multiple datastores, use a
datastoreobject to specify a failure domain in your cluster’sinstall-config.yamlconfiguration file. For more information, see "VMware vSphere region and zone enablement". - 8
- Optional: Provides an existing resource pool for machine creation. If you do not specify a value, the installation program uses the root resource pool of the vSphere cluster.
- 9
- Optional: Each VM created by OpenShift Container Platform is assigned a unique tag that is specific to the cluster. The assigned tag enables the installation program to identify and remove the associated VMs when a cluster is decommissioned. You can list up to ten additional tag IDs to be attached to the VMs provisioned by the installation program.
- 10
- The ID of the tag to be associated by the installation program. For example,
urn:vmomi:InventoryServiceTag:208e713c-cae3-4b7f-918e-4051ca7d1f97:GLOBAL. For more information about determining the tag ID, see the vSphere Tags and Attributes documentation. - 11
- The vSphere disk provisioning method.
- 12
- The location of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) image that is accessible from the bastion server.
- 13
- For
<local_registry>, specify the registry domain name, and optionally the port, that your mirror registry uses to serve content. For exampleregistry.example.comorregistry.example.com:5000. For<credentials>, specify the base64-encoded user name and password for your mirror registry. - 14
- Provide the contents of the certificate file that you used for your mirror registry.
- 15
- Provide the
imageContentSourcessection from the output of the command to mirror the repository.
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.12 and later, the apiVIP and ingressVIP configuration settings are deprecated. Instead, use a list format to enter values in the apiVIPs and ingressVIPs configuration settings.
2.6.6.2. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy during installation
To enable internet access in environments that deny direct connections, configure a cluster-wide proxy in the install-config.yaml file. This configuration ensures that the new OpenShift Container Platform cluster routes traffic through the specified HTTP or HTTPS proxy.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing
install-config.yamlfile. You have reviewed the sites that your cluster requires access to and determined whether any of them need to bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster egress traffic is proxied, including calls to hosting cloud provider APIs. You added sites to the
Proxyobject’sspec.noProxyfield to bypass the proxy if necessary.NoteThe
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is populated with the values of thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidr,networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, andnetworking.serviceNetwork[]fields from your installation configuration.For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint (169.254.169.254).
Procedure
Edit your
install-config.yamlfile and add the proxy settings. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
proxy.httpProxy-
Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. proxy.httpsProxy- Specifies a proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster.
proxy.noProxy-
Specifies a comma-separated list of destination domain names, IP addresses, or other network CIDRs to exclude from proxying. Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass the proxy for all destinations. You must include vCenter’s IP address and the IP range that you use for its machines. additionalTrustBundle-
If provided, the installation program generates a config map that is named
user-ca-bundlein theopenshift-confignamespace to hold the additional CA certificates. If you provideadditionalTrustBundleand at least one proxy setting, theProxyobject is configured to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleconfig map that merges the contents specified for thetrustedCAparameter with the RHCOS trust bundle. TheadditionalTrustBundlefield is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle. additionalTrustBundlePolicySpecifies the policy that determines the configuration of the
Proxyobject to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The allowed values areProxyonlyandAlways. UseProxyonlyto reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map only whenhttp/httpsproxy is configured. UseAlwaysto always reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map. The default value isProxyonly. Optional parameter.NoteThe installation program does not support the proxy
readinessEndpointsfield.NoteIf the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the
wait-forcommand of the installer. For example:+
./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Save the file and reference it when installing OpenShift Container Platform.
The installation program creates a cluster-wide proxy that is named
clusterthat uses the proxy settings in the providedinstall-config.yamlfile. If no proxy settings are provided, aclusterProxyobject is still created, but it will have a nilspec.NoteOnly the
Proxyobject namedclusteris supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
2.6.6.3. Configuring regions and zones for a VMware vCenter
You can modify the default installation configuration file, so that you can deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to multiple vSphere data centers that run in a single VMware vCenter.
The default install-config.yaml file configuration from the previous release of OpenShift Container Platform is deprecated. You can continue to use the deprecated default configuration, but the openshift-installer will prompt you with a warning message that indicates the use of deprecated fields in the configuration file.
The example uses the govc command. The govc command is an open source command available from VMware; it is not available from Red Hat. The Red Hat support team does not maintain the govc command. Instructions for downloading and installing govc are found on the VMware documentation website
Prerequisites
You have an existing
install-config.yamlinstallation configuration file.ImportantYou must specify at least one failure domain for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, so that you can provision data center objects for your VMware vCenter server. Consider specifying multiple failure domains if you need to provision virtual machine nodes in different data centers, clusters, datastores, and other components. To enable regions and zones, you must define multiple failure domains for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
Enter the following
govccommand-line tool commands to create theopenshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories:ImportantIf you specify different names for the
openshift-regionandopenshift-zonevCenter tag categories, the installation of the OpenShift Container Platform cluster fails.govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-region
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift region" openshift-regionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zone
$ govc tags.category.create -d "OpenShift zone" openshift-zoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a region tag for each region vSphere data center where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command in your terminal:
govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a zone tag for each vSphere cluster where you want to deploy your cluster, enter the following command:
govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>
$ govc tags.create -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach region tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>
$ govc tags.attach -c <region_tag_category> <region_tag_1> /<data_center_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach the zone tags to each vCenter data center object by entering the following command:
govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1
$ govc tags.attach -c <zone_tag_category> <zone_tag_1> /<data_center_1>/host/vcs-mdcnc-workload-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment according to your chosen installation requirements.
Sample
install-config.yamlfile with multiple data centers defined in a vSphere centerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.6.7. Services for a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , configure services for a user-managed load balancer.
Configuring a user-managed load balancer depends on your vendor’s load balancer.
The information and examples in this section are for guideline purposes only. Consult the vendor documentation for more specific information about the vendor’s load balancer.
Red Hat supports the following services for a user-managed load balancer:
- Ingress Controller
- OpenShift API
- OpenShift MachineConfig API
You can choose whether you want to configure one or all of these services for a user-managed load balancer. Configuring only the Ingress Controller service is a common configuration option. To better understand each service, view the following diagrams:
Figure 2.7. Example network workflow that shows an Ingress Controller operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

Figure 2.8. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

Figure 2.9. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift MachineConfig API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment

The following configuration options are supported for user-managed load balancers:
- Use a node selector to map the Ingress Controller to a specific set of nodes. You must assign a static IP address to each node in this set, or configure each node to receive the same IP address from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Infrastructure nodes commonly receive this type of configuration.
Target all IP addresses on a subnet. This configuration can reduce maintenance overhead, because you can create and destroy nodes within those networks without reconfiguring the load balancer targets. If you deploy your ingress pods by using a machine set on a smaller network, such as a
/27or/28, you can simplify your load balancer targets.TipYou can list all IP addresses that exist in a network by checking the machine config pool’s resources.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, consider the following information:
- For a front-end IP address, you can use the same IP address for the front-end IP address, the Ingress Controller’s load balancer, and API load balancer. Check the vendor’s documentation for this capability.
For a back-end IP address, ensure that an IP address for an OpenShift Container Platform control plane node does not change during the lifetime of the user-managed load balancer. You can achieve this by completing one of the following actions:
- Assign a static IP address to each control plane node.
- Configure each node to receive the same IP address from the DHCP every time the node requests a DHCP lease. Depending on the vendor, the DHCP lease might be in the form of an IP reservation or a static DHCP assignment.
- Manually define each node that runs the Ingress Controller in the user-managed load balancer for the Ingress Controller back-end service. For example, if the Ingress Controller moves to an undefined node, a connection outage can occur.
2.6.7.1. Configuring a user-managed load balancer
To integrate your infrastructure with existing network standards or gain more control over traffic management in OpenShift Container Platform , use a user-managed load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
Before you configure a user-managed load balancer, ensure that you read the "Services for a user-managed load balancer" section.
Read the following prerequisites that apply to the service that you want to configure for your user-managed load balancer.
MetalLB, which runs on a cluster, functions as a user-managed load balancer.
Prerequisites
The following list details OpenShift API prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
TCP ports 6443 and 22623 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer. Check the following items:
- Port 6443 provides access to the OpenShift API service.
- Port 22623 can provide ignition startup configurations to nodes.
- The front-end IP address and port 6443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address and port 22623 are reachable only by OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform control plane nodes on port 6443 and 22623.
The following list details Ingress Controller prerequisites:
- You defined a front-end IP address.
- TCP port 443 and port 80 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable by all nodes that operate in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform nodes that run the Ingress Controller on ports 80, 443, and 1936.
The following list details prerequisites for health check URL specifications:
You can configure most load balancers by setting health check URLs that determine if a service is available or unavailable. OpenShift Container Platform provides these health checks for the OpenShift API, Machine Configuration API, and Ingress Controller backend services.
The following example shows a Kubernetes API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Machine Config API health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10The following example shows a Ingress Controller health check specification for a backend service:
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 5 Interval: 10
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 5
Interval: 10Procedure
Configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller, so that you can enable access to the cluster from your load balancer on ports 6443, 22623, 443, and 80. Depending on your needs, you can specify the IP address of a single subnet or IP addresses from multiple subnets in your HAProxy configuration.
Example HAProxy configuration with one listed subnet
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example HAProxy configuration with multiple listed subnets
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and its resources are operational:Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Kubernetes API server resource, by running the following command and observing the response:
curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Machine config server resource, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>
$ curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cache
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>
$ curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure the DNS records for your cluster to target the front-end IP addresses of the user-managed load balancer. You must update records to your DNS server for the cluster API and applications over the load balancer. The following examples shows modified DNS records:
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantDNS propagation might take some time for each DNS record to become available. Ensure that each DNS record propagates before validating each record.
For your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use the user-managed load balancer, you must specify the following configuration in your cluster’s
install-config.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
loadBalancer.type-
Set
UserManagedfor thetypeparameter to specify a user-managed load balancer for your cluster. The parameter defaults toOpenShiftManagedDefault, which denotes the default internal load balancer. For services defined in anopenshift-kni-infranamespace, a user-managed load balancer can deploy thecorednsservice to pods in your cluster but ignoreskeepalivedandhaproxyservices. loadBalancer.<api_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the Kubernetes API can communicate with the user-managed load balancer. Mandatory parameter.
loadBalancer.<ingress_ip>- Specifies a user-managed load balancer. Specify the user-managed load balancer’s public IP address, so that the user-managed load balancer can manage ingress traffic for your cluster. Mandatory parameter.
Verification
Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the user-managed load balancer and DNS record configuration are operational:Verify that you can access the cluster API, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access the cluster machine configuration, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.6.8. Deploying the cluster
You can install OpenShift Container Platform on a compatible cloud platform.
You can run the create cluster command of the installation program only once, during initial installation.
Prerequisites
- You have the OpenShift Container Platform installation program and the pull secret for your cluster.
- You have verified that the cloud provider account on your host has the correct permissions to deploy the cluster. An account with incorrect permissions causes the installation process to fail with an error message that displays the missing permissions.
Optional: Before you create the cluster, configure an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
ImportantYou do not need to specify API and Ingress static addresses for your installation program. If you choose this configuration, you must take additional actions to define network targets that accept an IP address from each referenced vSphere subnet. See the section "Configuring a user-managed load balancer".
Procedure
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and initialize the cluster deployment:
./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \ --log-level=info$ ./openshift-install create cluster --dir <installation_directory> \1 --log-level=info2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
When the cluster deployment completes successfully:
-
The terminal displays directions for accessing your cluster, including a link to the web console and credentials for the
kubeadminuser. -
Credential information also outputs to
<installation_directory>/.openshift_install.log.
Do not delete the installation program or the files that the installation program creates. Both are required to delete the cluster.
Example output
-
The Ignition config files that the installation program generates contain certificates that expire after 24 hours, which are then renewed at that time. If the cluster is shut down before renewing the certificates and the cluster is later restarted after the 24 hours have elapsed, the cluster automatically recovers the expired certificates. The exception is that you must manually approve the pending
node-bootstrappercertificate signing requests (CSRs) to recover kubelet certificates. See the documentation for Recovering from expired control plane certificates for more information. - It is recommended that you use Ignition config files within 12 hours after they are generated because the 24-hour certificate rotates from 16 to 22 hours after the cluster is installed. By using the Ignition config files within 12 hours, you can avoid installation failure if the certificate update runs during installation.
2.6.9. Logging in to the cluster by using the CLI
To log in to your cluster as the default system user, export the kubeconfig file. This configuration enables the CLI to authenticate and connect to the specific API server created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
The kubeconfig file is specific to a cluster and is created during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Export the
kubeadmincredentials:export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<installation_directory>- Specifies the path to the directory that stores the installation files.
Verify you can run
occommands successfully using the exported configuration:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.6.10. Disabling the default OperatorHub catalog sources
Operator catalogs that source content provided by Red Hat and community projects are configured for OperatorHub by default during an OpenShift Container Platform installation. In a restricted network environment, you must disable the default catalogs as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Disable the sources for the default catalogs by adding
disableAllDefaultSources: trueto theOperatorHubobject:oc patch OperatorHub cluster --type json \ -p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/disableAllDefaultSources", "value": true}]'$ oc patch OperatorHub cluster --type json \ -p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/disableAllDefaultSources", "value": true}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Alternatively, you can use the web console to manage catalog sources. From the Administration
2.6.11. Creating registry storage
After you install the cluster, you must create storage for the Registry Operator.
2.6.11.1. Image registry removed during installation
On platforms that do not provide shareable object storage, the OpenShift Image Registry Operator bootstraps itself as Removed. This allows openshift-installer to complete installations on these platform types.
After installation, you must edit the Image Registry Operator configuration to switch the managementState from Removed to Managed. When this has completed, you must configure storage.
2.6.11.2. Image registry storage configuration
The Image Registry Operator is not initially available for platforms that do not provide default storage. After installation, you must configure your registry to use storage so that the Registry Operator is made available.
Configure a persistent volume, which is required for production clusters. Where applicable, you can configure an empty directory as the storage location for non-production clusters.
You can also allow the image registry to use block storage types by using the Recreate rollout strategy during upgrades.
2.6.11.2.1. Configuring registry storage for VMware vSphere
As a cluster administrator, following installation you must configure your registry to use storage.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions.
- A cluster on VMware vSphere.
Persistent storage provisioned for your cluster, such as Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation.
ImportantOpenShift Container Platform supports
ReadWriteOnceaccess for image registry storage when you have only one replica.ReadWriteOnceaccess also requires that the registry uses theRecreaterollout strategy. To deploy an image registry that supports high availability with two or more replicas,ReadWriteManyaccess is required.- Must have "100Gi" capacity.
Testing shows issues with using the NFS server on RHEL as storage backend for core services. This includes the OpenShift Container Registry and Quay, Prometheus for monitoring storage, and Elasticsearch for logging storage. Therefore, using RHEL NFS to back PVs used by core services is not recommended.
Other NFS implementations on the marketplace might not have these issues. Contact the individual NFS implementation vendor for more information on any testing that was possibly completed against these OpenShift Container Platform core components.
Procedure
To configure your registry to use storage, change the
spec.storage.pvcin theconfigs.imageregistry/clusterresource.NoteWhen you use shared storage, review your security settings to prevent outside access.
Verify that you do not have a registry pod:
oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=default
$ oc get pod -n openshift-image-registry -l docker-registry=defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespace
No resourses found in openshift-image-registry namespaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do have a registry pod in your output, you do not need to continue with this procedure.
Check the registry configuration:
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io
$ oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
storage: pvc: claim:storage: pvc: claim:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Leave the
claimfield blank to allow the automatic creation of animage-registry-storagepersistent volume claim (PVC). The PVC is generated based on the default storage class. However, be aware that the default storage class might provide ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volumes, such as a RADOS Block Device (RBD), which can cause issues when you replicate to more than one replica.Check the
clusteroperatorstatus:oc get clusteroperator image-registry
$ oc get clusteroperator image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE image-registry 4.7 True False False 6h50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.6.12. Telemetry access for OpenShift Container Platform
To provide metrics about cluster health and the success of updates, the Telemetry service requires internet access. When connected, this service runs automatically by default and registers your cluster to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After you confirm that your OpenShift Cluster Manager inventory is correct, either maintained automatically by Telemetry or manually by using OpenShift Cluster Manager,use subscription watch to track your OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions at the account or multi-cluster level. For more information about subscription watch, see "Data Gathered and Used by Red Hat’s subscription services" in the Additional resources section.
2.6.13. Next steps
- Customize your cluster.
- If necessary, you can Remote health reporting.
- If necessary, see Registering your disconnected cluster.
- Set up your registry and configure registry storage.