Chapter 37. Users and Groups
The control of users and groups is a core element of Red Hat Enterprise Linux system administration.
Users can be either people (meaning accounts tied to physical users) or accounts which exist for specific applications to use.
Groups are logical expressions of organization, tying users together for a common purpose. Users within a group can read, write, or execute files owned by that group.
Each user and group has a unique numerical identification number called a userid (UID) and a groupid (GID), respectively.
A user who creates a file is also the owner and group owner of that file. The file is assigned separate read, write, and execute permissions for the owner, the group, and everyone else. The file owner can be changed only by the root user, and access permissions can be changed by both the root user and file owner.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux also supports access control lists (ACLs) for files and directories which allow permissions for specific users outside of the owner to be set. For more information about ACLs, refer to Chapter 10, Access Control Lists.
37.1. User and Group Configuration
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The User Manager allows you to view, modify, add, and delete local users and groups.
To use the User Manager, you must be running the X Window System, have root privileges, and have the
system-config-users RPM package installed. To start the User Manager from the desktop, go to System (on the panel) > > . You can also type the command system-config-users at a shell prompt (for example, in an XTerm or a GNOME terminal).
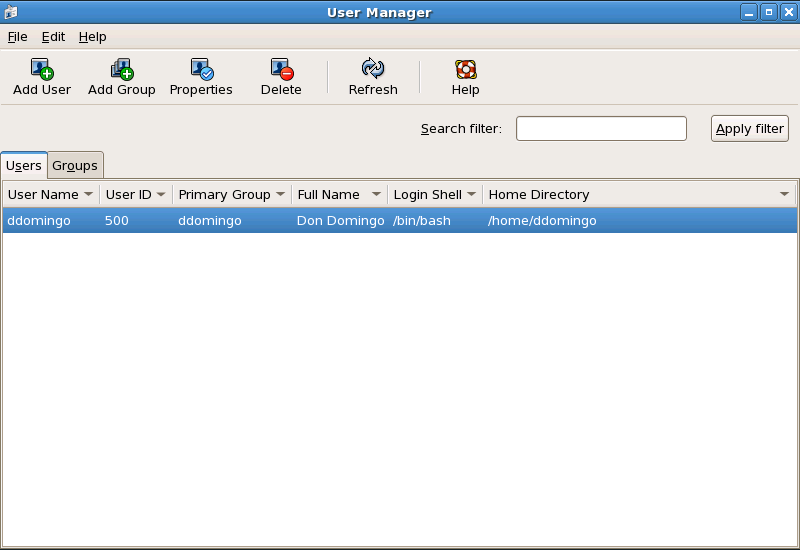
Figure 37.1. User Manager
To view a list of local users on the system, click the Users tab. To view a list of local groups on the system, click the Groups tab.
To find a specific user or group, type the first few letters of the name in the Search filter field. Press Enter or click the button. The filtered list is displayed.
To sort the users or groups, click on the column name. The users or groups are sorted according to the value of that column.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux reserves user IDs below 500 for system users. By default, User Manager does not display system users. To view all users, including the system users, go to > and uncheck from the dialog box.
37.1.1. Adding a New User
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To add a new user, click the button. A window as shown in Figure 37.2, “New User” appears. Type the username and full name for the new user in the appropriate fields. Type the user's password in the Password and Confirm Password fields. The password must be at least six characters.
Note
It is advisable to use a much longer password, as this makes it more difficult for an intruder to guess it and access the account without permission. It is also recommended that the password not be based on a dictionary term; use a combination of letters, numbers and special characters.
Select a login shell. If you are not sure which shell to select, accept the default value of
/bin/bash. The default home directory is /home/<username>/. You can change the home directory that is created for the user, or you can choose not to create the home directory by unselecting Create home directory.
If you select to create the home directory, default configuration files are copied from the
/etc/skel/ directory into the new home directory.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux uses a user private group (UPG) scheme. The UPG scheme does not add or change anything in the standard UNIX way of handling groups; it offers a new convention. Whenever you create a new user, by default, a unique group with the same name as the user is created. If you do not want to create this group, unselect Create a private group for the user.
To specify a user ID for the user, select . If the option is not selected, the next available user ID above 500 is assigned to the new user. Because Red Hat Enterprise Linux reserves user IDs below 500 for system users, it is not advisable to manually assign user IDs 1-499.
Click to create the user.
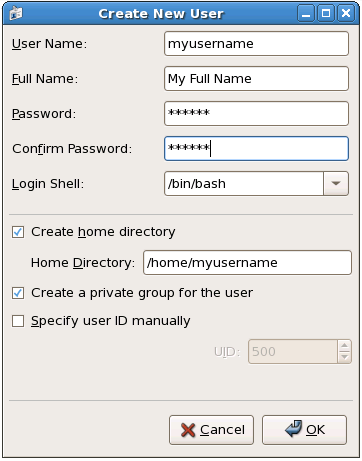
Figure 37.2. New User
To configure more advanced user properties, such as password expiration, modify the user's properties after adding the user. Refer to Section 37.1.2, “Modifying User Properties” for more information.
37.1.2. Modifying User Properties
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To view the properties of an existing user, click on the Users tab, select the user from the user list, and click from the menu (or choose > from the pulldown menu). A window similar to Figure 37.3, “User Properties” appears.
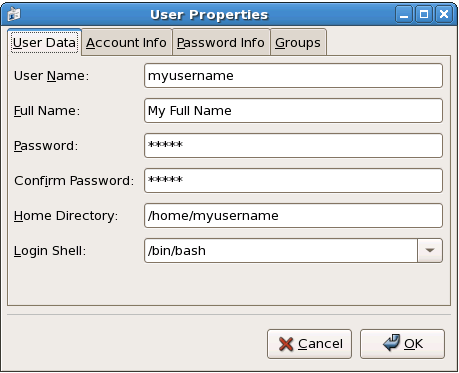
Figure 37.3. User Properties
The User Properties window is divided into multiple tabbed pages:
- User Data — Shows the basic user information configured when you added the user. Use this tab to change the user's full name, password, home directory, or login shell.
- Password Info — Displays the date that the user's password last changed. To force the user to change passwords after a certain number of days, select Enable password expiration and enter a desired value in the Days before change required: field. The number of days before the user's password expires, the number of days before the user is warned to change passwords, and days before the account becomes inactive can also be changed.
37.1.3. Adding a New Group
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To add a new user group, click the button. A window similar to Figure 37.4, “New Group” appears. Type the name of the new group to create. To specify a group ID for the new group, select and select the GID. Note that Red Hat Enterprise Linux also reserves group IDs lower than 500 for system groups.
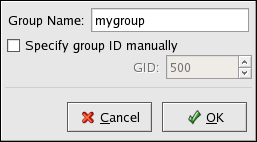
Figure 37.4. New Group
Click to create the group. The new group appears in the group list.
37.1.4. Modifying Group Properties
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To view the properties of an existing group, select the group from the group list and click from the menu (or choose > from the pulldown menu). A window similar to Figure 37.5, “Group Properties” appears.
Figure 37.5. Group Properties
The Group Users tab displays which users are members of the group. Use this tab to add or remove users from the group. Click to save your changes.