25.8.5. Generating a Key
cd command to change to the /etc/pki/tls/ directory. Remove the fake key and certificate that were generated during the installation with the following commands:
rm private/server.key rm certs/server.crt
rm private/server.key
rm certs/server.crtcrypto-utils package contains the genkey utility which you can use to generate keys as the name implies. To create your own private key, please ensure the crypto-utils package is installed. You can view more options by typing man genkey in your terminal. Assuming you wish to generate keys for www.example.com using the genkey utility, type in the following command in your terminal:
genkey www.example.com
genkey www.example.commake based process is no longer shipped with RHEL 5. This will start the genkey graphical user interface. The figure below illustrates the first screen. To navigate, use the keyboard arrow and tab keys. This windows indicates where your key will be stored and prompts you to proceed or cancel the operation. To proceed to the next step, select Next and press the Return (Enter) key.
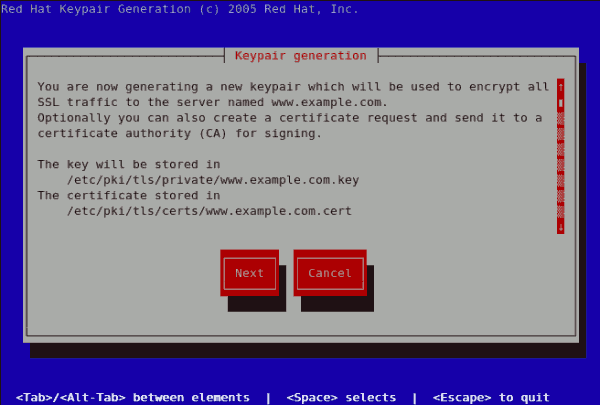
Figure 25.11. Keypair generation
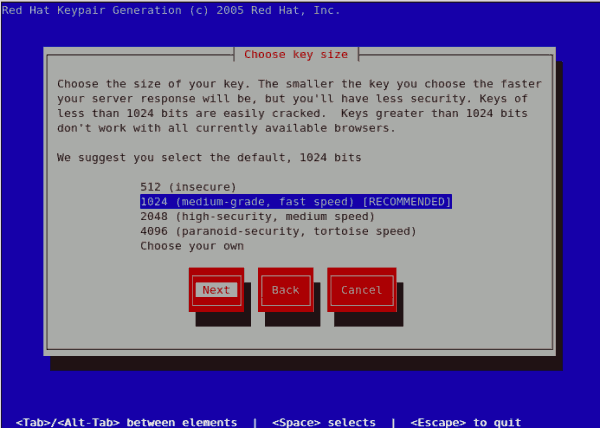
Figure 25.12. Choose key size
Figure 25.13. Generating random bits
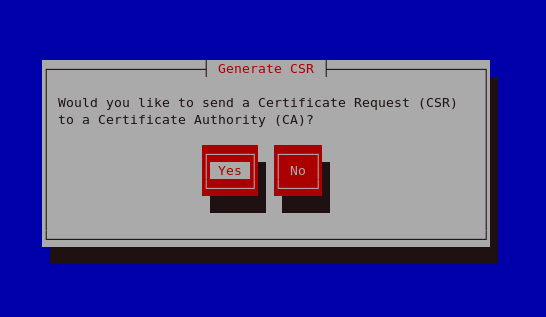
Figure 25.14. Generate CSR
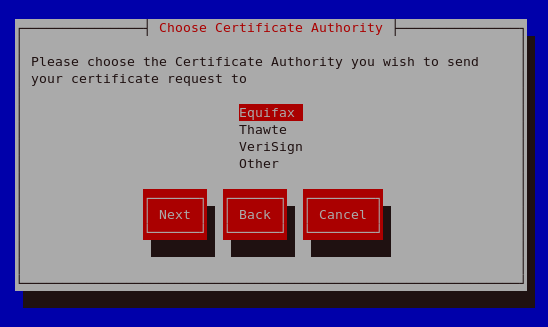
Figure 25.15. Choose Certificate Authority (CA)
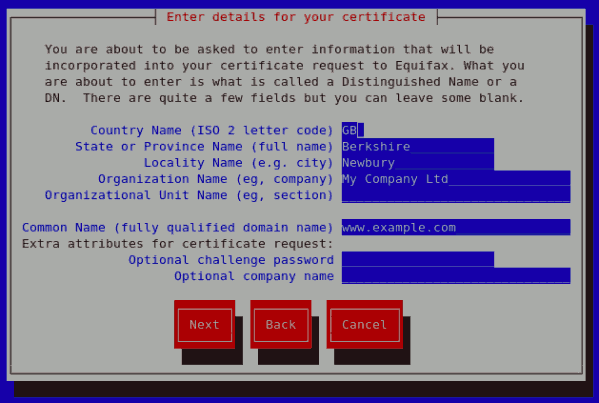
Figure 25.16. Enter details for your certificate
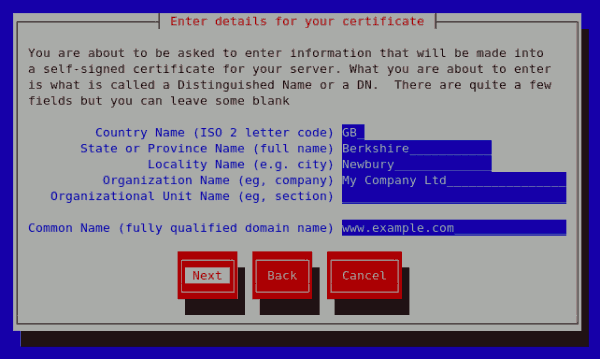
Figure 25.17. Generating a self signed certificate for your server
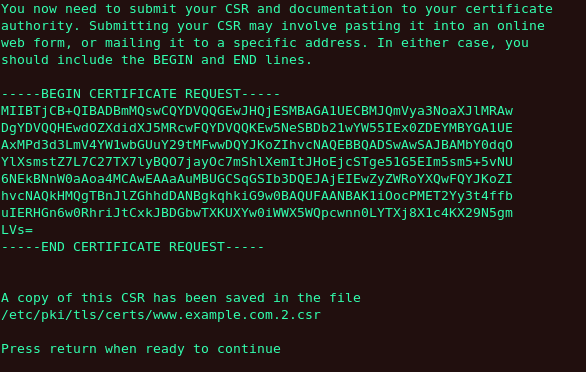
Figure 25.18. Begin certificate request

Figure 25.19. Protecting your private key
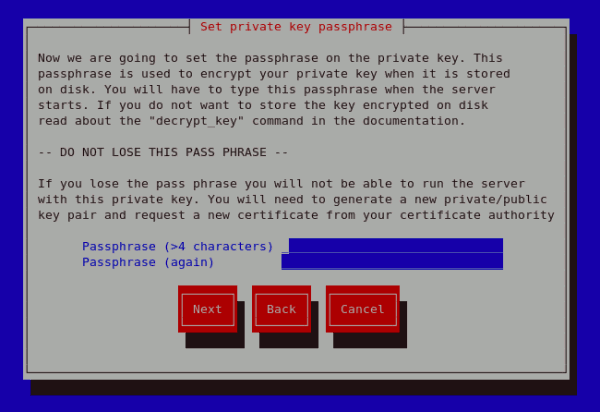
Figure 25.20. Set passphrase
genkey www.example.com on a server that already has an existing key pair for the particular hostname, an error message will be displayed as illustrated below. You need to delete your existing key file as indicated to generate a new key pair.
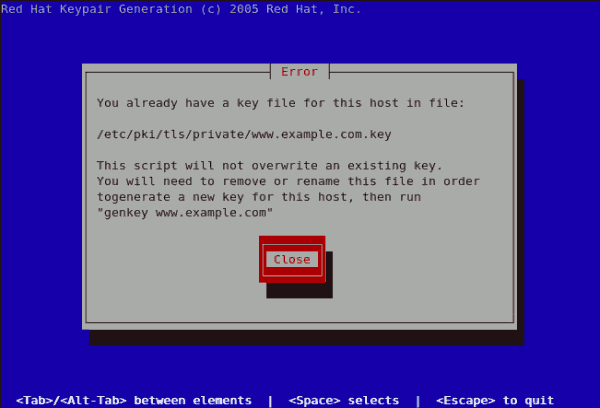
Figure 25.21. genkey error