5.22. Operator Lifecycle Manager Operators
Purpose
Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) helps users install, update, and manage the lifecycle of Kubernetes native applications (Operators) and their associated services running across their OpenShift Container Platform clusters. It is part of the Operator Framework, an open source toolkit designed to manage Operators in an effective, automated, and scalable way.
图 5.1. Operator Lifecycle Manager workflow
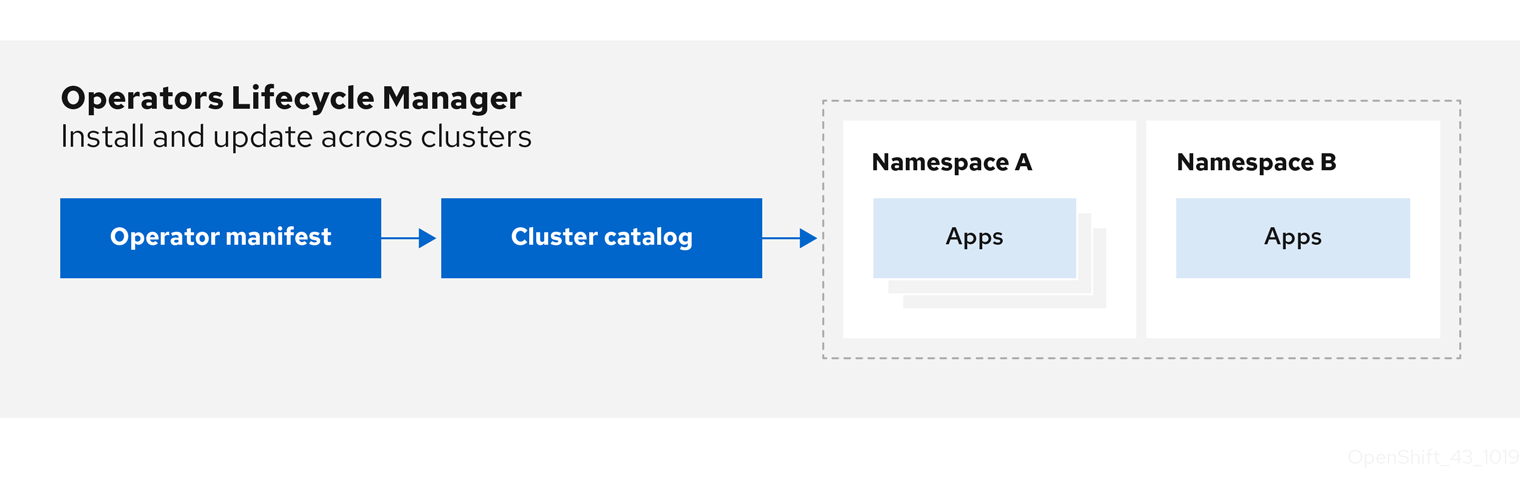
OLM runs by default in OpenShift Container Platform 4.5, which aids cluster administrators in installing, upgrading, and granting access to Operators running on their cluster. The OpenShift Container Platform web console provides management screens for cluster administrators to install Operators, as well as grant specific projects access to use the catalog of Operators available on the cluster.
For developers, a self-service experience allows provisioning and configuring instances of databases, monitoring, and big data services without having to be subject matter experts, because the Operator has that knowledge baked into it.
CRDs
Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) is composed of two Operators: the OLM Operator and the Catalog Operator.
Each of these Operators is responsible for managing the custom resource definitions (CRDs) that are the basis for the OLM framework:
| Resource | Short name | Owner | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| OLM | Application metadata: name, version, icon, required resources, installation, and so on. |
|
|
| Catalog | Calculated list of resources to be created to automatically install or upgrade a CSV. |
|
|
| Catalog | A repository of CSVs, CRDs, and packages that define an application. |
|
|
| Catalog | Used to keep CSVs up to date by tracking a channel in a package. |
|
|
| OLM |
Configures all Operators deployed in the same namespace as the |
Each of these Operators is also responsible for creating the following resources:
| Resource | Owner |
|---|---|
|
| OLM |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Catalog |
|
|
OLM Operator
The OLM Operator is responsible for deploying applications defined by CSV resources after the required resources specified in the CSV are present in the cluster.
The OLM Operator is not concerned with the creation of the required resources; you can choose to manually create these resources using the CLI or using the Catalog Operator. This separation of concern allows users incremental buy-in in terms of how much of the OLM framework they choose to leverage for their application.
The OLM Operator uses the following workflow:
- Watch for cluster service versions (CSVs) in a namespace and check that requirements are met.
If requirements are met, run the install strategy for the CSV.
注意A CSV must be an active member of an Operator group for the install strategy to run.
Catalog Operator
The Catalog Operator is responsible for resolving and installing cluster service versions (CSVs) and the required resources they specify. It is also responsible for watching catalog sources for updates to packages in channels and upgrading them, automatically if desired, to the latest available versions.
To track a package in a channel, you can create a Subscription object configuring the desired package, channel, and the CatalogSource object you want to use for pulling updates. When updates are found, an appropriate InstallPlan object is written into the namespace on behalf of the user.
The Catalog Operator uses the following workflow:
- Connect to each catalog source in the cluster.
Watch for unresolved install plans created by a user, and if found:
- Find the CSV matching the name requested and add the CSV as a resolved resource.
- For each managed or required CRD, add the CRD as a resolved resource.
- For each required CRD, find the CSV that manages it.
- Watch for resolved install plans and create all of the discovered resources for it, if approved by a user or automatically.
- Watch for catalog sources and subscriptions and create install plans based on them.
Catalog Registry
The Catalog Registry stores CSVs and CRDs for creation in a cluster and stores metadata about packages and channels.
A package manifest is an entry in the Catalog Registry that associates a package identity with sets of CSVs. Within a package, channels point to a particular CSV. Because CSVs explicitly reference the CSV that they replace, a package manifest provides the Catalog Operator with all of the information that is required to update a CSV to the latest version in a channel, stepping through each intermediate version.
Additional resources
For more information, see the sections on understanding Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM).