11.3. Using the API server source
An API server source is an event source that can be used to connect an event sink, such as a Knative service, to the Kubernetes API server. An API server source watches for Kubernetes events and forwards them to the Knative Eventing broker.
11.3.1. Prerequisites
- You must have a current installation of OpenShift Serverless, including Knative Serving and Eventing, in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This can be installed by a cluster administrator.
- Event sources need a service to use as an event sink. The sink is the service or application that events are sent to from the event source.
- You must create or update a service account, role and role binding for the event source.
Some of the following procedures require you to create YAML files.
If you change the names of the YAML files from those used in the examples, you must ensure that you also update the corresponding CLI commands.
Procedure
Create a service account, role, and role binding for the event source by creating a file named
authentication.yamland copying the following sample code into it:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 注意If you want to re-use an existing service account with the appropriate permissions, you must modify the
authentication.yamlfor that service account.Create the service account, role binding, and cluster binding by entering the following command:
oc apply --filename authentication.yaml
$ oc apply --filename authentication.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
- Navigate to the Add page and select Event Source.
In the Event Sources page, select ApiServerSource in the Type section.
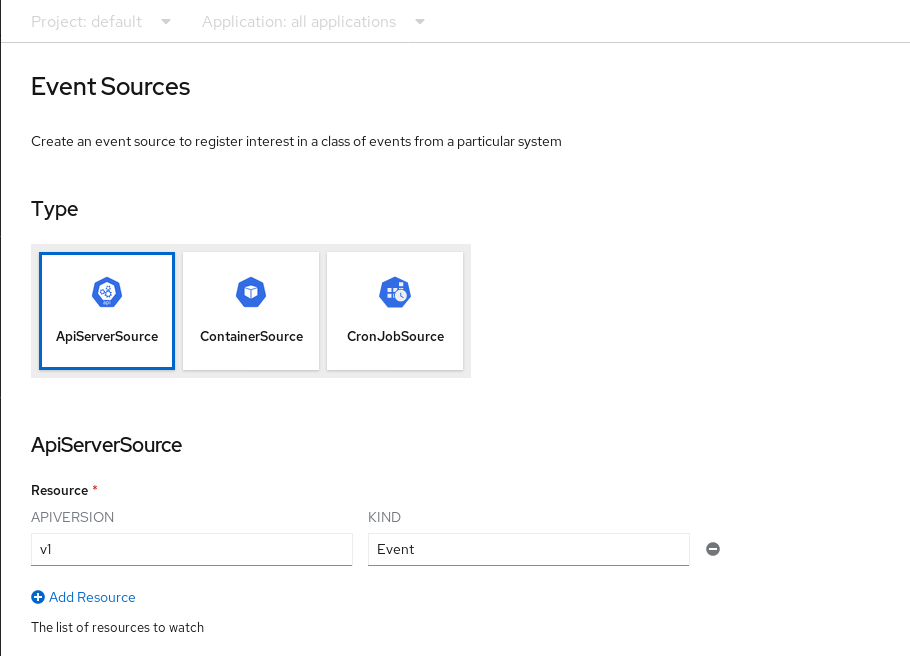
Configure the ApiServerSource settings:
-
Enter
v1as the APIVERSION, andEventas the KIND. Select the Service Account Name for the service account that you created.

-
Select the targeted Knative service from the dropdown menu in Sink
Knative Service.
-
Enter
- Click Create.
Verification
After you have created the ApiServerSource, you will see it connected to the service it is sinked to in the Topology view.
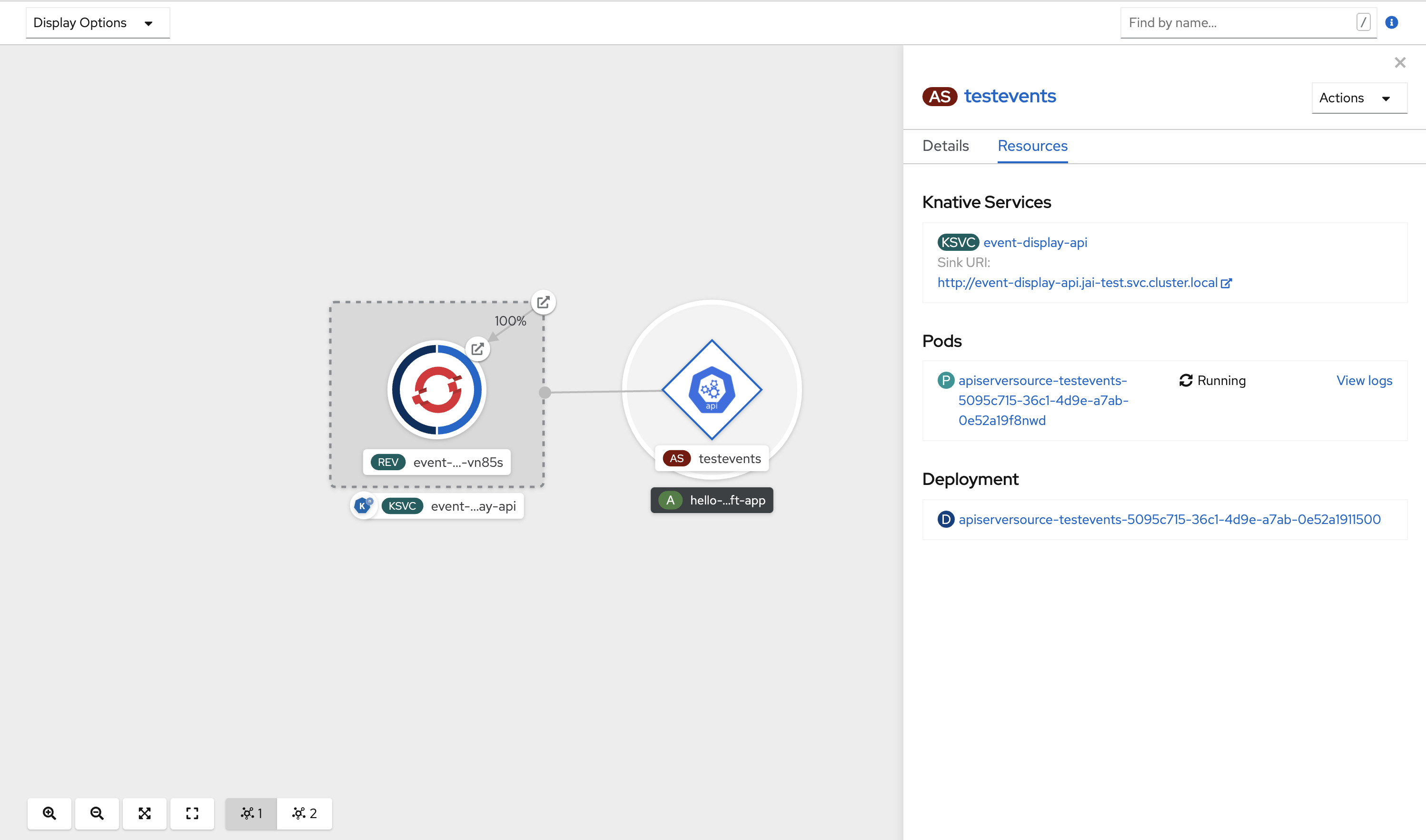
11.3.4. Deleting the ApiServerSource
Procedure
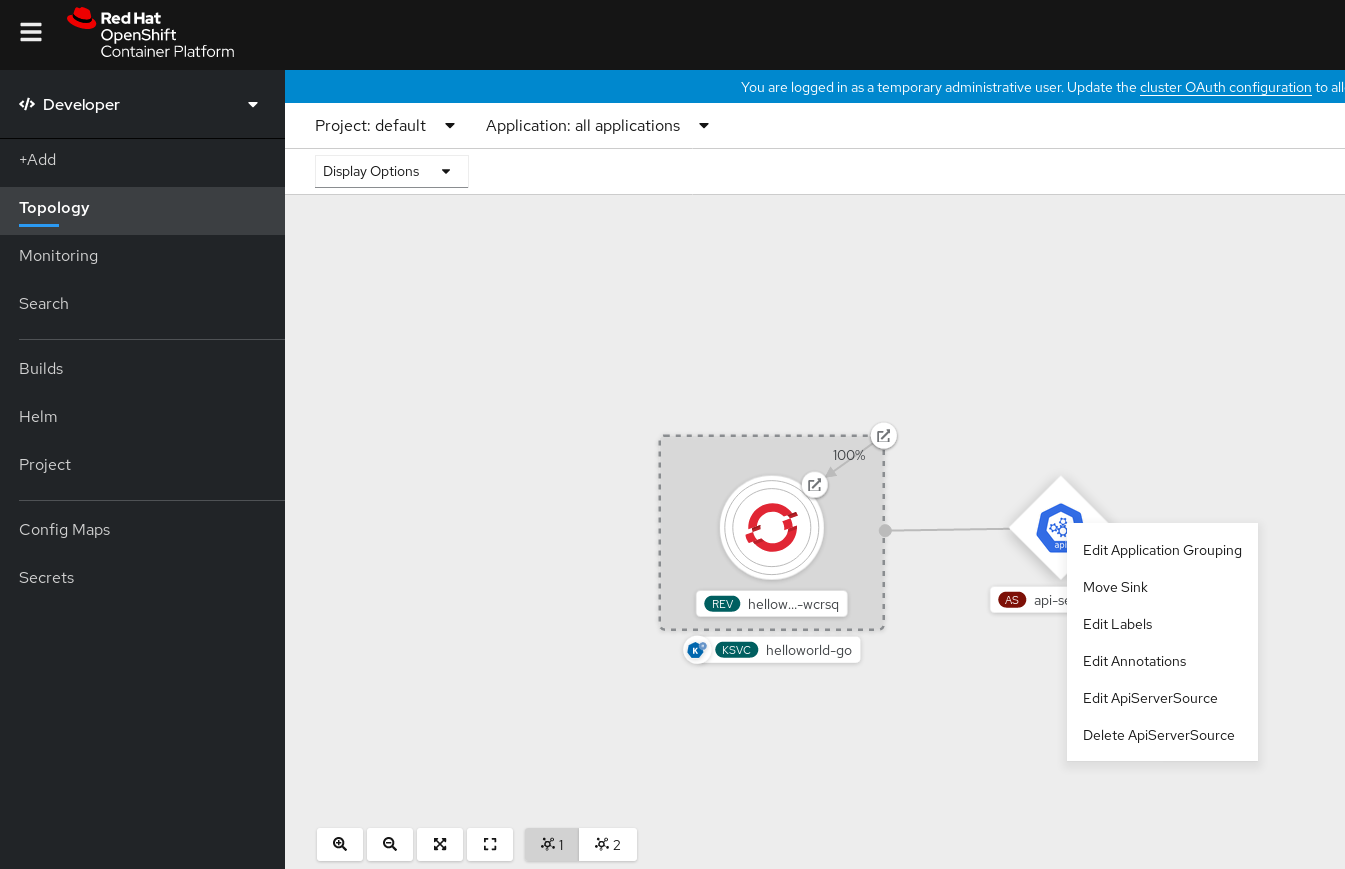
- Navigate to the Topology view.
Right-click the ApiServerSource and select Delete ApiServerSource.
11.3.5. Using the API server source with the Knative CLI
This section describes the steps required to create an ApiServerSource object using kn commands.
Prerequisites
- Knative Serving and Eventing are installed on your cluster.
-
You have created the
defaultbroker in the same namespace that the API server source will be installed in. -
You have the
knCLI installed.
Procedure
Create a service account, role, and role binding for the
ApiServerSourceobject.You can do this by creating a file named
authentication.yamland copying the following sample code into it:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 注意If you want to reuse an existing service account with the appropriate permissions, you must modify the
authentication.yamlfile for that service account.Create the service account, role binding, and cluster binding:
oc apply -f authentication.yaml
$ oc apply -f authentication.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an
ApiServerSourceobject that uses a broker as an event sink:kn source apiserver create <event_source_name> --sink broker:<broker_name> --resource "event:v1" --service-account <service_account_name> --mode Resource
$ kn source apiserver create <event_source_name> --sink broker:<broker_name> --resource "event:v1" --service-account <service_account_name> --mode ResourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a Knative service that dumps incoming messages to its log:
kn service create <service_name> --image quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-display:latest
$ kn service create <service_name> --image quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-display:latestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a trigger to filter events from the
defaultbroker to the service:kn trigger create <trigger_name> --sink ksvc:<service_name>
$ kn trigger create <trigger_name> --sink ksvc:<service_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create events by launching a pod in the default namespace:
oc create deployment hello-node --image=quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-display
$ oc create deployment hello-node --image=quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-displayCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the controller is mapped correctly by inspecting the output generated by the following command:
kn source apiserver describe testevents
$ kn source apiserver describe testeventsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can verify that the Kubernetes events were sent to Knative by looking at the message dumper function logs.
Get the pods:
oc get pods
$ oc get podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the message dumper function logs for the pods:
oc logs $(oc get pod -o name | grep event-display) -c user-container
$ oc logs $(oc get pod -o name | grep event-display) -c user-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This section describes the steps used to delete the ApiServerSource object, trigger, service, service account, cluster role, and cluster binding using the kn and oc commands.
Prerequisites
-
You must have the
knCLI installed.
Procedure
Delete the trigger:
kn trigger delete <trigger_name>
$ kn trigger delete <trigger_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the service:
kn service delete <service_name>
$ kn service delete <service_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the API server source:
kn source apiserver delete <source_name>
$ kn source apiserver delete <source_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Delete the service account, cluster role, and cluster binding:
oc delete -f authentication.yaml
$ oc delete -f authentication.yaml11.3.7. Creating an API server source using YAML files
This guide describes the steps required to create an ApiServerSource object using YAML files.
Prerequisites
- Knative Serving and Eventing are installed on your cluster.
-
You have created the
defaultbroker in the same namespace as the one defined in theApiServerSourceobject.
Procedure
To create a service account, role, and role binding for the API server source, create a file named
authentication.yamland copy the following sample code into it:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 注意If you want to re-use an existing service account with the appropriate permissions, you must modify the
authentication.yamlfor that service account.After you have created the
authentication.yamlfile, apply it:oc apply -f authentication.yaml
$ oc apply -f authentication.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create an
ApiServerSourceobject, create a file namedk8s-events.yamland copy the following sample code into it:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you have created the
k8s-events.yamlfile, apply it:oc apply -f k8s-events.yaml
$ oc apply -f k8s-events.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that the API server source is set up correctly, create a Knative service that dumps incoming messages to its log.
Copy the following sample YAML into a file named
service.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you have created the
service.yamlfile, apply it:oc apply -f service.yaml
$ oc apply -f service.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a trigger from the
defaultbroker that filters events to the service created in the previous step, create a file namedtrigger.yamland copy the following sample code into it:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you have created the
trigger.yamlfile, apply it:oc apply -f trigger.yaml
$ oc apply -f trigger.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create events, launch a pod in the
defaultnamespace:oc create deployment hello-node --image=quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-display
$ oc create deployment hello-node --image=quay.io/openshift-knative/knative-eventing-sources-event-displayCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that the controller is mapped correctly, enter the following command and inspect the output:
oc get apiserversource.sources.knative.dev testevents -o yaml
$ oc get apiserversource.sources.knative.dev testevents -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that the Kubernetes events were sent to Knative, you can look at the message dumper function logs.
Get the pods:
oc get pods
$ oc get podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the message dumper function logs for the pods:
oc logs $(oc get pod -o name | grep event-display) -c user-container
$ oc logs $(oc get pod -o name | grep event-display) -c user-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.3.8. Deleting the API server source
This section describes how to delete the ApiServerSource object, trigger, service, service account, cluster role, and cluster binding by deleting their YAML files.
Procedure
Delete the trigger:
oc delete -f trigger.yaml
$ oc delete -f trigger.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the service:
oc delete -f service.yaml
$ oc delete -f service.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the API server source:
oc delete -f k8s-events.yaml
$ oc delete -f k8s-events.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the service account, cluster role, and cluster binding:
oc delete -f authentication.yaml
$ oc delete -f authentication.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow