4.5. Using the Node Tuning Operator
Learn about the Node Tuning Operator and how you can use it to manage node-level tuning by orchestrating the tuned daemon.
The Node Tuning Operator helps you manage node-level tuning by orchestrating the Tuned daemon. The majority of high-performance applications require some level of kernel tuning. The Node Tuning Operator provides a unified management interface to users of node-level sysctls and more flexibility to add custom tuning specified by user needs.
The Operator manages the containerized Tuned daemon for OpenShift Container Platform as a Kubernetes daemon set. It ensures the custom tuning specification is passed to all containerized Tuned daemons running in the cluster in the format that the daemons understand. The daemons run on all nodes in the cluster, one per node.
Node-level settings applied by the containerized Tuned daemon are rolled back on an event that triggers a profile change or when the containerized Tuned daemon is terminated gracefully by receiving and handling a termination signal.
The Node Tuning Operator is part of a standard OpenShift Container Platform installation in version 4.1 and later.
4.5.1. Accessing an example Node Tuning Operator specification
Use this process to access an example Node Tuning Operator specification.
Procedure
Run:
$ oc get Tuned/default -o yaml -n openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator
The default CR is meant for delivering standard node-level tuning for the OpenShift Container Platform platform and it can only be modified to set the Operator Management state. Any other custom changes to the default CR will be overwritten by the Operator. For custom tuning, create your own Tuned CRs. Newly created CRs will be combined with the default CR and custom tuning applied to OpenShift Container Platform nodes based on node or pod labels and profile priorities.
While in certain situations the support for pod labels can be a convenient way of automatically delivering required tuning, this practice is discouraged and strongly advised against, especially in large-scale clusters. The default Tuned CR ships without pod label matching. If a custom profile is created with pod label matching, then the functionality will be enabled at that time. The pod label functionality might be deprecated in future versions of the Node Tuning Operator.
4.5.2. Custom tuning specification
The custom resource (CR) for the Operator has two major sections. The first section, profile:, is a list of Tuned profiles and their names. The second, recommend:, defines the profile selection logic.
Multiple custom tuning specifications can co-exist as multiple CRs in the Operator’s namespace. The existence of new CRs or the deletion of old CRs is detected by the Operator. All existing custom tuning specifications are merged and appropriate objects for the containerized Tuned daemons are updated.
Profile data
The profile: section lists Tuned profiles and their names.
profile:
- name: tuned_profile_1
data: |
# Tuned profile specification
[main]
summary=Description of tuned_profile_1 profile
[sysctl]
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
# ... other sysctl's or other Tuned daemon plug-ins supported by the containerized Tuned
# ...
- name: tuned_profile_n
data: |
# Tuned profile specification
[main]
summary=Description of tuned_profile_n profile
# tuned_profile_n profile settingsRecommended profiles
The profile: selection logic is defined by the recommend: section of the CR. The recommend: section is a list of items to recommend the profiles based on a selection criteria.
recommend: <recommend-item-1> # ... <recommend-item-n>
The individual items of the list:
- machineConfigLabels: 1 <mcLabels> 2 match: 3 <match> 4 priority: <priority> 5 profile: <tuned_profile_name> 6
- 1
- Optional.
- 2
- A dictionary of key/value
MachineConfiglabels. The keys must be unique. - 3
- If omitted, profile match is assumed unless a profile with a higher priority matches first or
machineConfigLabelsis set. - 4
- An optional list.
- 5
- Profile ordering priority. Lower numbers mean higher priority (
0is the highest priority). - 6
- A Tuned profile to apply on a match. For example
tuned_profile_1.
<match> is an optional list recursively defined as follows:
- label: <label_name> 1 value: <label_value> 2 type: <label_type> 3 <match> 4
If <match> is not omitted, all nested <match> sections must also evaluate to true. Otherwise, false is assumed and the profile with the respective <match> section will not be applied or recommended. Therefore, the nesting (child <match> sections) works as logical AND operator. Conversely, if any item of the <match> list matches, the entire <match> list evaluates to true. Therefore, the list acts as logical OR operator.
If machineConfigLabels is defined, machine config pool based matching is turned on for the given recommend: list item. <mcLabels> specifies the labels for a machine config. The machine config is created automatically to apply host settings, such as kernel boot parameters, for the profile <tuned_profile_name>. This involves finding all machine config pools with machine config selector matching <mcLabels> and setting the profile <tuned_profile_name> on all nodes that match the machine config pools' node selectors.
The list items match and machineConfigLabels are connected by the logical OR operator. The match item is evaluated first in a short-circuit manner. Therefore, if it evaluates to true, the machineConfigLabels item is not considered.
When using machine config pool based matching, it is advised to group nodes with the same hardware configuration into the same machine config pool. Not following this practice might result in Tuned operands calculating conflicting kernel parameters for two or more nodes sharing the same machine config pool.
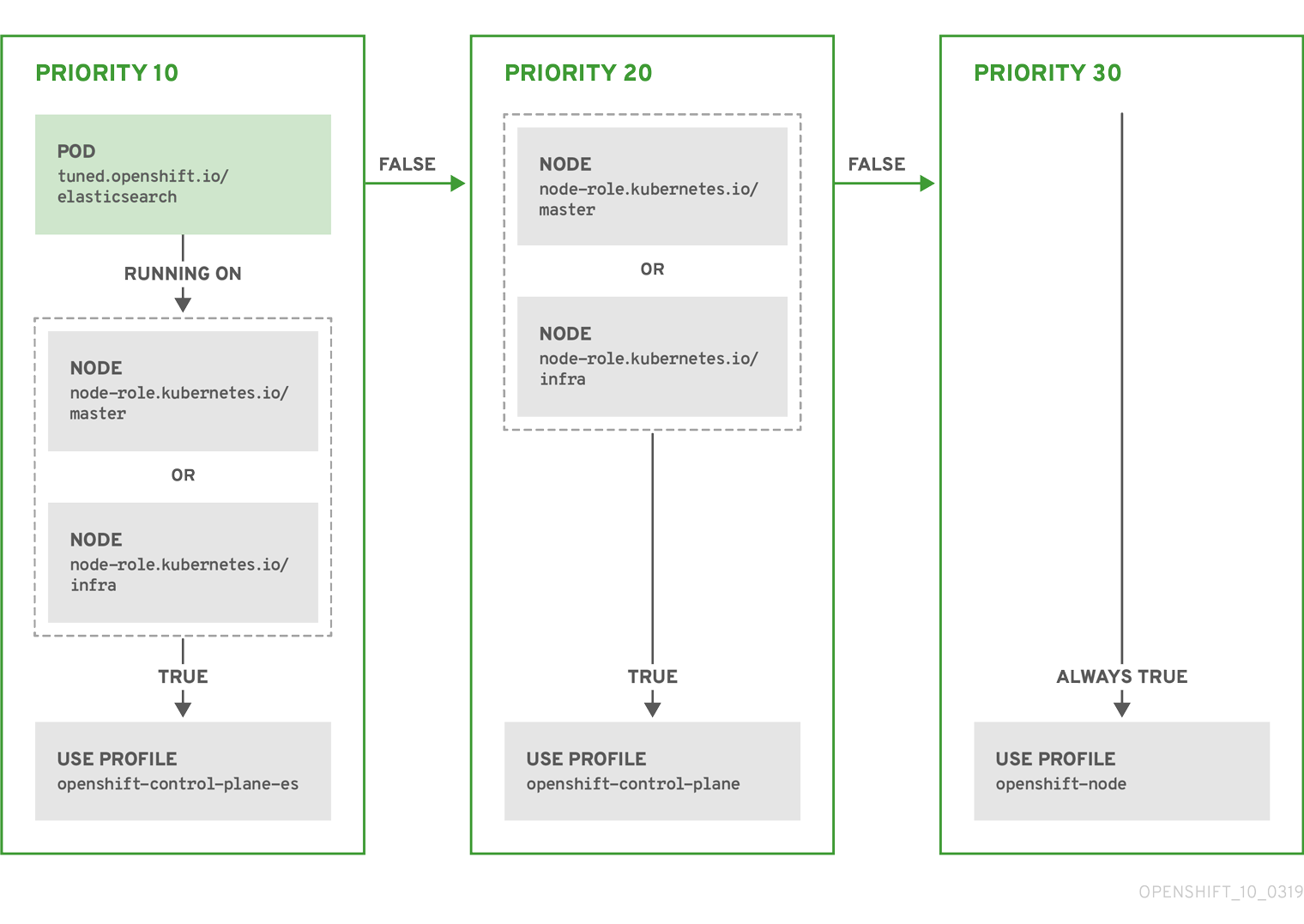
Example: node or pod label based matching
- match:
- label: tuned.openshift.io/elasticsearch
match:
- label: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
- label: node-role.kubernetes.io/infra
type: pod
priority: 10
profile: openshift-control-plane-es
- match:
- label: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
- label: node-role.kubernetes.io/infra
priority: 20
profile: openshift-control-plane
- priority: 30
profile: openshift-node
The CR above is translated for the containerized Tuned daemon into its recommend.conf file based on the profile priorities. The profile with the highest priority (10) is openshift-control-plane-es and, therefore, it is considered first. The containerized Tuned daemon running on a given node looks to see if there is a pod running on the same node with the tuned.openshift.io/elasticsearch label set. If not, the entire <match> section evaluates as false. If there is such a pod with the label, in order for the <match> section to evaluate to true, the node label also needs to be node-role.kubernetes.io/master or node-role.kubernetes.io/infra.
If the labels for the profile with priority 10 matched, openshift-control-plane-es profile is applied and no other profile is considered. If the node/pod label combination did not match, the second highest priority profile (openshift-control-plane) is considered. This profile is applied if the containerized Tuned pod runs on a node with labels node-role.kubernetes.io/master or node-role.kubernetes.io/infra.
Finally, the profile openshift-node has the lowest priority of 30. It lacks the <match> section and, therefore, will always match. It acts as a profile catch-all to set openshift-node profile, if no other profile with higher priority matches on a given node.
Example: machine config pool based matching
apiVersion: tuned.openshift.io/v1
kind: Tuned
metadata:
name: openshift-node-custom
namespace: openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator
spec:
profile:
- data: |
[main]
summary=Custom OpenShift node profile with an additional kernel parameter
include=openshift-node
[bootloader]
cmdline_openshift_node_custom=+skew_tick=1
name: openshift-node-custom
recommend:
- machineConfigLabels:
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role: "worker-custom"
priority: 20
profile: openshift-node-custom
To minimize node reboots, label the target nodes with a label the machine config pool’s node selector will match, then create the Tuned CR above and finally create the custom machine config pool itself.
4.5.3. Default profiles set on a cluster
The following are the default profiles set on a cluster.
apiVersion: tuned.openshift.io/v1
kind: Tuned
metadata:
name: default
namespace: openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator
spec:
profile:
- name: "openshift"
data: |
[main]
summary=Optimize systems running OpenShift (parent profile)
include=${f:virt_check:virtual-guest:throughput-performance}
[selinux]
avc_cache_threshold=8192
[net]
nf_conntrack_hashsize=131072
[sysctl]
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
kernel.pid_max=>4194304
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=1048576
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce=2
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh1=8192
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh2=32768
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh3=65536
net.ipv6.neigh.default.gc_thresh1=8192
net.ipv6.neigh.default.gc_thresh2=32768
net.ipv6.neigh.default.gc_thresh3=65536
vm.max_map_count=262144
[sysfs]
/sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/io_timeout=4294967295
/sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/max_retries=10
- name: "openshift-control-plane"
data: |
[main]
summary=Optimize systems running OpenShift control plane
include=openshift
[sysctl]
# ktune sysctl settings, maximizing i/o throughput
#
# Minimal preemption granularity for CPU-bound tasks:
# (default: 1 msec# (1 + ilog(ncpus)), units: nanoseconds)
kernel.sched_min_granularity_ns=10000000
# The total time the scheduler will consider a migrated process
# "cache hot" and thus less likely to be re-migrated
# (system default is 500000, i.e. 0.5 ms)
kernel.sched_migration_cost_ns=5000000
# SCHED_OTHER wake-up granularity.
#
# Preemption granularity when tasks wake up. Lower the value to
# improve wake-up latency and throughput for latency critical tasks.
kernel.sched_wakeup_granularity_ns=4000000
- name: "openshift-node"
data: |
[main]
summary=Optimize systems running OpenShift nodes
include=openshift
[sysctl]
net.ipv4.tcp_fastopen=3
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=65536
fs.inotify.max_user_instances=8192
recommend:
- profile: "openshift-control-plane"
priority: 30
match:
- label: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
- label: "node-role.kubernetes.io/infra"
- profile: "openshift-node"
priority: 404.5.4. Supported Tuned daemon plug-ins
Excluding the [main] section, the following Tuned plug-ins are supported when using custom profiles defined in the profile: section of the Tuned CR:
- audio
- cpu
- disk
- eeepc_she
- modules
- mounts
- net
- scheduler
- scsi_host
- selinux
- sysctl
- sysfs
- usb
- video
- vm
There is some dynamic tuning functionality provided by some of these plug-ins that is not supported. The following Tuned plug-ins are currently not supported:
- bootloader
- script
- systemd
See Available Tuned Plug-ins and Getting Started with Tuned for more information.